Chapter 2 38 Cha pter 2 The Thalamus is a sub
... The Thalamus is a sub-cortical, gray matter, oval or egg-shaped structure on either side of the Third ventricle. It is located at the top of the brainstem and superior to the hypothalamus. It is responsible for consciousness, sleep, wakefulness, motor control and all senses except olfactory. The fro ...
... The Thalamus is a sub-cortical, gray matter, oval or egg-shaped structure on either side of the Third ventricle. It is located at the top of the brainstem and superior to the hypothalamus. It is responsible for consciousness, sleep, wakefulness, motor control and all senses except olfactory. The fro ...
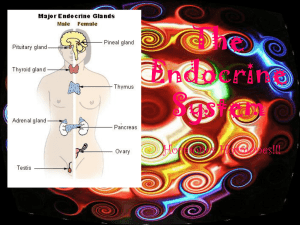
The Endocrine System
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. These products send messages throughout the entire body. • The response of hormones is slower and longer‐ lasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several ho ...
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. These products send messages throughout the entire body. • The response of hormones is slower and longer‐ lasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several ho ...
Pituitary Gland
... The anterior pituitary produces several types of hormones: Prolactin or PRL - PRL stimulates milk production from a woman's breasts after childbirth and can affect sex hormone levels from the ovaries in women and the testes in men. Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is impo ...
... The anterior pituitary produces several types of hormones: Prolactin or PRL - PRL stimulates milk production from a woman's breasts after childbirth and can affect sex hormone levels from the ovaries in women and the testes in men. Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is impo ...
The Endocrine System
... “A hormone is a chemical messenger produced by an endocrine gland and transported in the bloodstream to act in another part of the body where it has a specific effect” Many hormones are proteins Some are steroid or lipid based such as those of the reproductive system Hormones are involved in co-ordi ...
... “A hormone is a chemical messenger produced by an endocrine gland and transported in the bloodstream to act in another part of the body where it has a specific effect” Many hormones are proteins Some are steroid or lipid based such as those of the reproductive system Hormones are involved in co-ordi ...
Hormones general characteristics, classification
... Hormonoids (tissue hormones) – compounds that are produced not in glands but in different tissues and regulate metabolic processes on the local level, but some of them (serotonin, acetylcholine) enters blood and regulate processes on the organism level. ...
... Hormonoids (tissue hormones) – compounds that are produced not in glands but in different tissues and regulate metabolic processes on the local level, but some of them (serotonin, acetylcholine) enters blood and regulate processes on the organism level. ...
Dr Watson Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... 10. Calcium is put into the bones by food in the diet. Then it is released from the bones into the blood. The parathyroid glands regulate the release of calcium. With too much or too little, problems result. What are they? Disorder with very low level of calcium in the blood: ______________________ ...
... 10. Calcium is put into the bones by food in the diet. Then it is released from the bones into the blood. The parathyroid glands regulate the release of calcium. With too much or too little, problems result. What are they? Disorder with very low level of calcium in the blood: ______________________ ...
Lecture_37_2014_noquiz
... How could this system be fine-tuned to optimize specific traits under different contexts? A.) changes in TRH expression B.) changes in TSH expression C.) alterations of TSH receptors D.) alteration of T3/T4 receptors in specific cell types. ...
... How could this system be fine-tuned to optimize specific traits under different contexts? A.) changes in TRH expression B.) changes in TSH expression C.) alterations of TSH receptors D.) alteration of T3/T4 receptors in specific cell types. ...
Document
... endocrine system (hormones into blood) neuroendocrine (neurohormones into blood) paracrines (secreted into extracellular fluid and affect neighboring different target cells) autocrines (affect same cells) cytokines (peptides - 5,4 or 2 - interleukins, lymphokines, adipokines (leptin)) ...
... endocrine system (hormones into blood) neuroendocrine (neurohormones into blood) paracrines (secreted into extracellular fluid and affect neighboring different target cells) autocrines (affect same cells) cytokines (peptides - 5,4 or 2 - interleukins, lymphokines, adipokines (leptin)) ...
Endocrine Note Cards
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
Clues
... 29. The rapid decrease of hormone receptors in the target tissue due to the exposure to a hormone is called ___ regulation. 30. Too much insulin or too little food intake after an injection of insulin by a diabetic patient causes insulin ____. 32. Hypothalamic hormone that causes the release of ACTH ...
... 29. The rapid decrease of hormone receptors in the target tissue due to the exposure to a hormone is called ___ regulation. 30. Too much insulin or too little food intake after an injection of insulin by a diabetic patient causes insulin ____. 32. Hypothalamic hormone that causes the release of ACTH ...
Introduction to Health Science
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. These products send messages throughout the entire body. • The response of hormones is slower and longerlasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several hours or ...
... • The endocrine system is made up of glands that release their products (hormones) directly into the bloodstream. These products send messages throughout the entire body. • The response of hormones is slower and longerlasting than those of nerve impulses. The effects may last up to several hours or ...
What is the Endocrine System?
... Regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, sexual function and reproductive processes. Is in charge of slow body processes (cell growth), but is interdependent, interconnected, and interrelated, faster processes (breathing &body movement) ...
... Regulates mood, growth and development, tissue function, metabolism, sexual function and reproductive processes. Is in charge of slow body processes (cell growth), but is interdependent, interconnected, and interrelated, faster processes (breathing &body movement) ...
1. Group I hormones
... The lipophilic group I hormones diffuse through the plasma membrane of all cells but only encounter their specific, high-affinity intracellular receptors in target cells. These receptors can be located in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus of target cells. The hormone-receptor complex first undergoes a ...
... The lipophilic group I hormones diffuse through the plasma membrane of all cells but only encounter their specific, high-affinity intracellular receptors in target cells. These receptors can be located in the cytoplasm or in the nucleus of target cells. The hormone-receptor complex first undergoes a ...
Endocrine Disorders
... Adrenal gland- sits atop the kidneys Two sections Adrenal cortex (outer layer) Cortisol- hormone released to lower stress and inflammation Also releases stored glucose when energy levels run low Excessive use of Prednisone leads to adrenal shutdown. ...
... Adrenal gland- sits atop the kidneys Two sections Adrenal cortex (outer layer) Cortisol- hormone released to lower stress and inflammation Also releases stored glucose when energy levels run low Excessive use of Prednisone leads to adrenal shutdown. ...
MS Word Version - Interactive Physiology
... -Glucose acts as an _________ __________ leading to increased urine flow. -Increased lipolysis produces an increase in _______ ______ which when used as fuel produces _________. - The presence of these in plasma and urine is known respectively as ___________ and ___________. ...
... -Glucose acts as an _________ __________ leading to increased urine flow. -Increased lipolysis produces an increase in _______ ______ which when used as fuel produces _________. - The presence of these in plasma and urine is known respectively as ___________ and ___________. ...
Nervous, Sensory, Endocrine and Exocrine Systems
... Slama, K. and C.M. Williams. 1966. The juvinile hormone. The sensitivity of the bug, Pyrrhocoris apterus to a hormonally active factor in American paper-pulp. Biological Bulletin ...
... Slama, K. and C.M. Williams. 1966. The juvinile hormone. The sensitivity of the bug, Pyrrhocoris apterus to a hormonally active factor in American paper-pulp. Biological Bulletin ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers that control the amount of hormone that is available for the cells to use. The t ...
... through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers that control the amount of hormone that is available for the cells to use. The t ...
Endocrine System - WCED: Curriculum Development
... cavity or outside of body i.e. saliva, tears etc. ...
... cavity or outside of body i.e. saliva, tears etc. ...
At the crossroads of metabolism and reproduction in the brain
... Through elegant gene deletion-replacement experiments, Donato et al. (2011) showed that expressing functional leptin receptors exclusively in a little-studied part of the brain – the hypothalamic ventral premammillary nucleus (PMv) – is sufficient to mediate the hormone’s powerful stimulatory effect ...
... Through elegant gene deletion-replacement experiments, Donato et al. (2011) showed that expressing functional leptin receptors exclusively in a little-studied part of the brain – the hypothalamic ventral premammillary nucleus (PMv) – is sufficient to mediate the hormone’s powerful stimulatory effect ...
Chapter 25 Lecture notes
... D. Type II diabetes (non-insulin-dependent diabetes) is usually associated with people who are older (at least 40 years old) and obese and occurs when body cells do not respond correctly to insulin or when there is a true deficiency. Type II diabetes is usually controlled by diet, antidiabetic drugs ...
... D. Type II diabetes (non-insulin-dependent diabetes) is usually associated with people who are older (at least 40 years old) and obese and occurs when body cells do not respond correctly to insulin or when there is a true deficiency. Type II diabetes is usually controlled by diet, antidiabetic drugs ...
T4 to be maintained at a reasonable level
... should then produce mid range T3, but will of necessity produce a low normal or suppressed TSH. ( Alun Stevens MSc FIAA ) ...
... should then produce mid range T3, but will of necessity produce a low normal or suppressed TSH. ( Alun Stevens MSc FIAA ) ...
Endocrine System
... Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete their hormones into interstitial fluid, lymph, and blood. • Exocrine glands secrete products into ducts • Hormones are bloodborne “information” units. – Come from endocrine glands – Circulate in the bloodstream – Act on specific cells in the body ...
... Endocrine glands are ductless and secrete their hormones into interstitial fluid, lymph, and blood. • Exocrine glands secrete products into ducts • Hormones are bloodborne “information” units. – Come from endocrine glands – Circulate in the bloodstream – Act on specific cells in the body ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers ...
... Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers ...
PowerPoint Chapter 29
... VI. The Endocrine System and Hormones (29.6) A. Hormones influence a cell’s activities by entering the cell or binding to its membrane 1. Endocrine system makes chemical signals that help body grow, develop, and maintain homeostasis ...
... VI. The Endocrine System and Hormones (29.6) A. Hormones influence a cell’s activities by entering the cell or binding to its membrane 1. Endocrine system makes chemical signals that help body grow, develop, and maintain homeostasis ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.