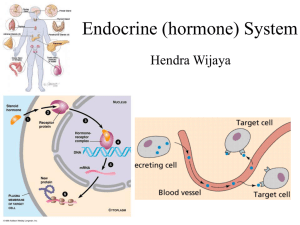
Hormones
... Consists of endocrine glands which secretes hormones Hormones – chemical substances that regulates the activities of organs and tissues ...
... Consists of endocrine glands which secretes hormones Hormones – chemical substances that regulates the activities of organs and tissues ...
Chapter 51 The Endocrine System
... 2. Thyroid Gland – located near the lower part of the larynx. The anterior pituitary releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyroid to release thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These two hormones are derived from the same amino acid and need iodine to be synthesized. They ...
... 2. Thyroid Gland – located near the lower part of the larynx. The anterior pituitary releases Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH), which in turn causes the thyroid to release thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These two hormones are derived from the same amino acid and need iodine to be synthesized. They ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... Hormones and other signaling molecules bind to target receptors, triggering specific response pathways • Intercellular Communication – The ways that signals are transmitted between animal cells are classified by two criteria • The type of secreting cell • The route taken by the signal in reaching it ...
... Hormones and other signaling molecules bind to target receptors, triggering specific response pathways • Intercellular Communication – The ways that signals are transmitted between animal cells are classified by two criteria • The type of secreting cell • The route taken by the signal in reaching it ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM – READING 1. Which endocrine gland is
... 1. Which endocrine gland is sometimes called the “master gland” and why? The pituitary gland is sometimes called the master gland because of its great influence on the other body organs. Its function is complex and important for overall well-being. 2. Which endocrine gland lies just above the pituit ...
... 1. Which endocrine gland is sometimes called the “master gland” and why? The pituitary gland is sometimes called the master gland because of its great influence on the other body organs. Its function is complex and important for overall well-being. 2. Which endocrine gland lies just above the pituit ...
Neuroscience & Behavior The Nervous & Endocrine Systems
... hormones into the bloodstream Hormones are chemical messengers that are mostly manufactured by the endocrine glands, which are most often produced in one part of the body and then sent through the blood to affect tissue in other parts of the body, Comparison of Endocrine and Nervous Systems: o Both ...
... hormones into the bloodstream Hormones are chemical messengers that are mostly manufactured by the endocrine glands, which are most often produced in one part of the body and then sent through the blood to affect tissue in other parts of the body, Comparison of Endocrine and Nervous Systems: o Both ...
Hormones and Target Cells
... glycogen is broken down into glucose. Muscle cells retain all the glucose they derive from this process, using it to power their own activities. Liver cells, meanwhile, move much of the glucose they liberate into general circulation. ...
... glycogen is broken down into glucose. Muscle cells retain all the glucose they derive from this process, using it to power their own activities. Liver cells, meanwhile, move much of the glucose they liberate into general circulation. ...
Powerpoint lecture
... hormones, the anterior pituitary secretes hormones into the secondary capillary plexus. This in turn empties into the general circulation. GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, PRL Anterior lobe of pituitary © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... hormones, the anterior pituitary secretes hormones into the secondary capillary plexus. This in turn empties into the general circulation. GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, PRL Anterior lobe of pituitary © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
and pituitary replacement hormones Hypopituitarism
... Growth Hormone (GH): this has effects on the various tissue of the body. In children, it is essential to reach normal growth. In adults, it appears to maintain normal energy levels and to keep body tissue, such as muscle and bones, strong and healthy. Gonadotrophins - Follicular Stimulating Hormone ...
... Growth Hormone (GH): this has effects on the various tissue of the body. In children, it is essential to reach normal growth. In adults, it appears to maintain normal energy levels and to keep body tissue, such as muscle and bones, strong and healthy. Gonadotrophins - Follicular Stimulating Hormone ...
Endocrine System - Salisbury Composite High School
... stimulates the production of gametes (sperm and egg) in the male and female reproductive systems Ex) Luteinizing Hormone (LH) – stimulates the production of hormones (estrogen, progesterone and testosterone) in the male and female reproductive systems ...
... stimulates the production of gametes (sperm and egg) in the male and female reproductive systems Ex) Luteinizing Hormone (LH) – stimulates the production of hormones (estrogen, progesterone and testosterone) in the male and female reproductive systems ...
Hormone Review Guide
... Influences the metabolism of glucose, protein, and fat in response to conditions that stress the body and require a greater supply of energy in the bloodstream Production of androgens; stimulate male characteristics and precursor for estrogen Increases blood levels of glucose by stimulating the brea ...
... Influences the metabolism of glucose, protein, and fat in response to conditions that stress the body and require a greater supply of energy in the bloodstream Production of androgens; stimulate male characteristics and precursor for estrogen Increases blood levels of glucose by stimulating the brea ...
193
... The pituitary gland or hypophysis is a small, bean-shaped gland located in the sella turcica. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior region (adenohypophysis) and a posterior region (neurohypophysis). The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland, which in turn transmits its own hormones th ...
... The pituitary gland or hypophysis is a small, bean-shaped gland located in the sella turcica. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior region (adenohypophysis) and a posterior region (neurohypophysis). The hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland, which in turn transmits its own hormones th ...
Topic: The Endocrine System
... • Ovaries – female sex • Testes – male sex gland that controls gland that controls female secondary male secondary sex sex characteristics characteristics • Secrete 2 hormones • Secrete a hormone called estrogen & called testosterone progesterone ...
... • Ovaries – female sex • Testes – male sex gland that controls gland that controls female secondary male secondary sex sex characteristics characteristics • Secrete 2 hormones • Secrete a hormone called estrogen & called testosterone progesterone ...
Hourly2_2012 - (canvas.brown.edu).
... T F 28. ON bipolar cells are depolarized by the glutamate released by rods and cones. T F 29. The center-surround antagonism of ganglion-cell receptive fields results in part from the lateral inhibitory influences of horizontal cells. T F 30. Axons in the spinal tract of the trigeminal (spinal V) or ...
... T F 28. ON bipolar cells are depolarized by the glutamate released by rods and cones. T F 29. The center-surround antagonism of ganglion-cell receptive fields results in part from the lateral inhibitory influences of horizontal cells. T F 30. Axons in the spinal tract of the trigeminal (spinal V) or ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Hormones Types of Hormones Hormone
... • Once inside, they bind and activate a specific intracellular receptor • The hormone-receptor complex travels to the nucleus and binds a DNA-associated receptor protein • This interaction prompts DNA transcription to produce mRNA ...
... • Once inside, they bind and activate a specific intracellular receptor • The hormone-receptor complex travels to the nucleus and binds a DNA-associated receptor protein • This interaction prompts DNA transcription to produce mRNA ...
Page 1 - Rochester Community Schools
... D) axons. E) thresholds. 7. Reuptake refers to the A) movement of neurotransmitter molecules across a synaptic gap. B) release of hormones into the bloodstream. C) inflow of positively charged ions through an axon membrane. D) reabsorption of excess neurotransmitter molecules by a sending neuron. E) ...
... D) axons. E) thresholds. 7. Reuptake refers to the A) movement of neurotransmitter molecules across a synaptic gap. B) release of hormones into the bloodstream. C) inflow of positively charged ions through an axon membrane. D) reabsorption of excess neurotransmitter molecules by a sending neuron. E) ...
Thyroid hormones
... Mode of Action: Chemical Signaling • 1- Plasma membrane reception • signal-transduction pathways (neurotransmitters, growth factors, most hormones) • 2- Cell nucleus reception • steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, some local regulators ...
... Mode of Action: Chemical Signaling • 1- Plasma membrane reception • signal-transduction pathways (neurotransmitters, growth factors, most hormones) • 2- Cell nucleus reception • steroid hormones, thyroid hormones, some local regulators ...
No Slide Title
... • Adult human these cells fuse with anterior lobe • Produce POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) which is processed into ACTH and endorphins ...
... • Adult human these cells fuse with anterior lobe • Produce POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) which is processed into ACTH and endorphins ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... release of the hormone oxytocin (the stimulus) which causes the breast to eject milk (the response) which increases suckling which leads to more oxytocin which cause more milk ejection etc. ...
... release of the hormone oxytocin (the stimulus) which causes the breast to eject milk (the response) which increases suckling which leads to more oxytocin which cause more milk ejection etc. ...
Slide 1
... Pancreas and other Endocrine Glands A 51-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician for a routine examination. He notes that his blood glucose concentration has been persistently high over the past 4 months and he gained 20 lbs during the holidays. His diabetes h ...
... Pancreas and other Endocrine Glands A 51-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician for a routine examination. He notes that his blood glucose concentration has been persistently high over the past 4 months and he gained 20 lbs during the holidays. His diabetes h ...
HERE
... Pancreas and other Endocrine Glands A 51-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician for a routine examination. He notes that his blood glucose concentration has been persistently high over the past 4 months and he gained 20 lbs during the holidays. His diabetes h ...
... Pancreas and other Endocrine Glands A 51-year-old man with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician for a routine examination. He notes that his blood glucose concentration has been persistently high over the past 4 months and he gained 20 lbs during the holidays. His diabetes h ...
Hypothalamic and Pituitary Hormones
... • Hormones from the Anterior Pituitary gland are divided into 2 on the basis of regulating the : • Growth/nutrition/functions of other endocrine glands in the ...
... • Hormones from the Anterior Pituitary gland are divided into 2 on the basis of regulating the : • Growth/nutrition/functions of other endocrine glands in the ...
Chapter 47
... d) Diabetes results in hyperglycemia, but the high sugar level falls after kidney clearance of the glucose e) Fat stores are mobilized and may lead to atherosclerosis f) Protein stores are depleted In hypoglycemia the glucose concentration is too low a) Excessive insulin secretion leads to low blood ...
... d) Diabetes results in hyperglycemia, but the high sugar level falls after kidney clearance of the glucose e) Fat stores are mobilized and may lead to atherosclerosis f) Protein stores are depleted In hypoglycemia the glucose concentration is too low a) Excessive insulin secretion leads to low blood ...
Endocrine System Endocrine glands - secrete chemical
... IP3 binds to calmodulin which activates enzymes that amplify cellular responses. Hormones are under the control of a negative feedback system: A produces substance B to effect C until C sends a signal back to A telling it that it has enough substance B, in turn A stops producing substance B. Sometim ...
... IP3 binds to calmodulin which activates enzymes that amplify cellular responses. Hormones are under the control of a negative feedback system: A produces substance B to effect C until C sends a signal back to A telling it that it has enough substance B, in turn A stops producing substance B. Sometim ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.