* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EARTH (⊕) Structure of the Earth
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geodesy wikipedia , lookup
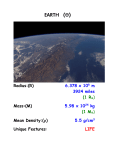
Structure of the Earth EARTH (⊕ ⊕) Deep Wells: - deepest is 12 km (7.5 miles) in Russia - temp at bottom = 190oC or 375oF ! Seismology Seismology - science of shock waves - caused by earthquakes, volcanoes, etc. - shows density and boundary of regions Two basic types of seismic waves: Shear (S (S) waves: waves - material displaced side-to-side Radius:(R) 6.378 x 106 m 3924 miles (1 R⊕) Mass:(M) 5.98 x 1024 kg (1 M⊕) Mean Density:(ρ ρ) 5.5 g/cm3 Unique Features: LIFE - need a solid, will not go through a liquid Pressure Pressure (P (P) waves: - material is compressed - can travel through any material RESULTS: Crust: Crust low density rock (2.5-3.5 g/cm3) variable thickness (5 – 50 km) rigid, brittle material Mantle: Mantle high density rock (4.5-10 g/cm3) 2900 km thick “plastic” - hot, solid but can flow Outer Core: Core liquid Iron (some Nickel) very high density (9-11 g/cm3) 2200 km thick Inner Core: Core solid material; (~ 13 g/cm3 ) crystallized iron-nickel ?? Differentiation - mixing material with different densities -lower density objects will "float" -higher density objects will "sink" - Ice floats on water - Rocks float on liquid iron Formation of Earth: -accretion/collisions of smaller objects -great amounts of heat released -original Earth molten - Causes many geographic features - mountain ranges, oceanic trenches and rifts, island chains Earth became differentiated: -densest elements "sink" to center -iron, nickel -lightest elements "rise" to surface -silicon, oxygen compounds Today, slowly cooling off: Interior of Earth still very hot at center (> 5300 oC or 9600 oF !) Surface of Earth Crust of Earth is broken into plates: - 15 major plates move ~ 10 cm/yr Plate Tectonics - causes many active features - volcanoes, earthquakes http://www.scotese.com/earth.htm Other processes that affect surface -Erosion, Deposition (from wind, water) -Life (Human activities) Mississippi Delta -Impact Cratering http://www.passc.net/EarthImpactDatabase/index.html Tswaing Crater, South Africa Earth’s Surface is geologically "young" - only 10 - 100 million years old