Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
... • Published in Science and Nature in February, 2001 ...
... • Published in Science and Nature in February, 2001 ...
Genetics
... of DNA as a template. This is called TRANSCRIPTION. *The segment of DNA that codes for a needed protein unzips, revealing open bases. Complementary bases of mRNA form on the DNA strand, then are moved off by ...
... of DNA as a template. This is called TRANSCRIPTION. *The segment of DNA that codes for a needed protein unzips, revealing open bases. Complementary bases of mRNA form on the DNA strand, then are moved off by ...
CANCER OCCURS when cell division gets out of control
... trigger cancer, be it through exposure to some environmental factor (e.g. tobacco smoke) or because of a genetic ...
... trigger cancer, be it through exposure to some environmental factor (e.g. tobacco smoke) or because of a genetic ...
The brain and spinal cord comprise the central nervous system
... • Relate cell division to the reproduction of unicellular organisms and the growth and repair of multicellular organisms. • Name two general functions of cell division. • Describe a duplicated eukaryotic chromosome. • State the stages of the eukaryotic cell cycle, and describe what happens during ea ...
... • Relate cell division to the reproduction of unicellular organisms and the growth and repair of multicellular organisms. • Name two general functions of cell division. • Describe a duplicated eukaryotic chromosome. • State the stages of the eukaryotic cell cycle, and describe what happens during ea ...
Lecture Outline
... Base modifying agents Alkylating agents add methyl and ethyl groups on all DNA bases effective in eukaryotes EMS, mustard gas, PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: found in smoke of all kinds) Deaminating agents affects cytosine and adenine nitrous acid Oxidative reactions reactive forms of oxyge ...
... Base modifying agents Alkylating agents add methyl and ethyl groups on all DNA bases effective in eukaryotes EMS, mustard gas, PAHs (polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: found in smoke of all kinds) Deaminating agents affects cytosine and adenine nitrous acid Oxidative reactions reactive forms of oxyge ...
genetics i - Indian School Al Wadi Al Kabir
... a) Write the name of the chemical substance used as a source of nitrogen in this experiment b) Why did they synthesize the light heavy DNA molecules in their experiment? c) How did the scientists make it possible to distinguish the heavy from light? Explain d) Write the conclusion the scientists arr ...
... a) Write the name of the chemical substance used as a source of nitrogen in this experiment b) Why did they synthesize the light heavy DNA molecules in their experiment? c) How did the scientists make it possible to distinguish the heavy from light? Explain d) Write the conclusion the scientists arr ...
Document
... Missense mutations are changes that cause the substitution of one amino acid for another in the encoded protein. Nonsense mutations are changes that cause the substitution of a stop codon for an amino acid in the encoded protein. Synonymous mutations are changes in the nucleic acid sequence in the c ...
... Missense mutations are changes that cause the substitution of one amino acid for another in the encoded protein. Nonsense mutations are changes that cause the substitution of a stop codon for an amino acid in the encoded protein. Synonymous mutations are changes in the nucleic acid sequence in the c ...
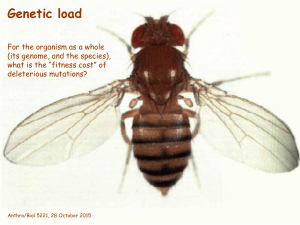
Genetic load
... But the multiplicative (independent-effects) model is just one of many! It’s pretty, but not well supported by logic or evidence! ...
... But the multiplicative (independent-effects) model is just one of many! It’s pretty, but not well supported by logic or evidence! ...
4 Heredity and Reproduction
... 2. Why can bacteria recognize a human gene and then produce a human protein? A. DNA replication in bacteria and humans is the same. B. Bacterial cells contain the same organelles as human cells. C. The basic components of DNA are the same in humans and bacteria. D. Bacterial cells and human cells co ...
... 2. Why can bacteria recognize a human gene and then produce a human protein? A. DNA replication in bacteria and humans is the same. B. Bacterial cells contain the same organelles as human cells. C. The basic components of DNA are the same in humans and bacteria. D. Bacterial cells and human cells co ...
How are protein made in our cells?
... mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, the amino acid on (top) tRNA will “pop” off (bottom) tRNA. Like an assemble line, amino acids will assemble onto each other and create a polypeptide (or a protein). ...
... mRNA will attach to anticodon on tRNA molecule. After this occurs, the amino acid on (top) tRNA will “pop” off (bottom) tRNA. Like an assemble line, amino acids will assemble onto each other and create a polypeptide (or a protein). ...
Genes - ASW Moodle
... C. Each organism has two alleles for every trait in their body. -One from the chromosomes* inherited from -One from the chromosomes inherited from -These pair of chromosomes are called *A chromosome is DNA that has been wound up into a rodlike shape *This is why organisms appear to be a physical “b ...
... C. Each organism has two alleles for every trait in their body. -One from the chromosomes* inherited from -One from the chromosomes inherited from -These pair of chromosomes are called *A chromosome is DNA that has been wound up into a rodlike shape *This is why organisms appear to be a physical “b ...
Study Guide Ch
... 29. Proteins are made up of smaller molecules called ___________________________________________________. 30. How many total amino acids? 31. 3 base code of nitrogen bases is called a ____________________________________. 32. (T/F) 1 codon codes for 3 amino acid. 33. Condition in which an organism h ...
... 29. Proteins are made up of smaller molecules called ___________________________________________________. 30. How many total amino acids? 31. 3 base code of nitrogen bases is called a ____________________________________. 32. (T/F) 1 codon codes for 3 amino acid. 33. Condition in which an organism h ...
Unit_biology_2_Genetic_variation
... chromosomes carries the genes that determine sex. In females the sex chromosomes are the same (XX); in males the sex chromosomes are different (XY). c) Some characteristics are controlled by a single gene. Each gene may have different forms called alleles. d) An allele that controls the development ...
... chromosomes carries the genes that determine sex. In females the sex chromosomes are the same (XX); in males the sex chromosomes are different (XY). c) Some characteristics are controlled by a single gene. Each gene may have different forms called alleles. d) An allele that controls the development ...
Y Y W Y Y
... 18. Edwards Syndrome is a serious condition causing 10% of those bom with it to die within their first years. The cause is trisomy 18, the presence of three chromosome 18s. All children with this condition are mentally retarded and suffer with breathing problems and possible seizures. The technique ...
... 18. Edwards Syndrome is a serious condition causing 10% of those bom with it to die within their first years. The cause is trisomy 18, the presence of three chromosome 18s. All children with this condition are mentally retarded and suffer with breathing problems and possible seizures. The technique ...
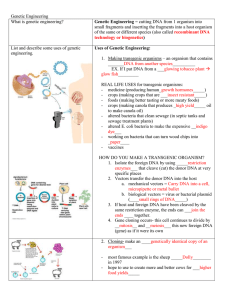
Genetic Engineering
... crime scene or the parent in a paternity test______ - Analyze fossil DNA and compare extinct species with living species Human Genome Project- an international effort to sequence the 35,000 -40,000 genes on the ___46____ human chromosomes - began in 1990, completed in 2003 BENEFITS: - ___Diagnosis__ ...
... crime scene or the parent in a paternity test______ - Analyze fossil DNA and compare extinct species with living species Human Genome Project- an international effort to sequence the 35,000 -40,000 genes on the ___46____ human chromosomes - began in 1990, completed in 2003 BENEFITS: - ___Diagnosis__ ...
Mrs. Paparella/ Living Environment Genetics Essential Questions
... Mrs. Paparella/ Living Environment ...
... Mrs. Paparella/ Living Environment ...
The Cell Cycle and Cancer - Clark Pleasant Community
... that code for the kinases and cyclins) • Oncogenes: genes that have a normal function, but that when mutated, may cause cancer. ...
... that code for the kinases and cyclins) • Oncogenes: genes that have a normal function, but that when mutated, may cause cancer. ...
Reproduction and Heredity
... cells – Haploid cells can be gametes • Unite to form zygote then divides – Haploid cells can be meiospores • Divides without uniting with another cell Meiosis • Meiosis produces genetic variability through genetic recombination – Crossing over, as well as possible haploid chromosome combinations Mei ...
... cells – Haploid cells can be gametes • Unite to form zygote then divides – Haploid cells can be meiospores • Divides without uniting with another cell Meiosis • Meiosis produces genetic variability through genetic recombination – Crossing over, as well as possible haploid chromosome combinations Mei ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.