Document
... Curie Point • The temperature at which the iron minerals ALIGN in the molten rock • Different for different rocks! ...
... Curie Point • The temperature at which the iron minerals ALIGN in the molten rock • Different for different rocks! ...
Tectonic Plate Theory PowerPoint Study Guide
... Therefore the landmasses must have been in different locations in the past. ...
... Therefore the landmasses must have been in different locations in the past. ...
Lecture 11 Review
... modulus measures the stiffness of the material lattice, i.e. ∆p change in pressure stress applied β= ...
... modulus measures the stiffness of the material lattice, i.e. ∆p change in pressure stress applied β= ...
Extreme Earth - Introduction
... Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions Long-term prediction Identify the distribution, frequency, style of eruption, etc. Determine local risks to specific hazards. Short-term prediction ...
... Prediction of Volcanic Eruptions Long-term prediction Identify the distribution, frequency, style of eruption, etc. Determine local risks to specific hazards. Short-term prediction ...
Chapter One
... Law of Superposition - the layer below is older than the layer above. Principle of fossil succession - life forms succeed one another in a definite and determinable order and therefor a time period can be determined by its fossils. Law of Cross-cutting Relationships - A rock is younger than any rock ...
... Law of Superposition - the layer below is older than the layer above. Principle of fossil succession - life forms succeed one another in a definite and determinable order and therefor a time period can be determined by its fossils. Law of Cross-cutting Relationships - A rock is younger than any rock ...
File
... b. Plate continues to move, volcano goes with it and becomes inactive, new one forms c. Hawaii was formed this way---by a hot spot. 3. Mid Ocean Ridges—forms from divergent plates a. Volcanoes on these ridges contain pillow lava (lava rapidly cooled by water) ...
... b. Plate continues to move, volcano goes with it and becomes inactive, new one forms c. Hawaii was formed this way---by a hot spot. 3. Mid Ocean Ridges—forms from divergent plates a. Volcanoes on these ridges contain pillow lava (lava rapidly cooled by water) ...
Plate Boundaries Quiz
... A. A solid, thin layer of Earth with temperature approximately equal to the surface of the sun B. The layer of Earth that has convection currents causing continental drift C. Earth’s thickest layer (semi-solid) D. Both B & C 4. Which layer is a solid consisting of Iron and Nickel? A C. B. D. 5. This ...
... A. A solid, thin layer of Earth with temperature approximately equal to the surface of the sun B. The layer of Earth that has convection currents causing continental drift C. Earth’s thickest layer (semi-solid) D. Both B & C 4. Which layer is a solid consisting of Iron and Nickel? A C. B. D. 5. This ...
Name Period ______ Date ______ Earth Science: National
... 18. During the break-up of Pangaea, S. America split off from ______________, N. America split off from ________________, and Australia split off from __________________ and drifted north. 19. As plates move across the Earth, crust and rock is dragged back down into the Earth at what type of zones? ...
... 18. During the break-up of Pangaea, S. America split off from ______________, N. America split off from ________________, and Australia split off from __________________ and drifted north. 19. As plates move across the Earth, crust and rock is dragged back down into the Earth at what type of zones? ...
Mountain Building - Hicksville Public Schools
... "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. – Parts of the crust will rise or subside (sink) until stab ...
... "standstill") is a term used in geology to refer to the state of gravitational equilibrium between the earth's lithosphere and asthenosphere such that the tectonic plates "float" at an elevation which depends on their thickness and density. – Parts of the crust will rise or subside (sink) until stab ...
A Little Geology Lesson - Department of Earth Sciences
... deposited in horizontal or near horizontal layers or strata and may be referred to as stratified rocks. A small fraction of sedimentary rocks deposited on steep slopes will show cross bedding where one layer stops abruptly along an interface where another layer eroded the first as it was laid atop t ...
... deposited in horizontal or near horizontal layers or strata and may be referred to as stratified rocks. A small fraction of sedimentary rocks deposited on steep slopes will show cross bedding where one layer stops abruptly along an interface where another layer eroded the first as it was laid atop t ...
Chapter 9 WS #1
... subduction zone transform faults passive margin (p.270)* active margin (p.273) arrows indicating direction of plate movement (p.191) *not included on diagram ...
... subduction zone transform faults passive margin (p.270)* active margin (p.273) arrows indicating direction of plate movement (p.191) *not included on diagram ...
Document
... Continental rifting occurs when divergent plate margins develop in continents. They are typified by normal faulting, shallow earthquakes, basaltic and rhyolitic magmatism. Many rift valleys are closed depressions and have been filled with water to form freshwater lakes. There are sedimentary rock s ...
... Continental rifting occurs when divergent plate margins develop in continents. They are typified by normal faulting, shallow earthquakes, basaltic and rhyolitic magmatism. Many rift valleys are closed depressions and have been filled with water to form freshwater lakes. There are sedimentary rock s ...
Layers of the Earth
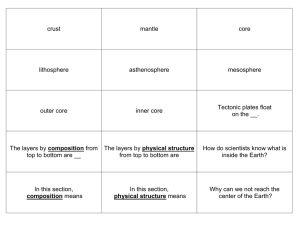
... • Be able to draw and label the three layers of the earth (crust, mantle, and core) as well as the 5 layers based on physical properties (lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer and inner core). ...
... • Be able to draw and label the three layers of the earth (crust, mantle, and core) as well as the 5 layers based on physical properties (lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer and inner core). ...
Final S2 ES Option one
... Summarize the limitations of using the rates of erosion and deposition to determine the absolute age of rock formations. Explain how the process of radioactive decay can be used to determine the absolute age of rocks. Describe four ways in which entire organisms can be preserved as fossils. List fiv ...
... Summarize the limitations of using the rates of erosion and deposition to determine the absolute age of rock formations. Explain how the process of radioactive decay can be used to determine the absolute age of rocks. Describe four ways in which entire organisms can be preserved as fossils. List fiv ...
Grade 6 Curriculum Map - Bibb County School District
... Discuss, compare/contrast weathering, erosion and deposition S6E5f Effects of human activity on erosion S6E5i Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move S6E5e This movement can cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. S6E5e Explain the effects of physical processes (plate t ...
... Discuss, compare/contrast weathering, erosion and deposition S6E5f Effects of human activity on erosion S6E5i Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move S6E5e This movement can cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. S6E5e Explain the effects of physical processes (plate t ...
Why Plates Move… - Mr Vincent Science
... The theory of plate tectonics explains how the plates move but not why. What do we know about the earth’s mantle and crust that might help us determine the mechanisms involved? Seismic data tells us that the mantle is fluid The core of the earth is quite hot – heat left over from the earth’s formati ...
... The theory of plate tectonics explains how the plates move but not why. What do we know about the earth’s mantle and crust that might help us determine the mechanisms involved? Seismic data tells us that the mantle is fluid The core of the earth is quite hot – heat left over from the earth’s formati ...
Structure of the Earth Study Guide with Answers
... 22) List the order of seismic waves as they reach a site from fastest to slowest. P WAVE, S WAVE, SURFACE WAVES 23) How fast do body waves move through the Earth? 11 KM/SEC 24) What are the layers of the Earth from inside out? INNER CORE, OUTER CORE, MANTLE, CRUST 25) What layer of the Earth is the ...
... 22) List the order of seismic waves as they reach a site from fastest to slowest. P WAVE, S WAVE, SURFACE WAVES 23) How fast do body waves move through the Earth? 11 KM/SEC 24) What are the layers of the Earth from inside out? INNER CORE, OUTER CORE, MANTLE, CRUST 25) What layer of the Earth is the ...
rocks - Warren County Schools
... were formed. Ripple marks formed in the sand will appear in the rock formed from the sand deposits. ...
... were formed. Ripple marks formed in the sand will appear in the rock formed from the sand deposits. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.























