PowerPoint Chapter 29
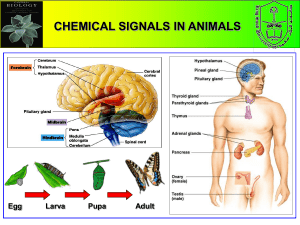
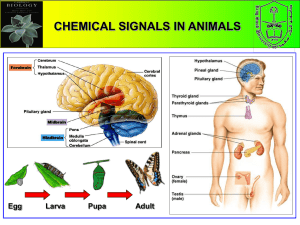
... VI. The Endocrine System and Hormones (29.6) A. Hormones influence a cell’s activities by entering the cell or binding to its membrane 1. Endocrine system makes chemical signals that help body grow, develop, and maintain homeostasis ...
... VI. The Endocrine System and Hormones (29.6) A. Hormones influence a cell’s activities by entering the cell or binding to its membrane 1. Endocrine system makes chemical signals that help body grow, develop, and maintain homeostasis ...
body and behavior
... • Divided into 2 parts: • 1) Central Nervous System: brain and spinal cord; nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between brain and body • 2) Peripheral NS: nerves branching out from the spinal cord ...
... • Divided into 2 parts: • 1) Central Nervous System: brain and spinal cord; nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between brain and body • 2) Peripheral NS: nerves branching out from the spinal cord ...
The Endocrine System - Florida International University
... Hormonal stimuli 1) Produce responses in the same or other endocrine glands. For example, the hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones or inhibiting hormones to the anterior pituitary gland. 2) Increased release of particular anterior pituitary hormone into blood stream tells the hypothalamus to d ...
... Hormonal stimuli 1) Produce responses in the same or other endocrine glands. For example, the hypothalamus secretes releasing hormones or inhibiting hormones to the anterior pituitary gland. 2) Increased release of particular anterior pituitary hormone into blood stream tells the hypothalamus to d ...
Hormones and Second Messengers
... release in pancreas. Insulin triggers: glucose uptake by muscle and adipose tissue, fat synthesis in liver and adipocytes, and gluconeogenesis (liver with ...
... release in pancreas. Insulin triggers: glucose uptake by muscle and adipose tissue, fat synthesis in liver and adipocytes, and gluconeogenesis (liver with ...
Endocrine Notes
... o Activated gene produces an enzyme (protein) that initiates a chemical reaction within the cell. 2. Non-Steroid Hormones – Hormones composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids. These hormones are NOT fat soluble. They are unable to enter cells because they are not solube in the cell membrane. ...
... o Activated gene produces an enzyme (protein) that initiates a chemical reaction within the cell. 2. Non-Steroid Hormones – Hormones composed of proteins, peptides or amino acids. These hormones are NOT fat soluble. They are unable to enter cells because they are not solube in the cell membrane. ...
chapter 14-the endocrine system
... A. This system is composed of glands that produce and release special chemicals known as hormones. Hormones are special chemicals that function by regulating processes in the human body. B. Hormones function by effecting special target cells in the body. C. Hormones secreted by endocrine glands are ...
... A. This system is composed of glands that produce and release special chemicals known as hormones. Hormones are special chemicals that function by regulating processes in the human body. B. Hormones function by effecting special target cells in the body. C. Hormones secreted by endocrine glands are ...
hormones
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
Slide 1
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
... cells that act to regulate the activity of other cells in the body. – Hormones affect all cells in the body and are made and secreted by endocrine glands. • Endocrine glands are ductless organs that secret hormones either into the bloodstream or the fluid around cells. • The endocrine glands can be ...
Endocrine System
... Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers ...
... Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers ...
Hormones
... The swimming path of the control rat was consistently near the target (T), indicating that its memory for the location of the platform was not impaired, while the swimming path of the rat that was shocked thirty minutes before being put in the water maze was random, indicating that its memory for t ...
... The swimming path of the control rat was consistently near the target (T), indicating that its memory for the location of the platform was not impaired, while the swimming path of the rat that was shocked thirty minutes before being put in the water maze was random, indicating that its memory for t ...
Endocrine System
... – two hormones acting together for greater effect ex. estrogen & LH are both needed for oocyte production ...
... – two hormones acting together for greater effect ex. estrogen & LH are both needed for oocyte production ...
Endocrine Ch 16-Fall 2016-PPT-Student
... (epinephrine and 1. Increased heart rate norepinephrine) 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases glucose to blood 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity ...
... (epinephrine and 1. Increased heart rate norepinephrine) 2. Increased blood pressure 3. Liver converts glycogen to glucose and releases glucose to blood 4. Dilation of bronchioles 5. Changes in blood flow patterns, leading to increased alertness and decreased digestive and kidney activity ...
Endocrine Jeopardy
... What term describes the changes that our bodies go through in adolescence that is primarily influenced by hormones? ...
... What term describes the changes that our bodies go through in adolescence that is primarily influenced by hormones? ...
pituitary gland - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... A characteristic of hormones and enzymes that allows them to work effectively with other organic molecules is their 1. specific shape 2. small size 3. concentration of carbon and hydrogen atoms 4. high-energy bonds ...
... A characteristic of hormones and enzymes that allows them to work effectively with other organic molecules is their 1. specific shape 2. small size 3. concentration of carbon and hydrogen atoms 4. high-energy bonds ...
Endocrine System
... blood flow to skeletal muscles, heart and brain dilation of airways (bronchodilation) fuel for energy-release of glucose from glycogen blood pressure ...
... blood flow to skeletal muscles, heart and brain dilation of airways (bronchodilation) fuel for energy-release of glucose from glycogen blood pressure ...
Name Date ______ Nervous System and Endocrine System Exam
... 11. The __________________________________ are at the end of the neuron. They release _________________________ into the synapse. 12. The space between 2 neurons is called the ________________________________. 13. The neurotransmitter released into the synapse attach to ________________________ on t ...
... 11. The __________________________________ are at the end of the neuron. They release _________________________ into the synapse. 12. The space between 2 neurons is called the ________________________________. 13. The neurotransmitter released into the synapse attach to ________________________ on t ...
Acrobat - GK-12 Biosensor Program at Colorado State University
... locations in the brain where they reside and function in adulthood. The distances they travel can be quite large compared to their own size. They also encounter obstacles along their path including other migrating neurons, glia and fibers. In this activity, you will model the migratory path of neuro ...
... locations in the brain where they reside and function in adulthood. The distances they travel can be quite large compared to their own size. They also encounter obstacles along their path including other migrating neurons, glia and fibers. In this activity, you will model the migratory path of neuro ...
Word 2007 - the GK-12 Program at Colorado State University!
... locations in the brain where they reside and function in adulthood. The distances they travel can be quite large compared to their own size. They also encounter obstacles along their path including other migrating neurons, glia and fibers. In this activity, you will model the migratory path of neuro ...
... locations in the brain where they reside and function in adulthood. The distances they travel can be quite large compared to their own size. They also encounter obstacles along their path including other migrating neurons, glia and fibers. In this activity, you will model the migratory path of neuro ...
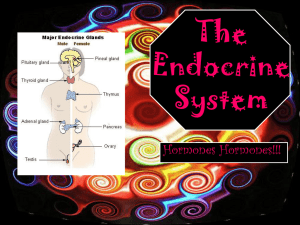
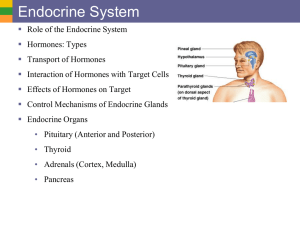
Endocrine System
... • Endocrine system consists of endocrine glands (organs) that coordinate body activities through hormones (signals for your body). – Glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream – Hormones are chemicals produced by one set of “cells” that affect another set of cells or target organ. ...
... • Endocrine system consists of endocrine glands (organs) that coordinate body activities through hormones (signals for your body). – Glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream – Hormones are chemicals produced by one set of “cells” that affect another set of cells or target organ. ...
The Endocrine System
... 1. Humoral: changing blood levels of different ions and nutrients example: PTH in response to calcium levels 2. Hormonal: endocrine organs stimulated to work due to presence of other hormones example: TSH stimulates thyroid ...
... 1. Humoral: changing blood levels of different ions and nutrients example: PTH in response to calcium levels 2. Hormonal: endocrine organs stimulated to work due to presence of other hormones example: TSH stimulates thyroid ...
File - Shifa Students Corner
... The major output of the striatum is to the pallidum, and it is inhibitory. Excitatory input to the pallidum comes from the subthalamic nucleus The output of the pallidum, which is also inhibitory, is to various thalamic nuclei. The thalamic nuclei project to and excite the premotor and supplemen ...
... The major output of the striatum is to the pallidum, and it is inhibitory. Excitatory input to the pallidum comes from the subthalamic nucleus The output of the pallidum, which is also inhibitory, is to various thalamic nuclei. The thalamic nuclei project to and excite the premotor and supplemen ...
1 Endocrine System
... glands (tropic hormones) Characteristics of all anterior pituitary hormones • They are proteins (or peptides) • They act through secondmessenger systems • They are regulated by hormonal stimuli, mostly negative feedback ...
... glands (tropic hormones) Characteristics of all anterior pituitary hormones • They are proteins (or peptides) • They act through secondmessenger systems • They are regulated by hormonal stimuli, mostly negative feedback ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.