Complete the following chart using your genetic code chart worksheet:
... 8. An agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a(n) a. Zygote b. Inversion c. Mutagen ...
... 8. An agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a(n) a. Zygote b. Inversion c. Mutagen ...
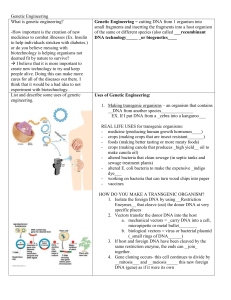
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... 35,000 -40,000 genes on the _46__ human chromosomes - began in 1990, completed in 2003 BENEFITS: - ___Diagnosis______ for diseases (ex. Test the cells from the fluid around fetus to see if baby has a genetic disorder) - better drugs - gene therapy = __insertion of normal genes into people who have d ...
... 35,000 -40,000 genes on the _46__ human chromosomes - began in 1990, completed in 2003 BENEFITS: - ___Diagnosis______ for diseases (ex. Test the cells from the fluid around fetus to see if baby has a genetic disorder) - better drugs - gene therapy = __insertion of normal genes into people who have d ...
PRE-AP Stage 3 – Learning Plan
... ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimidines, Chromosomal abnormalitites, gene mutations, cancer, enzymes GROUP: K’nex kits-building a DNA model, K’NEX kits-modeling DNA replication, transcription and translation ...
... ACCELERATE: PREAP – purines, pyrimidines, Chromosomal abnormalitites, gene mutations, cancer, enzymes GROUP: K’nex kits-building a DNA model, K’NEX kits-modeling DNA replication, transcription and translation ...
Table 3.
... Low PCR yield Optimize PCR to enhance product yield. Optimize PCR conditions to obtain clean product or design new primers without secondary structures. ...
... Low PCR yield Optimize PCR to enhance product yield. Optimize PCR conditions to obtain clean product or design new primers without secondary structures. ...
Life Science Vocabulary.xlsx
... one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are twisted together; 2 sister chromatids a ...
... one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are twisted together; 2 sister chromatids a ...
Word Definition Synonym 1 DNA replication the
... one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are twisted together; 2 sister chromatids a ...
... one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with thymine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with adenine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with cytosine one of 4 nitrogen bases that build DNA; pairs with guanine strands of DNA that are twisted together; 2 sister chromatids a ...
Chromosomal Mutations
... • Any new trait in a population, good or bad, is a result of a mutation! • Neutral: no effect on protein function • Harmful: cause genetic diseases • Beneficial: gives the organism a better chance of survival ...
... • Any new trait in a population, good or bad, is a result of a mutation! • Neutral: no effect on protein function • Harmful: cause genetic diseases • Beneficial: gives the organism a better chance of survival ...
HomeworkCh7
... c. What is a promotor? d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you think it’s called that? b. How many different codons are possible for providing a three nucleotide code for t ...
... c. What is a promotor? d. What are the three main phases of RNA synthesis? e. Can more than one copy of the gene be copied at the same time? 6. Translation a. What is translation? Why do you think it’s called that? b. How many different codons are possible for providing a three nucleotide code for t ...
Sources of Genetic Variation - University of Evansville Faculty Web
... • The union of gametes from this hybrid may give rise to a new species of interbreeding plants, reproductively isolated from both parent species ...
... • The union of gametes from this hybrid may give rise to a new species of interbreeding plants, reproductively isolated from both parent species ...
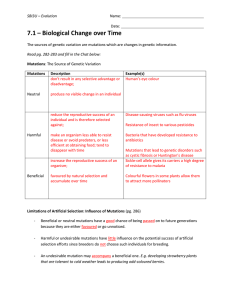
7.1 Solutions File
... selection efforts since breeders do not choose such individuals for breeding. ...
... selection efforts since breeders do not choose such individuals for breeding. ...
Esperimento di genetica 17.1
... patches. In these chromosomes, SCEs can be clearly identified as exchanges between light and dark chromatids. The steps in Perry and Wolff ’s protocol are shown in Figure EG17.1.2. They began with Chinese hamster ovary cells, a commonly used mammalian cell line, and exposed the cells to BrdU for two ...
... patches. In these chromosomes, SCEs can be clearly identified as exchanges between light and dark chromatids. The steps in Perry and Wolff ’s protocol are shown in Figure EG17.1.2. They began with Chinese hamster ovary cells, a commonly used mammalian cell line, and exposed the cells to BrdU for two ...
Genetics Review
... Mutation: damage to genetic material A mutation to genetic material is usually not beneficial. Mutagens are things that cause mutations, they include: 1. High Temperatures 2. Toxic Chemicals (pesticides, etc) 3. Radiation (nuclear and solar) Many common place items are capable of causing mutations: ...
... Mutation: damage to genetic material A mutation to genetic material is usually not beneficial. Mutagens are things that cause mutations, they include: 1. High Temperatures 2. Toxic Chemicals (pesticides, etc) 3. Radiation (nuclear and solar) Many common place items are capable of causing mutations: ...
View/Open - Technical University of Mombasa
... This paper consist of FIVE questions Answer question ONE (compulsory) and any other TWO questions ...
... This paper consist of FIVE questions Answer question ONE (compulsory) and any other TWO questions ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... size of a given amino acid can vary chemical composition of a given amino acid can vary. sequence and number of amino acids is different. the same amino acid can have many different properties. ...
... size of a given amino acid can vary chemical composition of a given amino acid can vary. sequence and number of amino acids is different. the same amino acid can have many different properties. ...
GENETICS EOCT STUDY GUIDE 1. DNA Bases: Guanine RNA
... size of a given amino acid can vary chemical composition of a given amino acid can vary. sequence and number of amino acids is different. the same amino acid can have many different properties. ...
... size of a given amino acid can vary chemical composition of a given amino acid can vary. sequence and number of amino acids is different. the same amino acid can have many different properties. ...
bio 201 – genetics
... is not repaired, errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal ...
... is not repaired, errors in the process of replication, or from the insertion or deletion of segments of DNA by mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce discernible changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal ...
Cell division exam
... Diploid, Haploid, Mitosis, Sexual reproduction, Asexual reproduction, Genetic variation _________________________: production of offspring from one parent _________________________: half the set of chromosomes, also known as 1n (23 for humans) _________________________: production of offspring from ...
... Diploid, Haploid, Mitosis, Sexual reproduction, Asexual reproduction, Genetic variation _________________________: production of offspring from one parent _________________________: half the set of chromosomes, also known as 1n (23 for humans) _________________________: production of offspring from ...
ws: DNA Alphabet Activity
... “A Coded Alphabet.” Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________ ...
... “A Coded Alphabet.” Identify the “start” and “stop” codes on the Coded Alphabet. These codes indicate where each DNA sequence begins and ends. Use the Coded Alphabet to de-code each DNA Sequence and write them in the spaces below. De-Coded Sentences #1: __________________________________________ ...
Nucleic acid review sheet
... If the sequence of bases of one of the two strands of DNA were A G T C C G T A G T T, what would be the sequence of the other strand? ...
... If the sequence of bases of one of the two strands of DNA were A G T C C G T A G T T, what would be the sequence of the other strand? ...
ABOUT-BREAST-CANCER
... compared to other patients suffering from breast cancer. [5] BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination which involves 1 major pathway of double stranded DNA repair. In comparison to BRCA1, BRCA2 does not have any impact on multiple DNA repair or in other words to nonhomologous end joining. The specifi ...
... compared to other patients suffering from breast cancer. [5] BRCA2 promotes homologous recombination which involves 1 major pathway of double stranded DNA repair. In comparison to BRCA1, BRCA2 does not have any impact on multiple DNA repair or in other words to nonhomologous end joining. The specifi ...
MUTATIONS - Valhalla High School
... protein that does not work correctly • In some rare cases, it may have a positive effect • Can be passed on to offspring ...
... protein that does not work correctly • In some rare cases, it may have a positive effect • Can be passed on to offspring ...
Name
... 23. What causes the following conditions? A. Down’s Syndrome? B. Turner’s Syndrome, C. Klinefelter’s syndrome, D. fragile X disease. 24. What is a “Hox” gene. What do these genes control? What could theoretically happen if the gene for a fly antennae were inserted into the human gene for the ...
... 23. What causes the following conditions? A. Down’s Syndrome? B. Turner’s Syndrome, C. Klinefelter’s syndrome, D. fragile X disease. 24. What is a “Hox” gene. What do these genes control? What could theoretically happen if the gene for a fly antennae were inserted into the human gene for the ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.