DNA Discovery
... – If two nucleotides coded for one amino acid, we still would not have enough combinations. – So we have three nitrogenous bases to code for one amino acid (although there are now 64 different combinations). • However, in some cases two or more codons code for the same amino acid ...
... – If two nucleotides coded for one amino acid, we still would not have enough combinations. – So we have three nitrogenous bases to code for one amino acid (although there are now 64 different combinations). • However, in some cases two or more codons code for the same amino acid ...
Cells and Inheritance - Gaiser Middle School
... RNA molecules that resemble DNA, carry protein info for protein production in the cell. - any change that happens in a gene or chromosome ...
... RNA molecules that resemble DNA, carry protein info for protein production in the cell. - any change that happens in a gene or chromosome ...
Point mutation - Chavis Biology
... A mutation is an alteration of an organism’s DNA and can range in severity. Most mutations are automatically repaired by the organism’s enzymes, but those that are not repaired may result in altered chromosomes or genes. Mutant body cells are not passed on to offspring but mutant gametes may be ...
... A mutation is an alteration of an organism’s DNA and can range in severity. Most mutations are automatically repaired by the organism’s enzymes, but those that are not repaired may result in altered chromosomes or genes. Mutant body cells are not passed on to offspring but mutant gametes may be ...
Competency Goal 2: The learner will develop an understanding of
... 47. What organism did Mendel use for his experiments? (263) 48. What three laws of genetics did he develop based on his results and observations? (265, 270) ...
... 47. What organism did Mendel use for his experiments? (263) 48. What three laws of genetics did he develop based on his results and observations? (265, 270) ...
11.3 Section Objectives – page 296
... environment, such as radiation, chemicals, and even high temperatures. • Any agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a mutagen. ...
... environment, such as radiation, chemicals, and even high temperatures. • Any agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a mutagen. ...
Genetics Glossary
... Adenine: One of four chemical base pairs that make up DNA Autosomal dominant: The mode of inheritance where an individual receives a mutation from one parent. This single mutation is sufficient to cause disease. Autosomal recessive: The mode of inheritance where an individual receives a mutation in ...
... Adenine: One of four chemical base pairs that make up DNA Autosomal dominant: The mode of inheritance where an individual receives a mutation from one parent. This single mutation is sufficient to cause disease. Autosomal recessive: The mode of inheritance where an individual receives a mutation in ...
Review Sheet—Cell Division
... A. Mutation B. Sensation C. Nucleus D. Whistler 32. What is crossing over and why is it important? It is when two chromosomes come in contact and their genes/chromosomes exchange. This is important because it causes variation. 33. Where is a change caused by a DNA mutation initially going to occur? ...
... A. Mutation B. Sensation C. Nucleus D. Whistler 32. What is crossing over and why is it important? It is when two chromosomes come in contact and their genes/chromosomes exchange. This is important because it causes variation. 33. Where is a change caused by a DNA mutation initially going to occur? ...
DATE - MrD-Home
... Circle the letter of the best answer. 1. Which of the following is the correct order in sexual reproduction? A. meiosis, gamete, fertilization, embryo B. gamete, meiosis, fertilization, embryo C. fertilization, meiosis, gamete, embryo D. gamete, fertilization, meiosis, embryo 2. Mitosis is similar t ...
... Circle the letter of the best answer. 1. Which of the following is the correct order in sexual reproduction? A. meiosis, gamete, fertilization, embryo B. gamete, meiosis, fertilization, embryo C. fertilization, meiosis, gamete, embryo D. gamete, fertilization, meiosis, embryo 2. Mitosis is similar t ...
Genetic Exchange - Pennsylvania State University
... copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequence at each side of the transposon (called direct repeats). • Speci ...
... copy to splice into DNA at a specific target sequences. • Endonuclease activity cuts target sequence, leaving single strand overhanging ends. •Transposon is ligated to ends. • Gaps are filled by DNA polymerase to yield a target sequence at each side of the transposon (called direct repeats). • Speci ...
BIOLOGY EOC PRACTICE TEST _1[1]
... amino acids to ribosomes, where amino acids are linked into the primary structure of a polypeptide. A mRNA B tRNA C intron D rRNA 20. The snowshoe rabbit has white fur in winter and dark fur in summer. What is the main advantage of this fur change to the rabbit? A The dark fur keeps the rabbit from ...
... amino acids to ribosomes, where amino acids are linked into the primary structure of a polypeptide. A mRNA B tRNA C intron D rRNA 20. The snowshoe rabbit has white fur in winter and dark fur in summer. What is the main advantage of this fur change to the rabbit? A The dark fur keeps the rabbit from ...
Biobowl 3
... 25. The experiments of Hershey and Chase used the isotope ______ to demonstrate that ________ (a molecule) entered E. coli and was therefore the genetic material. 26. Suppose Meselson and Stahl had grown E.coli on 14N, then switched them to 15N. What bands would they have seen in their centrifuge tu ...
... 25. The experiments of Hershey and Chase used the isotope ______ to demonstrate that ________ (a molecule) entered E. coli and was therefore the genetic material. 26. Suppose Meselson and Stahl had grown E.coli on 14N, then switched them to 15N. What bands would they have seen in their centrifuge tu ...
Answer all the questions Time allowed : 49 minutes 1. State two
... Mutation may occur spontaneously, or be induced by chemicals (e.g. colchicines ), radiations (e.g. X-rays and UV) and biological factors (e.g. viruses).
Mutation may involve
change in the number of chromosomes, e.g. polyploidy
changes in chromosome structure,
changes in DNA structure
Sub-tot ...
... Mutation may occur spontaneously, or be induced by chemicals (e.g. colchicines ), radiations (e.g. X-rays and UV) and biological factors (e.g. viruses).
DNA - SchoolRack
... chromosomal mutations usually dies. • In cases where the zygote lives, the mature organism with a chromosomal mutation is often sterile. ...
... chromosomal mutations usually dies. • In cases where the zygote lives, the mature organism with a chromosomal mutation is often sterile. ...
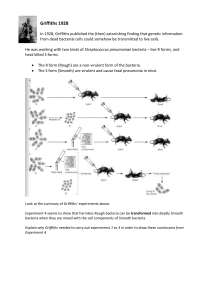
DNA experiments exercise
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
... Experiment 4 seems to show that harmless Rough bacteria can be transformed into deadly Smooth bacteria when they are mixed with the cell components of Smooth bacteria. Explain why Griffiths needed to carry out experiments 1 to 3 in order to draw these conclusions from Experiment 4. ...
Experience 2 Follow-up 1. Answer the following
... 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. ...
... 3. Please tell me the type of point mutation being described (be specific!) and describe the result of that mutation on the amino acid sequence AND polypeptide that is made from the mutated DNA. ...
Lecture 6
... Radiation was the first mutagenic agent known; its effects on genes were first reported in the 1920's. X-rays discovered by Roentgen in 1895 cause multiple mutations and DNA rearrangements (insertions, translocations). UV radiation causes the formation of thymine dimmers. Examples of chemical mutage ...
... Radiation was the first mutagenic agent known; its effects on genes were first reported in the 1920's. X-rays discovered by Roentgen in 1895 cause multiple mutations and DNA rearrangements (insertions, translocations). UV radiation causes the formation of thymine dimmers. Examples of chemical mutage ...
Genetics review sheet VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary
... VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary section will be fill in the blank with a word bank 1. gene ...
... VOCABULARY- on the test, the vocabulary section will be fill in the blank with a word bank 1. gene ...
Glossary 29Sept2012_Genetics
... chromosomes in 23 pairs. One member of each pair is inherited from the mother, the other from the father. Chromosomes coil when cells are about to divide. complementary DNA (cDNA): DNA that is synthesized from a messenger RNA template; the single-stranded form is often used as a probe in physical ma ...
... chromosomes in 23 pairs. One member of each pair is inherited from the mother, the other from the father. Chromosomes coil when cells are about to divide. complementary DNA (cDNA): DNA that is synthesized from a messenger RNA template; the single-stranded form is often used as a probe in physical ma ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE
... _____ A base change resulting in a codon specifying the same amino acid as found in the wild-type polypeptide. A. Missense B. Silent C. Nonsense D. Synonymous E. Frameshift _____ The fluctuation test of Luria and Delbruck (studying resistance to bacteriophge T1 infection) established that A. T1 phag ...
... _____ A base change resulting in a codon specifying the same amino acid as found in the wild-type polypeptide. A. Missense B. Silent C. Nonsense D. Synonymous E. Frameshift _____ The fluctuation test of Luria and Delbruck (studying resistance to bacteriophge T1 infection) established that A. T1 phag ...
Mutagen
In genetics, a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, of an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations above the natural background level. As many mutations can cause cancer, mutagens are therefore also likely to be carcinogens. Not all mutations are caused by mutagens: so-called ""spontaneous mutations"" occur due to spontaneous hydrolysis, errors in DNA replication, repair and recombination.











![BIOLOGY EOC PRACTICE TEST _1[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010109633_1-bd9d268f1e093bfaefdc12c3cf22deab-300x300.png)