Objectives Endocrine System
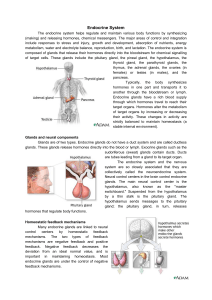
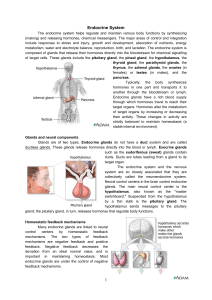
... which when released into the bloodstream, influence metabolic activities, growth, and development. Maintenance of homeostasis through feedback loops.. ...
... which when released into the bloodstream, influence metabolic activities, growth, and development. Maintenance of homeostasis through feedback loops.. ...
Lec.9د.عبد الجبار الحبيـطي The basal ganglia (nuclei)
... That secreted by the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle will pass via foramen of Monro to the 3rd ventricle where the choroid plexus of this ventricle add some fluid to it from its choroid plexus,then it pass via cerebral aquidut of Mid brain to reach the 4th ventricle and the choroid plexus of ...
... That secreted by the choroid plexus of the lateral ventricle will pass via foramen of Monro to the 3rd ventricle where the choroid plexus of this ventricle add some fluid to it from its choroid plexus,then it pass via cerebral aquidut of Mid brain to reach the 4th ventricle and the choroid plexus of ...
Neuron and Nervous System Review Guide
... Angular Gyrus: receives visual information and recodes it into auditory form ...
... Angular Gyrus: receives visual information and recodes it into auditory form ...
Endocrine System
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
... do not require continuous adjustment. In positive feedback mechanisms, the original stimulus is promoted rather than negated. Positive feedback increases the deviation from an ideal normal value. Unlike negative feedback that maintains hormone levels within narrow ranges, positive feedback is rarely ...
Endocrine System
... glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules in the kidneys. Conversely, if blood calcium increases too much, the parathyroid glands ...
... glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules in the kidneys. Conversely, if blood calcium increases too much, the parathyroid glands ...
LECTURE for dentistry students
... Individual endocrine cells are found in a variety of organs, e.g. the GIT and the kidneys. ...
... Individual endocrine cells are found in a variety of organs, e.g. the GIT and the kidneys. ...
File
... 2. What is the primary difference between an endocrine and exocrine an gland. Give one example of each. Hormone Action (pp. 291-294) 1. The specific site of a hormone’s action is called its __________________________. 2. What are prostaglandins (PGs)? Control of Hormonal Secretions (p. 294) 1. If a ...
... 2. What is the primary difference between an endocrine and exocrine an gland. Give one example of each. Hormone Action (pp. 291-294) 1. The specific site of a hormone’s action is called its __________________________. 2. What are prostaglandins (PGs)? Control of Hormonal Secretions (p. 294) 1. If a ...
Endocrine System
... the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin or the body does not effectively use the insulin it does produce. Because insulin is instrumental in helping the body convert sugars and starches into necessary energy, there can be serious consequences if diabetes is left undiagnosed and/o ...
... the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin or the body does not effectively use the insulin it does produce. Because insulin is instrumental in helping the body convert sugars and starches into necessary energy, there can be serious consequences if diabetes is left undiagnosed and/o ...
chapt11_lecture
... the retention of water in the kidneys (also called arginine vasopressin – AVP) 2) Oxytocin, which stimulates contractions in childbirth and milk let-down in lactation ...
... the retention of water in the kidneys (also called arginine vasopressin – AVP) 2) Oxytocin, which stimulates contractions in childbirth and milk let-down in lactation ...
Lymphatic System
... Adrenal glands • The adrenal cortex produces about 30 hormones that can be classified into three basic groups. • - Glucocorticoids reduce inflammation, metabolize food, and make new cells. • - Mineralocorticoids control the body’s fluid level and electrolyte balance. They influence the rate at whic ...
... Adrenal glands • The adrenal cortex produces about 30 hormones that can be classified into three basic groups. • - Glucocorticoids reduce inflammation, metabolize food, and make new cells. • - Mineralocorticoids control the body’s fluid level and electrolyte balance. They influence the rate at whic ...
Endocrine Glands and the General Principles of
... Secrete into a duct and to the outside of a body surface sweat, tear, saliva Secrete (hormone) into the blood Hormone circulates in blood and acts at target organs where hormone receptor is expressed insulin ...
... Secrete into a duct and to the outside of a body surface sweat, tear, saliva Secrete (hormone) into the blood Hormone circulates in blood and acts at target organs where hormone receptor is expressed insulin ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... Primarily under inhibitory control. This means that if there is an injury to the hypophyseal portal system which blocks hypothalamic regulation of the pituitary gland, PRL levels increase. All other pituitary hormone levels decrease when this happens. ...
... Primarily under inhibitory control. This means that if there is an injury to the hypophyseal portal system which blocks hypothalamic regulation of the pituitary gland, PRL levels increase. All other pituitary hormone levels decrease when this happens. ...
review the enodcrine system
... 3. __________________ demineralizes bone and raises blood calcium levels. 4. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus may often control their disease by diet and exercise. 5. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus normally have to take insulin shots to control their diabetes. 6. ...
... 3. __________________ demineralizes bone and raises blood calcium levels. 4. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus may often control their disease by diet and exercise. 5. Individuals with ______________ diabetes mellitus normally have to take insulin shots to control their diabetes. 6. ...
45_InstGuide_AR
... Describe the nature and location of intracellular receptors for hormones that pass easily through cell membranes. Explain how their role compares to the signal-transduction pathway noted above, and describe the changes they are likely to trigger within the target cell. ...
... Describe the nature and location of intracellular receptors for hormones that pass easily through cell membranes. Explain how their role compares to the signal-transduction pathway noted above, and describe the changes they are likely to trigger within the target cell. ...
Chapter 18
... Adrenal medulla develops just as other sympathetic ganglia but the cells secrete hormones- called chromaffin cells ...
... Adrenal medulla develops just as other sympathetic ganglia but the cells secrete hormones- called chromaffin cells ...
Hormone
... • The endocrine system assists the nervous system with communication and control of the body • Endocrine glands • They are ductless • They secrete hormones into bloodstream • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Exocrine glands • They have du ...
... • The endocrine system assists the nervous system with communication and control of the body • Endocrine glands • They are ductless • They secrete hormones into bloodstream • There are also similar glands called paracrine and autocrine glands that are quasi-endocrine • Exocrine glands • They have du ...
Science Fair Project
... If someone feels one way, then they’re going to act on it as a human instinct. ...
... If someone feels one way, then they’re going to act on it as a human instinct. ...
Lesson
... Needs iodine to be produced Stimulate glucose oxidation (via cellular resp.) Maintains BP, HR, muscle tone, digestion & reproductive functions. ...
... Needs iodine to be produced Stimulate glucose oxidation (via cellular resp.) Maintains BP, HR, muscle tone, digestion & reproductive functions. ...
L#15 - Dr. Faisal Mohammed - Done by: marah madain
... -aspirin is a pain killer because it inhibits cyclooxygenase thus inhibiting the formation of prostaglandin. Glycoproteins: called glycoproteins because they are attached to 1 or more carbohydrate groups. FSH, LH, TSH and hCG Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG): this hormone is used to diagnose the p ...
... -aspirin is a pain killer because it inhibits cyclooxygenase thus inhibiting the formation of prostaglandin. Glycoproteins: called glycoproteins because they are attached to 1 or more carbohydrate groups. FSH, LH, TSH and hCG Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG): this hormone is used to diagnose the p ...
The Endocrine System
... The thyroid gland (Figure 17.8) consists of follicles whose cells secrete the two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name ...
... The thyroid gland (Figure 17.8) consists of follicles whose cells secrete the two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name ...
Endocrine System
... The thyroid gland (Figure 17.8) consists of follicles whose cells secrete the two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name ...
... The thyroid gland (Figure 17.8) consists of follicles whose cells secrete the two thyroid hormones, T4 and T3. T4, also called thyroxine or tetraiodothyronine, is the inactive form, while T3, triiodothyronine, is the active hormone. T4 has four iodine atoms while T3 has three. Thyronine is the name ...
The Endocrine System
... affect specific target cells. Tropic hormones, such as TSH, affect endocrine glands. • Hormones bind to receptor proteins on the surface of, or within, target cells. This triggers changes within the target cells, such as the secretion of another hormone. Insulin and hGH are examples of protein hormo ...
... affect specific target cells. Tropic hormones, such as TSH, affect endocrine glands. • Hormones bind to receptor proteins on the surface of, or within, target cells. This triggers changes within the target cells, such as the secretion of another hormone. Insulin and hGH are examples of protein hormo ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology
... Primarily under inhibitory control. This means that if there is an injury to the hypophyseal portal system which blocks hypothalamic regulation of the pituitary gland, PRL levels increase. All other pituitary hormone levels decrease when this happens. ...
... Primarily under inhibitory control. This means that if there is an injury to the hypophyseal portal system which blocks hypothalamic regulation of the pituitary gland, PRL levels increase. All other pituitary hormone levels decrease when this happens. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.