P-waves
... Most common types of earthquake waves: P-waves and S-waves – Body waves Primary waves travel the fastest in the crust and usually are the first waves to ...
... Most common types of earthquake waves: P-waves and S-waves – Body waves Primary waves travel the fastest in the crust and usually are the first waves to ...
01 00_Earth_Layers 1
... The inner core of the Earth has temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are ...
... The inner core of the Earth has temperatures and pressures so great that the metals are ...
Study Notes: Chapter 27- Planets of the Solar System
... 4. When early Earth’s atmosphere formed, _________________ and hydrogen gases were lost because Earth’s ______________ was too weak. 5. Copernicus proposed a _________________ model of the universe, in which the planets revolve at different speeds around the sun. 6. Mars’s volcanoes are ____________ ...
... 4. When early Earth’s atmosphere formed, _________________ and hydrogen gases were lost because Earth’s ______________ was too weak. 5. Copernicus proposed a _________________ model of the universe, in which the planets revolve at different speeds around the sun. 6. Mars’s volcanoes are ____________ ...
Earthlike planets
... 16. The greenhouse effect keeps Venus hot because a. the atmosphere contains free oxygen. b. the atmosphere is rich in carbon dioxide. c. the surface converts infrared into visible radiation. d. the surface is free of sulfur compounds. e. the magnetic field traps a large number of particles from the ...
... 16. The greenhouse effect keeps Venus hot because a. the atmosphere contains free oxygen. b. the atmosphere is rich in carbon dioxide. c. the surface converts infrared into visible radiation. d. the surface is free of sulfur compounds. e. the magnetic field traps a large number of particles from the ...
Geophysical tools for site investigations Guy MARQUIS, EOST
... you need to tighten a screw, using a hammer - even if it’s a very good one - won’t be much help... Before presenting the geophysical prospecting methods per se, we are first going to have a quick look at the main physical properties of earth materials so that we can have an idea of what geophysics a ...
... you need to tighten a screw, using a hammer - even if it’s a very good one - won’t be much help... Before presenting the geophysical prospecting methods per se, we are first going to have a quick look at the main physical properties of earth materials so that we can have an idea of what geophysics a ...
Earth Science Study Guide - Darlington Middle School
... activity depends upon the types of crust that meet more dense oceanic plate slides under less dense continental plate or another oceanic plate subduction zone, some crust is destroyed two continental plates converge both plates buckle and push up into mountain ranges o Transform boundary—w ...
... activity depends upon the types of crust that meet more dense oceanic plate slides under less dense continental plate or another oceanic plate subduction zone, some crust is destroyed two continental plates converge both plates buckle and push up into mountain ranges o Transform boundary—w ...
Unit D Test Review - Bibb County Schools
... of the earth’s crust have moved toward and away from each other to form continents, mountains, and oceans. ...
... of the earth’s crust have moved toward and away from each other to form continents, mountains, and oceans. ...
EGU2017-5944
... When combined with information from mineral physics and geodynamics, seismic anisotropy is one of the most direct ways to constrain mantle deformation and flow. However, it can be challenging to image it globally due to limited data’s sensitivity and difficulties in separating shallow and deep Earth ...
... When combined with information from mineral physics and geodynamics, seismic anisotropy is one of the most direct ways to constrain mantle deformation and flow. However, it can be challenging to image it globally due to limited data’s sensitivity and difficulties in separating shallow and deep Earth ...
C1b 6.1 Structure of the Earth
... • How many parts make up the Earths core? What are they? • Challenge: Why is the hotter part of the core solid, while the cooler part is liquid? ...
... • How many parts make up the Earths core? What are they? • Challenge: Why is the hotter part of the core solid, while the cooler part is liquid? ...
Unit Vocab
... above the inner core Inner Core: solid center made of heavy metals; hottest layer Hydrosphere: all the water on Earth Page 1 of 2 ...
... above the inner core Inner Core: solid center made of heavy metals; hottest layer Hydrosphere: all the water on Earth Page 1 of 2 ...
Pixelgost`s Dynamic Planet test
... 1. What makes the Crust move? How does this work? 2. What is an Orogen? 3. What is the term describing the ground acting like a fluid? 4. What is ISostasy? 5. What are the two kinds of surface waves? 6. What is the kind of deformation for when a Rock snaps? 7. What is the kind of deformation when a ...
... 1. What makes the Crust move? How does this work? 2. What is an Orogen? 3. What is the term describing the ground acting like a fluid? 4. What is ISostasy? 5. What are the two kinds of surface waves? 6. What is the kind of deformation for when a Rock snaps? 7. What is the kind of deformation when a ...
file_n_2
... Richter Scale: Open scale designed to measure the energy developed by a seism, i.e. its magnitude. Measure of the maximum amplitude of the seismic waves recorded by a standard seismograph at a distance of 100 km of the epicentre Epicentre: Point on the Earth surface located vertically to the focus. ...
... Richter Scale: Open scale designed to measure the energy developed by a seism, i.e. its magnitude. Measure of the maximum amplitude of the seismic waves recorded by a standard seismograph at a distance of 100 km of the epicentre Epicentre: Point on the Earth surface located vertically to the focus. ...
Warm- Up
... 6. Put the following in order of increasing density: outer core, continental crust, asthenosphere, oceanic crust, 7. What are the 3 types of convergent boundaries? 8. At which type of boundary is crust neither created nor destroyed? 9. If two oceanic plates collide, which plate will go under the oth ...
... 6. Put the following in order of increasing density: outer core, continental crust, asthenosphere, oceanic crust, 7. What are the 3 types of convergent boundaries? 8. At which type of boundary is crust neither created nor destroyed? 9. If two oceanic plates collide, which plate will go under the oth ...
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
... • The Earth’s crust is divided into _________major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to _____________________________ • ________________ against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. ...
... • The Earth’s crust is divided into _________major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to _____________________________ • ________________ against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” features. ...
2-Unit4Part2EarthsInteriors
... 3. L-waves (Long waves or Love Waves) • Surface waves that cause horizontal shearing of the ground – Travel on the surface of the earth and shake rocks sideways as they move across the surface – Generated by the epicenter – Particles travel in a rolling motion ...
... 3. L-waves (Long waves or Love Waves) • Surface waves that cause horizontal shearing of the ground – Travel on the surface of the earth and shake rocks sideways as they move across the surface – Generated by the epicenter – Particles travel in a rolling motion ...
Earth Science Vocabulary
... 19. Mid-Ocean Ridge – the undersea mountain chain in the Atlantic Ocean where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary 20. Pangaea – large ancient landmass that was composed of all the continents joined together 21. Plasticity – a substance that has the properties of a solid, but has ...
... 19. Mid-Ocean Ridge – the undersea mountain chain in the Atlantic Ocean where new ocean floor is produced; a divergent plate boundary 20. Pangaea – large ancient landmass that was composed of all the continents joined together 21. Plasticity – a substance that has the properties of a solid, but has ...
What are the three types of convergent boundaries? oceanic
... Unit Assessment Review (Plate Tectonics, Volcanoes, and Earthquakes) About two-thirds of Earth’s volcanism occurs at divergent boundaries. The Hawaiian islands formed as a result of a hot spot. The physical property that describes a material’s resistance to flow is called viscosity. A(n) crater is a ...
... Unit Assessment Review (Plate Tectonics, Volcanoes, and Earthquakes) About two-thirds of Earth’s volcanism occurs at divergent boundaries. The Hawaiian islands formed as a result of a hot spot. The physical property that describes a material’s resistance to flow is called viscosity. A(n) crater is a ...
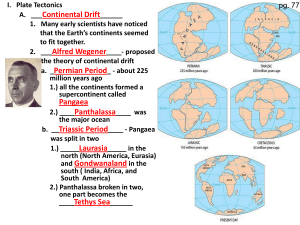
la teoria della deriva dei continenti e della tettonica a zolle
... The cause of plate movements is in the Earth’s mantle , precisely in the middle layer called the ASTHENOSPHERE where the convective motions occur. ...
... The cause of plate movements is in the Earth’s mantle , precisely in the middle layer called the ASTHENOSPHERE where the convective motions occur. ...
Lecture 18 Earth`s Interior
... The core • Formation: The core was formed early in Earth's history as heavy molten iron alloy migrated toward the center of the planet. High temperatures (~5000K) keep the bulk of the core liquid. As the Earth cooled through mantle convection, molten iron began to solidify under enormous pressure ( ...
... The core • Formation: The core was formed early in Earth's history as heavy molten iron alloy migrated toward the center of the planet. High temperatures (~5000K) keep the bulk of the core liquid. As the Earth cooled through mantle convection, molten iron began to solidify under enormous pressure ( ...
Earth Scavenger Hunt
... Neptunists thought the entire earth had been covered by oceans at one time and had since evaporated, leaving dry land in some places. ♦ In 2005, scientists of the American Geophysical Union reported that the earth’s north magnetic pole had been moving rapidly towards Siberia. Scientists believe that ...
... Neptunists thought the entire earth had been covered by oceans at one time and had since evaporated, leaving dry land in some places. ♦ In 2005, scientists of the American Geophysical Union reported that the earth’s north magnetic pole had been moving rapidly towards Siberia. Scientists believe that ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.