Module 4 psych
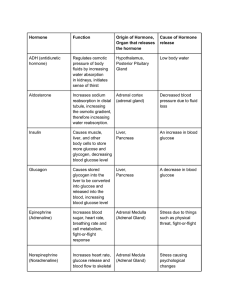
... The adrenal medulla (inside part) secretes two hormones that arouse the body to deal with stress and emergencies: ...
... The adrenal medulla (inside part) secretes two hormones that arouse the body to deal with stress and emergencies: ...
The Endocrine System - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... The Pituitary Gland is divided into Anterior and Posterior Parts Hormones from the pituitary control control the function of many other endocrine glands such as the ovaries , testes, thyroid gland and adrenal coortex Also secretes hormones that affect growth, kidney function, birth and milk producti ...
... The Pituitary Gland is divided into Anterior and Posterior Parts Hormones from the pituitary control control the function of many other endocrine glands such as the ovaries , testes, thyroid gland and adrenal coortex Also secretes hormones that affect growth, kidney function, birth and milk producti ...
1-JAN 18 PG
... 2) Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis): connected to hypothalamus through hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract, Stores hormones secreted by hypothalamic nuclei. ...
... 2) Posterior lobe (Neurohypophysis): connected to hypothalamus through hypothalamo-hypophyseal tract, Stores hormones secreted by hypothalamic nuclei. ...
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
... • Alpha—glucagon ( nec. when fasting increased BG) • Beta—insulin (released after a meal decreased BG, stim. protein syn. and fatty acid uptake & storage) ...
... • Alpha—glucagon ( nec. when fasting increased BG) • Beta—insulin (released after a meal decreased BG, stim. protein syn. and fatty acid uptake & storage) ...
Endocrine System - faculty at Chemeketa
... is formed during digestion; absorbed from intestines into blood of portal vein; in passage through liver, is converted into glycogen ...
... is formed during digestion; absorbed from intestines into blood of portal vein; in passage through liver, is converted into glycogen ...
Endocrinology
... the blood stream or lymph, Their production called hormones which they have either stimulating or inhibitor effects upon the development or function of the body organs. There is no anatomical continuity between these glands, except on a physiological level. Note: Not all ductless organs are endocrin ...
... the blood stream or lymph, Their production called hormones which they have either stimulating or inhibitor effects upon the development or function of the body organs. There is no anatomical continuity between these glands, except on a physiological level. Note: Not all ductless organs are endocrin ...
Endocrine System
... is formed during digestion; absorbed from intestines into blood of portal vein; in passage through liver, is converted into glycogen ...
... is formed during digestion; absorbed from intestines into blood of portal vein; in passage through liver, is converted into glycogen ...
PAC 01 Endocrine Physiology (Josh)
... Endocrine Physiology The difference between postive and negative feedback is important. Most hormones work on negative feedback mechanisms, but not all. Hormones produce biologic effects that directly or indirectly inhibit their further secretion. The endocrine hormones are incredibly powerful and a ...
... Endocrine Physiology The difference between postive and negative feedback is important. Most hormones work on negative feedback mechanisms, but not all. Hormones produce biologic effects that directly or indirectly inhibit their further secretion. The endocrine hormones are incredibly powerful and a ...
Hormone Summary Chart
... into glucose and released into the blood, increasing blood glucose level ...
... into glucose and released into the blood, increasing blood glucose level ...
Biology 2402 Notes - Endocrine System Ch
... Thyroid - located just below the larynx and anterior to the trachea in the neck. The thyroid is composed of spheres of glandular cells (follicular cells) with a cavity in the center. This structure is called a follicle. The central space is used to store a colloidal mixture that contains precursor ...
... Thyroid - located just below the larynx and anterior to the trachea in the neck. The thyroid is composed of spheres of glandular cells (follicular cells) with a cavity in the center. This structure is called a follicle. The central space is used to store a colloidal mixture that contains precursor ...
Unit07
... effect on a target cell, tissue, or organ Over 50 different hormones Most only affect a few, specific types of cells ...
... effect on a target cell, tissue, or organ Over 50 different hormones Most only affect a few, specific types of cells ...
Anterior pituitary
... -Includes endocrine glands, which are specialized to secrete hormones -Also organs, like the liver, that secrete hormones in addition to other functions Exocrine glands secrete their products, such as saliva or milk, into a duct for transport to the outside ...
... -Includes endocrine glands, which are specialized to secrete hormones -Also organs, like the liver, that secrete hormones in addition to other functions Exocrine glands secrete their products, such as saliva or milk, into a duct for transport to the outside ...
Biol 2402, Glidewell, Exam 1
... Thyroid - located just below the larynx and anterior to the trachea in the neck. The thyroid is composed of spheres of glandular cells (follicular cells) with a cavity in the center. This structure is called a follicle. The central space is used to store a colloidal mixture that contains precursor ...
... Thyroid - located just below the larynx and anterior to the trachea in the neck. The thyroid is composed of spheres of glandular cells (follicular cells) with a cavity in the center. This structure is called a follicle. The central space is used to store a colloidal mixture that contains precursor ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... Explain how it is that steroid and thyroid hormones remain in the blood much longer than catecholamine and peptide hormones? Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond to each and every hormone? What determines whether a cell can respond to a given ho ...
... Explain how it is that steroid and thyroid hormones remain in the blood much longer than catecholamine and peptide hormones? Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond to each and every hormone? What determines whether a cell can respond to a given ho ...
1 Chapter 11: The Endocrine System • Exocrine glands will produce
... Male: Testosterone produced in the gonad—testes that aids in the production of sperm cells and contributes to the male secondary sexual characteristics • Female: Estrogen and progesterone produced in the ovaries and in the placenta during pregnancy that regulation the female reproductive cycle. Est ...
... Male: Testosterone produced in the gonad—testes that aids in the production of sperm cells and contributes to the male secondary sexual characteristics • Female: Estrogen and progesterone produced in the ovaries and in the placenta during pregnancy that regulation the female reproductive cycle. Est ...
lecture #10
... therefore absolutely requires the expression of receptors on the cell surface – integral membrane proteins that act as first messenger the receptor protein activates a series of signaling events within the cells – e.g. epinephrine binds to receptor and activates an adjacent G-protein in membrane – G ...
... therefore absolutely requires the expression of receptors on the cell surface – integral membrane proteins that act as first messenger the receptor protein activates a series of signaling events within the cells – e.g. epinephrine binds to receptor and activates an adjacent G-protein in membrane – G ...
endocrine problems
... system regulates… * body energy levels * reproduction * growth and development * internal balance of body systems, called homeostasis * responses to surroundings, stress and injury ...
... system regulates… * body energy levels * reproduction * growth and development * internal balance of body systems, called homeostasis * responses to surroundings, stress and injury ...
File
... Treatment: anti-thyroid drugs, removal or destruction of part of the thyroid(surgically or radioactive iodine) ...
... Treatment: anti-thyroid drugs, removal or destruction of part of the thyroid(surgically or radioactive iodine) ...
THYROID/P.M.S (Pre Menstrual Syndrome) It has been found that a
... In short, the well defined patter of women’s monthly cycles is tightly regulated by messages from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The control of these messages by higher brain centres and counter effects of hormones on brain functioning are reminiscent of how the thyroid hormone system works. ...
... In short, the well defined patter of women’s monthly cycles is tightly regulated by messages from the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The control of these messages by higher brain centres and counter effects of hormones on brain functioning are reminiscent of how the thyroid hormone system works. ...
An Introduction to Endocrinology
... • Regulation of salt and water balance • Regulation of calcium balance • Regulation of energy balance/metabolism • Coping with a hostile environment (induce adaptive changes) • Co-ordination of growth • Reproduction and lactation • Regulation of circulation and digestion ...
... • Regulation of salt and water balance • Regulation of calcium balance • Regulation of energy balance/metabolism • Coping with a hostile environment (induce adaptive changes) • Co-ordination of growth • Reproduction and lactation • Regulation of circulation and digestion ...
Endocrine PowerPoint - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... The endocrine system also fulfils a homeostatic function by regulating the internal environment of the body by controlling processes such as blood glucose level, water and mineral balance, temperature and metabolic rate. The endocrine system operates on a series of feedback mechanisms where the ...
... The endocrine system also fulfils a homeostatic function by regulating the internal environment of the body by controlling processes such as blood glucose level, water and mineral balance, temperature and metabolic rate. The endocrine system operates on a series of feedback mechanisms where the ...
Endocrine System
... under the eyes and swelling of the face. Arteriosclerosis: due to increase in blood cholesterol Cretinism: extreme hypothyroidism during infancy and childhood ...
... under the eyes and swelling of the face. Arteriosclerosis: due to increase in blood cholesterol Cretinism: extreme hypothyroidism during infancy and childhood ...
Endocrine/Reproduction/Genetics Study Guide
... Describe how endocrine reflexes are controlled Humoral control Hormonal control Neural control Describe the functional differences between lipid hormones and protein hormones; 2 nd messenger system or direct gene activation; enter cell membrane or not. ...
... Describe how endocrine reflexes are controlled Humoral control Hormonal control Neural control Describe the functional differences between lipid hormones and protein hormones; 2 nd messenger system or direct gene activation; enter cell membrane or not. ...
Základní vyšetření v endokrinologii
... Transport protein - IGFBP 3 Primary investigation for acromegaly and giantism diagnosis ...
... Transport protein - IGFBP 3 Primary investigation for acromegaly and giantism diagnosis ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.