Layers Directed Reading
... Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? ...
... Why do less dense compounds make up Earth’s crust while the densest compounds make up the core? ...
Plate Tectonics
... ◦ As plates move, new volcanoes are formed along the floor bottom above the hot spot ◦ Hawaii – age of features increase as you move away from the hot spot (Kilauea) ◦ Therefore: The plates are moving over the hot spot and forming new volcanic features. ...
... ◦ As plates move, new volcanoes are formed along the floor bottom above the hot spot ◦ Hawaii – age of features increase as you move away from the hot spot (Kilauea) ◦ Therefore: The plates are moving over the hot spot and forming new volcanic features. ...
Chapter 21- Planet Earth
... deep inside the mantle, melt as they rise, and erupt from volcanoes at hot spots at the surface. ...
... deep inside the mantle, melt as they rise, and erupt from volcanoes at hot spots at the surface. ...
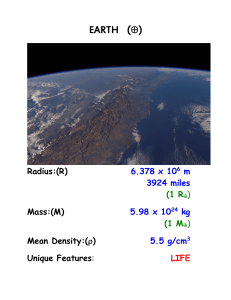
EARTH (¿)
... -lightest elements "rise" to surface -silicon, oxygen compounds Today, slowly cooling off: Interior of Earth still very hot at center (> 5300 oC or 9600 oF !) ...
... -lightest elements "rise" to surface -silicon, oxygen compounds Today, slowly cooling off: Interior of Earth still very hot at center (> 5300 oC or 9600 oF !) ...
Evolution and the History of Life
... • Pangaea is the name given to the Earth’s early landmass by Alfred Wegner. • Wegener published his theory called Continental Drift in his 1915 book, On the Origin of Continents and Oceans. • In it he also proposed the existence of the supercontinent Pangaea, and named it (Pangaea means "all the lan ...
... • Pangaea is the name given to the Earth’s early landmass by Alfred Wegner. • Wegener published his theory called Continental Drift in his 1915 book, On the Origin of Continents and Oceans. • In it he also proposed the existence of the supercontinent Pangaea, and named it (Pangaea means "all the lan ...
Earth has several layers
... Because of Ocean trenches: ►These are sights where dense oceanic curst is sinking into the asthensphere. ►Old crust is destroyed at the same rate that new crust is made. This keeps the Earth at the same size. ...
... Because of Ocean trenches: ►These are sights where dense oceanic curst is sinking into the asthensphere. ►Old crust is destroyed at the same rate that new crust is made. This keeps the Earth at the same size. ...
Earth has several layers
... Because of Ocean trenches: ►These are sights where dense oceanic curst is sinking into the asthensphere. ►Old crust is destroyed at the same rate that new crust is made. This keeps the Earth at the same size. ...
... Because of Ocean trenches: ►These are sights where dense oceanic curst is sinking into the asthensphere. ►Old crust is destroyed at the same rate that new crust is made. This keeps the Earth at the same size. ...
Chapter 5 - Mrs. Wiley`s Environmental Science Site
... By how they are formed. Why is ice a mineral but not liquid water? Because a mineral must be a solid. What is lithification? When sediments are turned into rocks. Using your textbook, draw and label a diagram of the rock cycle. ...
... By how they are formed. Why is ice a mineral but not liquid water? Because a mineral must be a solid. What is lithification? When sediments are turned into rocks. Using your textbook, draw and label a diagram of the rock cycle. ...
Blank Review for Core - Mantle
... You must be able to accurately label a diagram of the layers of the Earth (including the discontinuities) You must be able to answer question about any of the experiments conducted in class. Direct Observation Definition What do we study with it? ...
... You must be able to accurately label a diagram of the layers of the Earth (including the discontinuities) You must be able to answer question about any of the experiments conducted in class. Direct Observation Definition What do we study with it? ...
Plate Tectonic Outline Notes
... C. ________________ - place inside the earth where the quake actually occurs D. _________________ - pt. On Earth's surface directly above the focus of the quake E. 3 Forces Rocks Experience 1. _______________________________ - stress that squeezes compacts 2. _____________________ - stress that caus ...
... C. ________________ - place inside the earth where the quake actually occurs D. _________________ - pt. On Earth's surface directly above the focus of the quake E. 3 Forces Rocks Experience 1. _______________________________ - stress that squeezes compacts 2. _____________________ - stress that caus ...
Picture
... that form rocks and minerals and cycle Earth’s materials. Unit 3, Lesson 1: Minerals 1. Define mineral, matter, elements, and compounds. 2. List the characteristics that ALL minerals share. 3. Summarize the 3 ways in which mineral crystallization occurs. Give an example of each. 4. Explain the two w ...
... that form rocks and minerals and cycle Earth’s materials. Unit 3, Lesson 1: Minerals 1. Define mineral, matter, elements, and compounds. 2. List the characteristics that ALL minerals share. 3. Summarize the 3 ways in which mineral crystallization occurs. Give an example of each. 4. Explain the two w ...
Earth Science
... winds, and clouds in a particular area Comet: a ball of ice and dust whose orbit is a long, narrow ellipse Compound: a substance in which two or more elements are chemically joined Condensation: the process by which a gas changes to a liquid Conduction: the transfer of heat from one substance to an ...
... winds, and clouds in a particular area Comet: a ball of ice and dust whose orbit is a long, narrow ellipse Compound: a substance in which two or more elements are chemically joined Condensation: the process by which a gas changes to a liquid Conduction: the transfer of heat from one substance to an ...
Colorado State Science Content Standards
... In grades 6-8, students know and can demonstrate understanding that: Earth’s Composition, Processes and History 1. inter-relationships exist between minerals, rocks, and soils 2. humans use renewable and nonrenewable resources (for example: forests and fossil fuels) 3. natural processes shape the Ea ...
... In grades 6-8, students know and can demonstrate understanding that: Earth’s Composition, Processes and History 1. inter-relationships exist between minerals, rocks, and soils 2. humans use renewable and nonrenewable resources (for example: forests and fossil fuels) 3. natural processes shape the Ea ...
Earth - edl.io
... Rock layers (strata) are laid down in succession with each strata representing a “slice” of time. ...
... Rock layers (strata) are laid down in succession with each strata representing a “slice” of time. ...
Name Student ID Exam 2b – GEOL 1113 Fall 2009 ____
... _____ 18. The foot wall block is ______ of the fault plane a. left b. right _____ 19. The fault is ___________ than formation C. We know this because of the principle of ___________ a. younger, superposition b. younger, cross-cutting relationships c. older, superposition d. older, cross-cutting rela ...
... _____ 18. The foot wall block is ______ of the fault plane a. left b. right _____ 19. The fault is ___________ than formation C. We know this because of the principle of ___________ a. younger, superposition b. younger, cross-cutting relationships c. older, superposition d. older, cross-cutting rela ...
Name Student ID Exam 2c – GEOL 1113 Fall 2009 ____
... _____ 45. The low velocity zone in the mantle corresponds to the asthenosphere of plate tectonic theory. True (T) False (F) _____ 46. Geologists study the composition of the earth's core using deep drill holes. True (T) ...
... _____ 45. The low velocity zone in the mantle corresponds to the asthenosphere of plate tectonic theory. True (T) False (F) _____ 46. Geologists study the composition of the earth's core using deep drill holes. True (T) ...
Section 1 - Pelham City Schools
... • National Hazards Maps used by cities, counties & local governments to update & create more ...
... • National Hazards Maps used by cities, counties & local governments to update & create more ...
3202 Unit 1-1 PlateTectonics
... melt. As the magma heats up it expands and moves upward through cracks to the surface. A mild eruption will have lava flows. Thick lava tends to solidify, forming a plug. When gases build up behind this a violent explosion may occur. Molten rock below the surface of the Earth is known as magma. Afte ...
... melt. As the magma heats up it expands and moves upward through cracks to the surface. A mild eruption will have lava flows. Thick lava tends to solidify, forming a plug. When gases build up behind this a violent explosion may occur. Molten rock below the surface of the Earth is known as magma. Afte ...
Chapter 12 Plate Tectonics
... D. Magnetic stripes 1. Record history of Earth's magnetism 2. Magnetic poles tend to reverse themselves 3. Pattern of stripes provides evidence E. Destruction of ocean floor 1. Trenches are deepest part of ocean floor 2. Subduction occurs 3. Crust remains the same size a. New rocks form b. Old rocks ...
... D. Magnetic stripes 1. Record history of Earth's magnetism 2. Magnetic poles tend to reverse themselves 3. Pattern of stripes provides evidence E. Destruction of ocean floor 1. Trenches are deepest part of ocean floor 2. Subduction occurs 3. Crust remains the same size a. New rocks form b. Old rocks ...
Unit 2: Plate Tectonics Test Review
... a. a divergent boundary b. a hot spot in the Pacific Ocean c. a convergent boundary ...
... a. a divergent boundary b. a hot spot in the Pacific Ocean c. a convergent boundary ...
Unit 2 Review
... a. a divergent boundary b. a hot spot in the Pacific Ocean c. a convergent boundary ...
... a. a divergent boundary b. a hot spot in the Pacific Ocean c. a convergent boundary ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.