NVCC Bio 212
... • may be converted to estrogen in the blood (♀) • When secreted in normal amounts, neither adrenal androgens or estrogens affect sexual characteristics (may affect sex drive in ♀) • Produced in the Zona Reticularis • Tumors of this region can lead to androgenital ...
... • may be converted to estrogen in the blood (♀) • When secreted in normal amounts, neither adrenal androgens or estrogens affect sexual characteristics (may affect sex drive in ♀) • Produced in the Zona Reticularis • Tumors of this region can lead to androgenital ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... fashion to control unconscious, visceral functions such as breathing and cardiovascular activity • Sympathetic system - Norepinephrine • Parasympathetic system - Acetylcholine ...
... fashion to control unconscious, visceral functions such as breathing and cardiovascular activity • Sympathetic system - Norepinephrine • Parasympathetic system - Acetylcholine ...
Endocrine System Facts Review
... Which gland controls calcium levels in the blood? There are two of theses. They sit on top of each kidney, like a cap. This hormone increases heart rate, blood pressure, and causes vasodilation of blood vessels in the heart and respiratory system. It also stimulates the liver to break down stored gl ...
... Which gland controls calcium levels in the blood? There are two of theses. They sit on top of each kidney, like a cap. This hormone increases heart rate, blood pressure, and causes vasodilation of blood vessels in the heart and respiratory system. It also stimulates the liver to break down stored gl ...
Hormones
... T4’s neg. feedback pathway: •if the metabolic rate decreases, receptors in the hypothalamus are activated. •the hypothalamus secretes Thyroid releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the release of Thyroic stimulating hormone (TSH), •TSH travels in the bloodstream to the thyroid gland and initiate ...
... T4’s neg. feedback pathway: •if the metabolic rate decreases, receptors in the hypothalamus are activated. •the hypothalamus secretes Thyroid releasing hormone (TRH), which stimulates the release of Thyroic stimulating hormone (TSH), •TSH travels in the bloodstream to the thyroid gland and initiate ...
AP Biology - kristashunkwiler
... Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
... Regulation Why are hormones needed? chemical messages from one body part to another communication needed to coordinate whole body daily homeostasis & regulation of large scale changes ...
S10 Clinicalbiochem2 DrNansy Hypothalamus And Pituitary
... stimulated by testosterone in males and oestrogens in females; thereafter the rate of secretion declines to a steady level before falling to low levels in old age. • Secretion can be stimulated by stress, exercise, a fall in blood glucose concentration, fasting and ingestion of certain amino acids. ...
... stimulated by testosterone in males and oestrogens in females; thereafter the rate of secretion declines to a steady level before falling to low levels in old age. • Secretion can be stimulated by stress, exercise, a fall in blood glucose concentration, fasting and ingestion of certain amino acids. ...
The Major endocrine glands 3.
... Water soluble circulate in blood plasma in ‘free’ form Lipid Soluble bound to transport proteins (synthesized in liver) ...
... Water soluble circulate in blood plasma in ‘free’ form Lipid Soluble bound to transport proteins (synthesized in liver) ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Duodenum (first part) of small intestine – Gastrin – delivered to stomach to inhibit HCl – Secretin – stimulates pancreas to release high pH juice; stimulates release of bile from liver – Cholecystokinin (CCK) – stimulates pancreas to release enzymes; gallbladder to release stored bile ...
... • Duodenum (first part) of small intestine – Gastrin – delivered to stomach to inhibit HCl – Secretin – stimulates pancreas to release high pH juice; stimulates release of bile from liver – Cholecystokinin (CCK) – stimulates pancreas to release enzymes; gallbladder to release stored bile ...
E.4.4 List three examples of excitatory and three examples of
... Pain receptors are located in the skin and on organs. Pain signals are sent along these nerve endings along nerve fibers on the spinal cord. The signals pass synapses to neurons that carry them up in an ascending tract to the stem or thalamus of the brain. The signals may pass on in other neurons to ...
... Pain receptors are located in the skin and on organs. Pain signals are sent along these nerve endings along nerve fibers on the spinal cord. The signals pass synapses to neurons that carry them up in an ascending tract to the stem or thalamus of the brain. The signals may pass on in other neurons to ...
Parts of the Brain - LHS-Social
... An overactive gland will cause you to feel nervous and jittery An under-active gland will make you feel slow and depressed (and likely gain ...
... An overactive gland will cause you to feel nervous and jittery An under-active gland will make you feel slow and depressed (and likely gain ...
endo_publicexam_questions
... 18. The graph below shows the blood glucose levels of a healthy person over a short period of time. Which hormone is most likely secreted by the pancreas at point Y? ...
... 18. The graph below shows the blood glucose levels of a healthy person over a short period of time. Which hormone is most likely secreted by the pancreas at point Y? ...
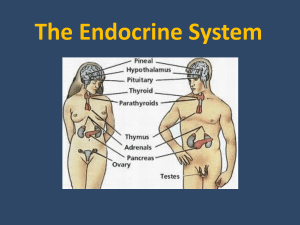
The Endocrine System
... Anterior Pituitary: produces thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) growth hormone (GH) ...
... Anterior Pituitary: produces thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH) growth hormone (GH) ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... Thalamus Relay station in brain Processes most information to and ...
... Thalamus Relay station in brain Processes most information to and ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology
... – alpha cells produce glucagon » it raises blood sugar by increasing liver glycogenolysis – beta cells produce insulin » it lowers blood sugar by escorting glucose into the cells – lack or improper response to insulin gives diabetes mellitus ...
... – alpha cells produce glucagon » it raises blood sugar by increasing liver glycogenolysis – beta cells produce insulin » it lowers blood sugar by escorting glucose into the cells – lack or improper response to insulin gives diabetes mellitus ...
Methods S1.
... control group (registered to MNI standard space using the FSL FMRIB58_FA_1mm_brain template) (1) to ensure that segmentations were exactly registered with the maps being considered and (2) because the signal intensity contrast in the FA maps was better for delineating the subcortical anatomy than th ...
... control group (registered to MNI standard space using the FSL FMRIB58_FA_1mm_brain template) (1) to ensure that segmentations were exactly registered with the maps being considered and (2) because the signal intensity contrast in the FA maps was better for delineating the subcortical anatomy than th ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 47 1
... – Steroids - lipids derived from cholesterol sex steroids - testosterone, estadiol, progesterone, and cortisol – secreted by testes, ovaries, placenta and adrenal cortex Corticosteroids - adrenal cortex cortisol and aldosterone (regulates glucose and salt balance) – All hormones can be categoriz ...
... – Steroids - lipids derived from cholesterol sex steroids - testosterone, estadiol, progesterone, and cortisol – secreted by testes, ovaries, placenta and adrenal cortex Corticosteroids - adrenal cortex cortisol and aldosterone (regulates glucose and salt balance) – All hormones can be categoriz ...
UNIT 5 Lecture 16 CONTROL SYSTEMS
... and below the thalamus. Because of its central location, it can receive information from all over the brain. It is composed of many regions made up of groups of nerve cell bodies, which are called nuclei. Several of these nuclei control the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothala ...
... and below the thalamus. Because of its central location, it can receive information from all over the brain. It is composed of many regions made up of groups of nerve cell bodies, which are called nuclei. Several of these nuclei control the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. The hypothala ...
What is Oestrogen? Oestrogen is the name given to a class of
... Oestrogen is the name given to a class of hormones. There are three major oestrogens produced by women called oestriol, oestradiol and oestrone. Oestradiol is the most potent. Often spelt as estrogen, estrone, estradiol, estriol What is natural progesterone? Progesterone is a naturally occurring hor ...
... Oestrogen is the name given to a class of hormones. There are three major oestrogens produced by women called oestriol, oestradiol and oestrone. Oestradiol is the most potent. Often spelt as estrogen, estrone, estradiol, estriol What is natural progesterone? Progesterone is a naturally occurring hor ...
Biosc_48_Chapter_8_part_2
... Contains the choroid plexus over the third ventricle where cerebrospinal fluid is produced Also contains the pineal gland, which secretes the hormone melatonin that helps regulate circadian rhythms ...
... Contains the choroid plexus over the third ventricle where cerebrospinal fluid is produced Also contains the pineal gland, which secretes the hormone melatonin that helps regulate circadian rhythms ...
• Two hormones are produced: (vasopressin) Thyroid Gland The
... o There are also similar glands called which affect neighboring cells and glands which affect only the secreting cell itself. ...
... o There are also similar glands called which affect neighboring cells and glands which affect only the secreting cell itself. ...
BioSignature - Division St. CrossFit
... Charles Poliquin has discovered 12 specific sites on the body that can be measured to scientifically determine what hormones need to be optimized. BioSignature Modulation allows us to look at specific hormones and how they can affect weight loss and the overall condition of the body. BioSig is able ...
... Charles Poliquin has discovered 12 specific sites on the body that can be measured to scientifically determine what hormones need to be optimized. BioSignature Modulation allows us to look at specific hormones and how they can affect weight loss and the overall condition of the body. BioSig is able ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.