History of the Earth Chapter 2: The Hadean
... Basic Plate Tectonics • Earth’s “surface” (lithosphere) is broken into plates • Plates move on asthenosphere • “Geology happens” where the plates interact with one another ...
... Basic Plate Tectonics • Earth’s “surface” (lithosphere) is broken into plates • Plates move on asthenosphere • “Geology happens” where the plates interact with one another ...
File
... oldest layers are always on the bottom and the youngest layers are always on the top. As new layers of sedimentary rock form, the strata can be identified. Dating – Relative ...
... oldest layers are always on the bottom and the youngest layers are always on the top. As new layers of sedimentary rock form, the strata can be identified. Dating – Relative ...
The Theory of Plate Tectonics - Ouray School District R-1
... slowly when under pressure. Lithosphere is broken into separate plates that “ride” on the athenosphere. 30 plates have been identified. Some are moving together…some apart this constant movement has created earth’s major surface features. ...
... slowly when under pressure. Lithosphere is broken into separate plates that “ride” on the athenosphere. 30 plates have been identified. Some are moving together…some apart this constant movement has created earth’s major surface features. ...
The Geosphere
... Seismic waves travel through different material at different rates. When seismic waves change direction or speed, it means they have moved through different layers ...
... Seismic waves travel through different material at different rates. When seismic waves change direction or speed, it means they have moved through different layers ...
The Geosphere
... Seismic waves travel through different material at different rates. When seismic waves change direction or speed, it means they have moved through different layers ...
... Seismic waves travel through different material at different rates. When seismic waves change direction or speed, it means they have moved through different layers ...
The Rock Cycle - WNMS8thScience
... Solid – cannot move through liquid Side-to-side motion Slower Shadow zone – told us that the Earth’s interior is liquid ...
... Solid – cannot move through liquid Side-to-side motion Slower Shadow zone – told us that the Earth’s interior is liquid ...
The Rock Cycle
... What happened next was worse than you could image. Chip and I were constantly being hit by wind and rain. That wasn’t the horrible part. Over a long period of time, little pieces of us began to break off. The wind and rain would carry our pieces to a nearby river, which flowed into the sea. Before l ...
... What happened next was worse than you could image. Chip and I were constantly being hit by wind and rain. That wasn’t the horrible part. Over a long period of time, little pieces of us began to break off. The wind and rain would carry our pieces to a nearby river, which flowed into the sea. Before l ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword - Science
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
Plate Tectonics Crossword
... It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
... It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
plate tectonics crossword
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
... 3. The zone below the lithosphere. It is more 'plastic' than the lithosphere so it is easier to bend and move. ...
No Slide Title
... The Earth’s outer layer is called the lithosphere. It is made of the rigid upper mantle and the crust. The lithosphere moves on the asthenosphere, part of the mantle that flows. ...
... The Earth’s outer layer is called the lithosphere. It is made of the rigid upper mantle and the crust. The lithosphere moves on the asthenosphere, part of the mantle that flows. ...
msess2 - North Bergen School District
... What rocks are produced by different processes such as sedimentation, melting etc.? ...
... What rocks are produced by different processes such as sedimentation, melting etc.? ...
File
... Geoscience includes all the sciences (geology, geophysics, geochemistry) that study the structure, evolution and dynamics of the planet Earth and its natural mineral and energy resources. Geoscience investigates the processes that have shaped the Earth through its 4600 million year history and uses ...
... Geoscience includes all the sciences (geology, geophysics, geochemistry) that study the structure, evolution and dynamics of the planet Earth and its natural mineral and energy resources. Geoscience investigates the processes that have shaped the Earth through its 4600 million year history and uses ...
Chapter 3 – The Dynamic Earth Section 1: The Geosphere
... • Consists of densest elements • Radius approximately 3400 km ...
... • Consists of densest elements • Radius approximately 3400 km ...
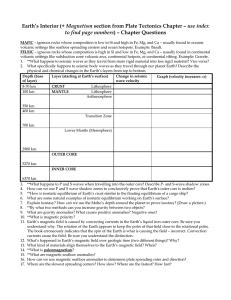
Earth`s Interior (+ Magnetism section from Plate Tectonics Chapter
... MAFIC – igneous rocks whose composition is low in Si and high in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in oceanic volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in contin ...
... MAFIC – igneous rocks whose composition is low in Si and high in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in oceanic volcanic settings like seafloor spreading centers and ocean hotspots. Example: Basalt. FELSIC – igneous rocks whose composition is high in Si and low in Fe, Mg, and Ca – usually found in contin ...
Geology 12 Field trip: Sierra College Blvd Exit off I
... made of gray andesite and the matrix between the cobbles is hard and resists erosion) diorite Find all four rock types. For each rock type, describe these properties: Color of the rock, both fresh and weathered Lithology – rock name and texture, plus a description of the minerals or fragments ...
... made of gray andesite and the matrix between the cobbles is hard and resists erosion) diorite Find all four rock types. For each rock type, describe these properties: Color of the rock, both fresh and weathered Lithology – rock name and texture, plus a description of the minerals or fragments ...
The Earth*s Physical Geography
... Ex. Volcano Hills have rounded tops, but are lower and less steep than mountains Plateau is large and mostly flat . It rises above the surrounding land One steep slope Plains are large areas of flat land, but can also be gently rolling ...
... Ex. Volcano Hills have rounded tops, but are lower and less steep than mountains Plateau is large and mostly flat . It rises above the surrounding land One steep slope Plains are large areas of flat land, but can also be gently rolling ...
Chapter 1 Introduction to Earth Science Chapter Test Earth Science
... b. biosphere c. hydrosphere d. geosphere 5. The asthenosphere and lithosphere are parts of Earth’s a. geosphere. b. biosphere. c. hydrosphere. d. atmosphere. 6. What are the three main parts of the geosphere? a. atmosphere, crust, core b. lithosphere, mantle, core c. crust, mantle, core d. asthenosp ...
... b. biosphere c. hydrosphere d. geosphere 5. The asthenosphere and lithosphere are parts of Earth’s a. geosphere. b. biosphere. c. hydrosphere. d. atmosphere. 6. What are the three main parts of the geosphere? a. atmosphere, crust, core b. lithosphere, mantle, core c. crust, mantle, core d. asthenosp ...
Rock types Soil-forming factor 1: Parent material
... surface conditions and not the underlying bedrock. It should be noted that the general nature of this map means that at a local level, the conditions may be quite different to that shown. Other than the terms alluvium (deposited by water), aeolian (deposited by wind), organic (peat deposits) and col ...
... surface conditions and not the underlying bedrock. It should be noted that the general nature of this map means that at a local level, the conditions may be quite different to that shown. Other than the terms alluvium (deposited by water), aeolian (deposited by wind), organic (peat deposits) and col ...
Interior of Earth Graphic Organizer
... Earth has a diameter of about 12,756 km (7,972 mi). The Earth's interior consists of rock and metal. It is made up of four main layers: 1) the inner core: a solid metal core made up of nickel and iron (2440 km diameter) 2) the outer core: a liquid molten core of nickel and iron 3) the mantle: dense ...
... Earth has a diameter of about 12,756 km (7,972 mi). The Earth's interior consists of rock and metal. It is made up of four main layers: 1) the inner core: a solid metal core made up of nickel and iron (2440 km diameter) 2) the outer core: a liquid molten core of nickel and iron 3) the mantle: dense ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.