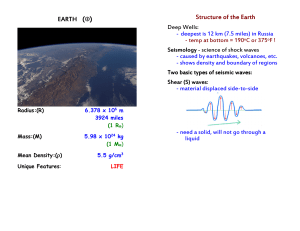
EARTH (⊕) Structure of the Earth
... -iron, nickel -lightest elements "rise" to surface -silicon, oxygen compounds Today, slowly cooling off: Interior of Earth still very hot at center (> 5300 oC or 9600 oF !) ...
... -iron, nickel -lightest elements "rise" to surface -silicon, oxygen compounds Today, slowly cooling off: Interior of Earth still very hot at center (> 5300 oC or 9600 oF !) ...
Deforming the Earth`s Crust
... mountains form. • The layers of the crust break and drop in elevation compared to surrounding layers. • The Tetons are an ...
... mountains form. • The layers of the crust break and drop in elevation compared to surrounding layers. • The Tetons are an ...
Notes on Igneous Rocks:
... _______________-moving, THINNER= LOW Viscosity, less resistance to flowing, more fluid Crystallize to _____________ __________________ minerals Resulting rocks have relatively _____________ __________________. Mafic igneous rocks make up the _________________ ____________________. Examples ...
... _______________-moving, THINNER= LOW Viscosity, less resistance to flowing, more fluid Crystallize to _____________ __________________ minerals Resulting rocks have relatively _____________ __________________. Mafic igneous rocks make up the _________________ ____________________. Examples ...
Class Notes: Introduction to Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Tectonic
... Class Opener: Do mapping activity and answer the following questions once complete A. Are all the earthquakes and volcanoes evenly spaced randomly across earth’s surface? If not, describe where there appear to be the most… B. Look at the “Earth’s fractured surface” map and read the introduction (bac ...
... Class Opener: Do mapping activity and answer the following questions once complete A. Are all the earthquakes and volcanoes evenly spaced randomly across earth’s surface? If not, describe where there appear to be the most… B. Look at the “Earth’s fractured surface” map and read the introduction (bac ...
Chapter 1, Section 1 – Earth`s Interior
... a. Two main methods of exploring Earth’s interior: i. Direct evidence – rock samples ii. Indirect evidence – seismic waves 1. examine the speed and paths of seismic waves b. Seismic waves i. Produced from earthquakes ii. Measured with seismographs iii. Two most common types: 1. P waves (primary wave ...
... a. Two main methods of exploring Earth’s interior: i. Direct evidence – rock samples ii. Indirect evidence – seismic waves 1. examine the speed and paths of seismic waves b. Seismic waves i. Produced from earthquakes ii. Measured with seismographs iii. Two most common types: 1. P waves (primary wave ...
Alfred Wegener - Colts Neck Township Schools
... America, Africa, India, and Australia –Coral reefs found in Northern Canada –Coal formation in North America ...
... America, Africa, India, and Australia –Coral reefs found in Northern Canada –Coal formation in North America ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources G. Tyler Miller`s
... There are three types of boundaries for lithospheric plates. The boundaries are divergent plate boundaries, where plates move apart in opposite directions, and convergent plate boundaries, where plates are pushed together by internal forces and one plate rides up over the other. A trench generally o ...
... There are three types of boundaries for lithospheric plates. The boundaries are divergent plate boundaries, where plates move apart in opposite directions, and convergent plate boundaries, where plates are pushed together by internal forces and one plate rides up over the other. A trench generally o ...
How do you think it formed?
... The Earth’s Structure The Asthenosphere Soft layer in upper mantle. ...
... The Earth’s Structure The Asthenosphere Soft layer in upper mantle. ...
The Theory of Continental Drift (Now Plate Tectonics)
... plates about ____km’s thick - These plates ________ on the earth’s semi-molten asthenosphere (the top layer of the earth’s mantle) and are driven by convection (______) cycles in the mantle. - __________ plates move about 10 cm/year - _________________ plates about 2 cm/year - It is believed that th ...
... plates about ____km’s thick - These plates ________ on the earth’s semi-molten asthenosphere (the top layer of the earth’s mantle) and are driven by convection (______) cycles in the mantle. - __________ plates move about 10 cm/year - _________________ plates about 2 cm/year - It is believed that th ...
Ocean waves that wear away an island`s shoreline
... 3. The part of the mantle called the ____________________ is made of soft rock that bends like plastic. 4. Oceanic crust is made up mostly of dense rock called ____________________. 5. When you touch a hot plate, the transfer of heat from the plate to your hand is called ____________________. 6. The ...
... 3. The part of the mantle called the ____________________ is made of soft rock that bends like plastic. 4. Oceanic crust is made up mostly of dense rock called ____________________. 5. When you touch a hot plate, the transfer of heat from the plate to your hand is called ____________________. 6. The ...
7-1 Inside the Earth RG
... _____ 11. the outermost, rigid layer of the Earth _____ 12. a layer of slowly flowing rock in the mantle _____ 13. the liquid layer of the core ...
... _____ 11. the outermost, rigid layer of the Earth _____ 12. a layer of slowly flowing rock in the mantle _____ 13. the liquid layer of the core ...
Planet Earth/Atmosphere Name Learning Targets Period _____
... Learning Targets Vocabulary: crust lithosphere fault epicenter Magnitude scale Stratosphere troposphere thermosphere ...
... Learning Targets Vocabulary: crust lithosphere fault epicenter Magnitude scale Stratosphere troposphere thermosphere ...
Notes 11 – Earth`s Interior
... • 1. Theory of Continental Drift – all continents were once connected and called Pangaea, they have since drifted apart. • A. Alfred Wegener ...
... • 1. Theory of Continental Drift – all continents were once connected and called Pangaea, they have since drifted apart. • A. Alfred Wegener ...
Folding and Faulting
... DOMING 2 Types; -When rising magma raises rock upwards -The result of compression Eg; Slieve Bloom Mountains, Laois/Offaly ...
... DOMING 2 Types; -When rising magma raises rock upwards -The result of compression Eg; Slieve Bloom Mountains, Laois/Offaly ...
Name
... yesterday, or even last decade. So we would naturally be forced to think this is false, which is what scientists did when Wegener conceived this hypothesis. After initially being dismissed, evidence came forth that facilitated the proving of plate tectonics. It was found that the continents have a " ...
... yesterday, or even last decade. So we would naturally be forced to think this is false, which is what scientists did when Wegener conceived this hypothesis. After initially being dismissed, evidence came forth that facilitated the proving of plate tectonics. It was found that the continents have a " ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary
... Plate Tectonics Vocabulary 1. Continental drift- the hypothesis that a single large landmass broke up into smaller landmasses to form the continents, which then drifted to their present locations; the movement of continents 2. Plate tectonics- the theory that Earth’s outer layer is made up of large, ...
... Plate Tectonics Vocabulary 1. Continental drift- the hypothesis that a single large landmass broke up into smaller landmasses to form the continents, which then drifted to their present locations; the movement of continents 2. Plate tectonics- the theory that Earth’s outer layer is made up of large, ...
Rock Cycle 200 - FitzBrownBodleTeam
... crust meet the more dense oceanic crust will sink below the less dense continental crust 3. Where the continental crust and continental crust meet, mountains will form as the land is thrust upwards. ...
... crust meet the more dense oceanic crust will sink below the less dense continental crust 3. Where the continental crust and continental crust meet, mountains will form as the land is thrust upwards. ...
PPT on Minerals and Review Ch14
... Heat added to crust by magmas causes regional and contact metamorphism Heat added also produced more felsic magma ...
... Heat added to crust by magmas causes regional and contact metamorphism Heat added also produced more felsic magma ...
Rocks Powerpoint Notes
... Once a rock is formed, does it stay the same rock forever?_____________ Rocks are continually changed by many ___________________, such as weathering, _______________, compaction, ________________________, melting, and cooling Rocks can ____________________ to and from the three types How are rocks ...
... Once a rock is formed, does it stay the same rock forever?_____________ Rocks are continually changed by many ___________________, such as weathering, _______________, compaction, ________________________, melting, and cooling Rocks can ____________________ to and from the three types How are rocks ...
Earth`s Structure and Plate Tectonics Unit Test Study Guide Format
... 4. Where do most volcanoes and earthquakes occur? At plate boundaries 5. Energy is released from earthquakes in the form of what? Seismic Waves 6. What is the difference between surface waves, primary waves, and secondary waves? Surface waves travel the slowest and do the most damage, primary waves ...
... 4. Where do most volcanoes and earthquakes occur? At plate boundaries 5. Energy is released from earthquakes in the form of what? Seismic Waves 6. What is the difference between surface waves, primary waves, and secondary waves? Surface waves travel the slowest and do the most damage, primary waves ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.























