* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence for Continental Drift
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Composition of Mars wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
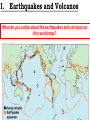
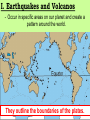
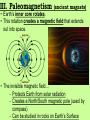
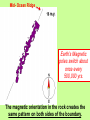
Aim: What New Evidence is used to explain Plate tectonics? Do Now: What evidence did Wegener use to help explain his theory of Continental Drift? (REVIEW) Theory of Plate Tectonics - the lithosphere is broken up into many segments each carrying a continent or a part of a continent. (like a cracked egg shell) - continents are attached to the lithosphere (crust) which move on the asthenosphere I. Earthquakes and Volcanos What do you notice about the earthquakes and volcanos on this world map? I. Earthquakes and Volcanos - Occur in specific areas on our planet and create a pattern around the world. They outline the boundaries of the plates. II. Sea-Floor Spreading Which continents appear to fit best together on the world map? How have these continents moved relative to each other? - as magma rises up through the crust (lithosphere), the sea floor spreads apart and gets wider. - rising magma makes new oceanic crust (young) - This new oceanic crust pushes continents away from each other. Where would the youngest oceanic crust be located on the diagram? • at the ridge, where new magma rises and solidifies. Where would the oldest oceanic crust be located on the diagram? • at the edge of the plate closest to the continents Ridge III. Paleomagnetism (ancient magnets) • Earth’s inner core rotates. • This rotation creates a magnetic field that extends out into space. • The invisible magnetic field… - Protects Earth from solar radiation - Creates a North/South magnetic pole (used by compass) - Can be studied in rocks on Earth’s Surface What minerals make up the core and mantle? - iron in the rising magma aligns to Earth's magnetic field (like a compass). - the magma cools and solidifies the iron in place within the rock. The iron in the rock shows the record of Earth’s magnetic history. ~ 1 MYA • Normal polarity - when rocks show the same magnetism as today • Reverse polarity - when rocks show the opposite magnetism as today ~ 500,000 years ago Present Mid- Ocean Ridge Earth’s Magnetic poles switch about once every 500,000 yrs. The magnetic orientation in the rock creates the same pattern on both sides of the boundary. IV. Hot Spots • Fixed concentrations of magma in the mantle that rise to the surface as a plume. •The Hawaiian Islands were formed as the Pacific plate moved over one of these hot spots Push me Closure 1: What if the sea-floor was not spreading? Evidence that supports sea-floor is spreading Age of sea-floor? - sea-floor shows different aged rocks (younger at the ridge and older at the continents) - sea-floor would have the same age throughout the entire ocean. Paleomagnetism? - rocks would show the same magnetism - rocks show matching patterns of alternating magnetism on both sides of the ridge. Closure 2: Review Book Page 105-107 #1-10 1. 1 2. 2 3. 1 4. 4 5. 1 6. 2 7. 3 8. 3 9. 4 10.3