* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Animal Body Systems
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Remote control animal wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
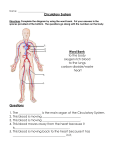
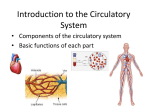
Bell Ringer WHAT IS A VERTEBRATE? Animal Body Systems Objectives Summarize the functions of digestive, circulatory, nervous, skeletal, and excretory systems. Compare a gastrovascular cavity with a one-way digestive system. Differentiate open and closed circulatory systems. Distinguish asexual and sexual reproduction Digestion Single celled organisms and sponges digest their food within their cells, all other animals digest food extracellularly. Simple animals like hydras and flatworms have a gastrovascular cavity with only one opening. Respiration In simple animals, oxygen gas and carbon dioxide are exchanged directly by diffusion. Uptake of oxygen, respiration, can take place across a moist surface. Aquatic animals respire with gills. Thin projections filled with blood vessels. Gills Each gills has a double row of tiny projections called gill filaments. These are rich in blood vessels, which have a large surface area. Fish take in water through their mouths and move it over the gill filaments. Gas exchange occurs Circulation Oxygen must be transported to cells in the body. The circulatory system transports blood. Circulation Open Circulatory System – heart pumps fluid containing oxygen and nutrients through a series of vessels than into a body cavity. Closed Circulatory System- heart pumps blood through a series of vessels. Nerve Impulses Nerve cells (Neurons) carry messages in form of electrical signals What is an open circulatory system? Bilaterally Symmetrical animals have clusters of neurons called ganglia. Complex organisms have various structures associated with ganglia. Example: Eyes Support Hydrostatic skeleton- skeleton that consists of water that is contained under pressure in a closed cavity. Muscle forces exerted against the hydrostatic skeleton aid in movement. Exoskeleton- rigid external skeleton that encloses the whole animal. The muscles of animals with an exoskeleton are attached to the inside of the skeleton. Exoskeletons also protect the soft internal organs. Endoskeleton- composed of hard material, such as bone, imbedded in an animal. Muscles attached to the endoskeleton contract and relax to help the animals move. Excretion Excretion- removal of waste by cellular metabolism. Waste leaves the cell by crossing the cell membrane. Some waste products are poisonous and must be removed from the organism. Example: Ammonia In some aquatic animals ammonia is eliminated by diffusion through the skin. Results in loss of water. Eliminating of metabolic wastes is linked to maintaining the bodies water balance. In mammals, kidneys filter fluid from the blood. The kidneys then concentrate the wastes filtered from the fluid and excrete them as concentrated urine. Reproductive Strategies Asexual Reproduction-reproduction that does not involve the fusion of two gametes. A sponge reproduces by budding, or fragmenting its body. Each piece that is fragmented develops into another sponge. Bell Ringer What organ filters our blood? Asexual Reproduction Parthogenesis-a new individual develops from unfertilized eggs. Sexual Reproduction Sexual Reproduction-new individuals formed by the union of male and female gametes. Gametes-sex cells Hermaphrodite-species of animal that has both testes and ovaries. What would prevent against self fertilization? External fertilization-egg is fertilized outside of the female’s body. Large gametes are released during external fertilization. Internal fertilization-union of sperm and egg within the females body.