Endocrine 2
... (which results in increased _______________ and blood volume) and increased excretion of ____ We will discuss this in more detail while exploring the Excretory (Urinary) system. ...
... (which results in increased _______________ and blood volume) and increased excretion of ____ We will discuss this in more detail while exploring the Excretory (Urinary) system. ...
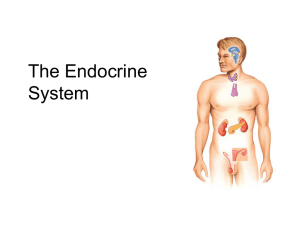
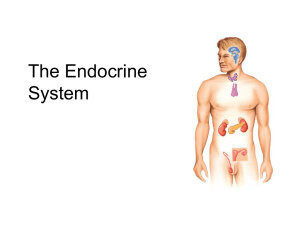
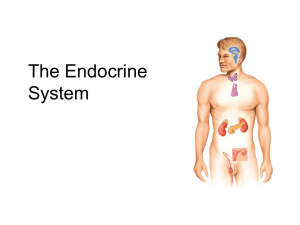
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
Endocrine System
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
Endocrine System
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
... stimulates growth of the graafian follicle to grow in the: Ovaries The function of the thyroid hormones is to: ...
11-Jun-15 1 - Winston Knoll Collegiate
... into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell membranes for the hormone. ...
... into the blood stream so they can then reach the target cells. cells. Target cells have receptors on their cell membranes for the hormone. ...
Orexin-A excites rat lateral vestibular nucleus neurons and improves
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
... lateral hypothalamic area and perifornical area. Lack of orexin neurons causes narcolepsy-cataplexy, which is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness, premature transitions to REM sleep, and sudden skeletal muscle weakness without impairment of consciousness. However, most studies so far on th ...
Growth Hormone Treatment
... with IGF/1 (growth hormone) and other hormones. The horse conjugated estrogen then travels to the cells where it causes even more chaos! ...
... with IGF/1 (growth hormone) and other hormones. The horse conjugated estrogen then travels to the cells where it causes even more chaos! ...
English - Children`s Oncology Group Long-Term Follow
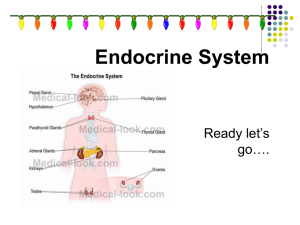
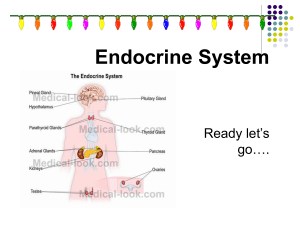
... regulate many body functions including growth, puberty, energy level, urine production, and stress response. Glands of the endocrine system include the pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries (in females), and testes (in males). The hypothalamus and pituitary are sometimes call ...
... regulate many body functions including growth, puberty, energy level, urine production, and stress response. Glands of the endocrine system include the pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries (in females), and testes (in males). The hypothalamus and pituitary are sometimes call ...
Author template for journal articles
... health problem and is a leading cause of marital discord in countries such as Algeria. Endocrine disorders that can be associated with significant medical pathology remain an important factor to be considered in the etiology of male infertility, and those disorders are usually associated with altera ...
... health problem and is a leading cause of marital discord in countries such as Algeria. Endocrine disorders that can be associated with significant medical pathology remain an important factor to be considered in the etiology of male infertility, and those disorders are usually associated with altera ...
Endocrine Problems after Childhood Cancer: Precocious Puberty
... The endocrine system is a group of glands that regulate body functions including growth, puberty, energy level, urine production, and stress response. Glands of the endocrine system include the pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries (in females), and testes (in males). The hypo ...
... The endocrine system is a group of glands that regulate body functions including growth, puberty, energy level, urine production, and stress response. Glands of the endocrine system include the pituitary, hypothalamus, thyroid, adrenal, pancreas, ovaries (in females), and testes (in males). The hypo ...
11. Principal Glands
... broken down into glucose. Glucose is: 1. Delivered to our body cells to be used immediately as a source of energy 2. Transported to the liver and converted to a substance called glycogen 3. Stored in muscle cells, also as glycogen ...
... broken down into glucose. Glucose is: 1. Delivered to our body cells to be used immediately as a source of energy 2. Transported to the liver and converted to a substance called glycogen 3. Stored in muscle cells, also as glycogen ...
System 2
... metabolism of their target organs, help regulate total body metabolism, growth, reprodution. Neurohormones are secreted into blood by specialized neurons. ...
... metabolism of their target organs, help regulate total body metabolism, growth, reprodution. Neurohormones are secreted into blood by specialized neurons. ...
Endocrine System: http://science.nhmccd.edu/biol/ap1int.htm
... In males increases blood flow to penis-acts in few seconds and then breaks down. Viagra interferes with the breakdown of NO (erectile dysfunction). NO also acts as a neurotransmitter when secreted by WBCs to kill bacteria and cancer cells. ...
... In males increases blood flow to penis-acts in few seconds and then breaks down. Viagra interferes with the breakdown of NO (erectile dysfunction). NO also acts as a neurotransmitter when secreted by WBCs to kill bacteria and cancer cells. ...
The Anterior Pituitary Gland
... 2009.
"Site Map." Faculty of Life Sciences ELP: e-Learning Projects. 06 June 2009
.
...
... 2009
thyroid hormone
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
Slide 1
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
thyroid releasing hormone
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
Endocrine System
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
The Endocrine System
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
... Target cells respond to the hormones for which they have receptors The effects are dependent on the programmed response of the target cells ...
Document
... “The adrenal glands produce hormones that adjust metabolic activities at specific sites, affecting either the pattern of nutrient utilization, mineral ion balance, or the rate of energy consumption by active tissues.” ...
... “The adrenal glands produce hormones that adjust metabolic activities at specific sites, affecting either the pattern of nutrient utilization, mineral ion balance, or the rate of energy consumption by active tissues.” ...
Endocrine fill-in guided notes
... III. Endocrine Glands A. __________________________ Function: “____________ gland” that communicates with the hypothalamus to control many body activities Link between ___________ and endocrine systems Location: Tiny structure about the size of a grape at the base of the brain Connected to t ...
... III. Endocrine Glands A. __________________________ Function: “____________ gland” that communicates with the hypothalamus to control many body activities Link between ___________ and endocrine systems Location: Tiny structure about the size of a grape at the base of the brain Connected to t ...
Central Nervous System
... Functions include the following: 1. Regulation of body temperature 2. Regulation of hunger and thirst sensations 3. Regulation of sleep-wake cycles 4. Control of the autonomic nervous system 5. Control of the endocrine system ...
... Functions include the following: 1. Regulation of body temperature 2. Regulation of hunger and thirst sensations 3. Regulation of sleep-wake cycles 4. Control of the autonomic nervous system 5. Control of the endocrine system ...
The Endocrine System
... Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
... Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
2,3,4-Anterior Pituitary 12017-02-05 00:361.9 MB
... anterior pituitary by the hypothalamichypophysial-portal system. CRH stimulates the synthesis of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). ACTH stimulates the synthesis of adrenal steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids (cortisol) released into the systemic circulation exert negative feedback inhibition of CRF ...
... anterior pituitary by the hypothalamichypophysial-portal system. CRH stimulates the synthesis of adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH). ACTH stimulates the synthesis of adrenal steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids (cortisol) released into the systemic circulation exert negative feedback inhibition of CRF ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.