Catching Cancer by Dr. David L. (“Woody”) Woodland (as published
... tumor and migrating to other parts of the body. In general, this loss of growth control has two fundamental causes. First, mutations in the genome may cause the brakes on the cells’ growth program to fail. Anything that damages our DNA can lead to cancer, such as a strong dose of UV light when out i ...
... tumor and migrating to other parts of the body. In general, this loss of growth control has two fundamental causes. First, mutations in the genome may cause the brakes on the cells’ growth program to fail. Anything that damages our DNA can lead to cancer, such as a strong dose of UV light when out i ...
DNA AND BIOTECHNOLOGY
... TO PRODUCE A DESIRED PRODUCT GENETIC ENGINEERING= THE ALTERATION OF THE GENOME OF VIRUSES, BACTERIA AND OTHER ...
... TO PRODUCE A DESIRED PRODUCT GENETIC ENGINEERING= THE ALTERATION OF THE GENOME OF VIRUSES, BACTERIA AND OTHER ...
Genetics of AHC - Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood Foundation
... New technology to look at all of the genes in a person’s cells ...
... New technology to look at all of the genes in a person’s cells ...
Biology 303 EXAM II 3/14/00 NAME
... Hemophilia is caused by several genetic factors; one, a sex-linked recessive gene, is the subject of this problem. Assume that a man with hemophilia marries a normal woman whose father had hemophilia. What is the probability that they will have a daughter with hemophilia? (Note: in this problem you ...
... Hemophilia is caused by several genetic factors; one, a sex-linked recessive gene, is the subject of this problem. Assume that a man with hemophilia marries a normal woman whose father had hemophilia. What is the probability that they will have a daughter with hemophilia? (Note: in this problem you ...
Genetics Science Learning Center
... "What is a Trait?" 22. Give an example of a physical trait: _________________________________________________ 23. A dog fetching a bone is an example of what kind of trait? _________________________________ 24. Scientists describe the set of information for each form of trait as an ________________ ...
... "What is a Trait?" 22. Give an example of a physical trait: _________________________________________________ 23. A dog fetching a bone is an example of what kind of trait? _________________________________ 24. Scientists describe the set of information for each form of trait as an ________________ ...
View PDF
... proteins they code for can vary from person to person. For example, skin color comes from a protein called melanin. The amount of melanin an individual produces affects the color of their skin. Given the huge number of base pairs in the DNA of any organism, it is not surprising that errors occur whe ...
... proteins they code for can vary from person to person. For example, skin color comes from a protein called melanin. The amount of melanin an individual produces affects the color of their skin. Given the huge number of base pairs in the DNA of any organism, it is not surprising that errors occur whe ...
molecular genetics unit review
... c) Explain translation: initiation, elongation and termination d) Understand the genetic code: i. codons (including start and stop) ii. anticodons iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is contr ...
... c) Explain translation: initiation, elongation and termination d) Understand the genetic code: i. codons (including start and stop) ii. anticodons iii. DNA mRNA polypeptide/protein (know how to transcribe DNA and translate mRNA if given a sequence) What are the four ways gene expression is contr ...
Nucleic Acids Test Topics
... - If the DNA molecule is seen as a ladder, the rungs would be nitrogen containing bases and the uprights would be phosphate groups and 5 carbon sugars (deoxyribose) RNA Characteristics - A single strand of nucleotides that contains uracil instead of thymine - RNA is a nucleic acid macromolecule - RN ...
... - If the DNA molecule is seen as a ladder, the rungs would be nitrogen containing bases and the uprights would be phosphate groups and 5 carbon sugars (deoxyribose) RNA Characteristics - A single strand of nucleotides that contains uracil instead of thymine - RNA is a nucleic acid macromolecule - RN ...
Chapter 11: Organization of DNA in Eukaryotes 11.2: mtDNA
... Describe the Endosymbiotic hypothesis. Essentially, modern cells are a product of ancient eukaryotes engulfing free-living mitochondria and/or chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria ...
... Describe the Endosymbiotic hypothesis. Essentially, modern cells are a product of ancient eukaryotes engulfing free-living mitochondria and/or chloroplasts, allowing these (believed to be) prokaryotes to reside inside of the cytoplasm in a symbiotic relationship. After some time, these mitochondria ...
Final Exam Review - Blue Valley Schools
... What is a homologous structure? How do homologous structures help support the idea of common ancestry? What is a vestigial structure? What do they tell us about the evolutionary history of organisms? Natural Selection How do we summarize natural selection? 1. Variation exists among individuals withi ...
... What is a homologous structure? How do homologous structures help support the idea of common ancestry? What is a vestigial structure? What do they tell us about the evolutionary history of organisms? Natural Selection How do we summarize natural selection? 1. Variation exists among individuals withi ...
will dna technology let parents design their kids?
... such technology might be regarded as SEX S E L E C T I O N inferior. But would they grow up to be At fertility clinics, parents can choose the sex of their child if they wish to. Both lesser human beings? males and females normally carry 23 pairs of chromosomes, structures inside the cells that cont ...
... such technology might be regarded as SEX S E L E C T I O N inferior. But would they grow up to be At fertility clinics, parents can choose the sex of their child if they wish to. Both lesser human beings? males and females normally carry 23 pairs of chromosomes, structures inside the cells that cont ...
5-Year Cancer Mortality Rates in the US
... who carry one copy of a gene mutation that, when present in two copies, causes a genetic disorder. ...
... who carry one copy of a gene mutation that, when present in two copies, causes a genetic disorder. ...
Document
... acid that the codon codes 2. Does not cause alteration on the amino acid that the codon codes 3. Alters codon in the way that it becomes stop-codon for protein synthesis ...
... acid that the codon codes 2. Does not cause alteration on the amino acid that the codon codes 3. Alters codon in the way that it becomes stop-codon for protein synthesis ...
DNA,RNA & Protein synthesis game
... the debate regarding hereditary material over these two molecules ...
... the debate regarding hereditary material over these two molecules ...
NAME Period___________ Modern Genetics Outline
... alcohol, are also known to cause changes in ____ and ___________. Unborn children can be injured when their pregnant mothers are exposed to ____________ agents. ...
... alcohol, are also known to cause changes in ____ and ___________. Unborn children can be injured when their pregnant mothers are exposed to ____________ agents. ...
Modern Genetics Outline
... alcohol, are also known to cause changes in ____ and ___________. Unborn children can be injured when their pregnant mothers are exposed to ____________ agents. ...
... alcohol, are also known to cause changes in ____ and ___________. Unborn children can be injured when their pregnant mothers are exposed to ____________ agents. ...
Stg Chp 11 - Edublogs @ Macomb ISD
... 6. When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, the result is a(n) a. translocation. b. insertion. c. inversion. d. deletion. 7. Many chromosome mutations result when chromosomes fail to separate properly during a. mitosis. b. meiosis. c. crossing over. d. linkage. ...
... 6. When part of one chromosome breaks off and is added to a different chromosome, the result is a(n) a. translocation. b. insertion. c. inversion. d. deletion. 7. Many chromosome mutations result when chromosomes fail to separate properly during a. mitosis. b. meiosis. c. crossing over. d. linkage. ...
DNA
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
... *is passed from one generation to the next in chromosomes. *looks like a ladder, twisted around itself, called a double helix DNA Timeline Facts… Early 1950’s o 1st picture of DNA taken by Rosalind Franklin using an X-ray machine. ...
genet_174(2)_cover 4.qxd
... Elie S. Dolgin and Brian Charlesworth In sexual populations, transposable elements (TEs) can be contained by purifying selection. However, an asexual population could potentially be driven to extinction by an unchecked proliferation of TEs. Here the authors provide a theoretical framework for analyz ...
... Elie S. Dolgin and Brian Charlesworth In sexual populations, transposable elements (TEs) can be contained by purifying selection. However, an asexual population could potentially be driven to extinction by an unchecked proliferation of TEs. Here the authors provide a theoretical framework for analyz ...
the element makes na RNA copy of itself which is reversed
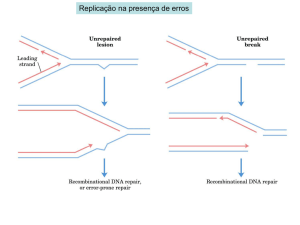
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
... • Breakage and joining also directed by enzymes. • Homologous recombination occurs during synapsis in meiosis I, general recombination in bacteria, and viral genetic exchange. • Molecular mechanism proposed by Holliday and Whitehouse (1964). • Depends on complementary base pairing. ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.