chapter 18 study guide
... (know functions as a “package” - I won’t ask about individual functions in isolation from the other functions) ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ hormone exocrine gland endocrine gland down regulation up regulation circulating hormones ...
... (know functions as a “package” - I won’t ask about individual functions in isolation from the other functions) ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ hormone exocrine gland endocrine gland down regulation up regulation circulating hormones ...
CHAPTER 18 STUDY GUIDE
... (know functions as a “package” - I won’t ask about individual functions in isolation from the other functions) ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ hormone exocrine gland endocrine gland down regulation up regulation circulating hormones ...
... (know functions as a “package” - I won’t ask about individual functions in isolation from the other functions) ___________________________________________________________________________________________________ hormone exocrine gland endocrine gland down regulation up regulation circulating hormones ...
Sleep
... * Cytokines enter Blood Stream where they send Signals to distant Organs Including Brain * Important Regulator of Cytokines Production is Brain that, through Neural Signals to Tissues or Hormones, can switch Cytokines on or off ...
... * Cytokines enter Blood Stream where they send Signals to distant Organs Including Brain * Important Regulator of Cytokines Production is Brain that, through Neural Signals to Tissues or Hormones, can switch Cytokines on or off ...
The Two Messenger Services of the Brain
... Hormones Hormones are chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands that are secreted in the bloodstream. Hormones affect the brain and many other tissues of the body. For example, epinephrine (adrenaline) increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar and feelings of excitement during emergency ...
... Hormones Hormones are chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands that are secreted in the bloodstream. Hormones affect the brain and many other tissues of the body. For example, epinephrine (adrenaline) increases heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar and feelings of excitement during emergency ...
A single bout of moderate exercise results in long
... 1. True or False: A single bout of moderate exercise results in long-term changes in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. 2. True or False: Delayed menarche is an effect of intense exercise on the female reproductive system. 3. True or False: Gonadal hormones drop after intense exercise. 4. Tr ...
... 1. True or False: A single bout of moderate exercise results in long-term changes in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. 2. True or False: Delayed menarche is an effect of intense exercise on the female reproductive system. 3. True or False: Gonadal hormones drop after intense exercise. 4. Tr ...
Appendix
... nerve travels medial to the coccygeus, within the pelvic diaphragm, to reach its ultimate destination. It is therefore necessary to remove much of the ventral aspect of the pelvis in order to properly visualize its intrapelvic course. ...
... nerve travels medial to the coccygeus, within the pelvic diaphragm, to reach its ultimate destination. It is therefore necessary to remove much of the ventral aspect of the pelvis in order to properly visualize its intrapelvic course. ...
Chapter 47
... When a hormone binds to a receptor, calcium ion channels open and calcium moves into the cell. Certain receptors are linked by a G protein to calcium ion channels. Calcium in the cell binds to the protein calmodulin and changes conformation. ...
... When a hormone binds to a receptor, calcium ion channels open and calcium moves into the cell. Certain receptors are linked by a G protein to calcium ion channels. Calcium in the cell binds to the protein calmodulin and changes conformation. ...
19 Cardiovascular System: BLOOD
... d) prolactin (PRL) is secreted by lactotrophs e) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) are secreted by corticotrophs Secretion of AP hormones is regulated by hypothalamic regulating hormones and by negative feedback mechanisms. __________________________________ ...
... d) prolactin (PRL) is secreted by lactotrophs e) adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and melanocyte stimulating hormone (MSH) are secreted by corticotrophs Secretion of AP hormones is regulated by hypothalamic regulating hormones and by negative feedback mechanisms. __________________________________ ...
A Balanced Approach to Menopause
... alter the type of therapy or kind of hormone delivery approach that is used. For some women, oral forms of hormones may not be best, but transdermal (through the skin) or across mucus membranes may be preferable. There may be problems not just with “females” hormones of estrogen and progesterone, bu ...
... alter the type of therapy or kind of hormone delivery approach that is used. For some women, oral forms of hormones may not be best, but transdermal (through the skin) or across mucus membranes may be preferable. There may be problems not just with “females” hormones of estrogen and progesterone, bu ...
Lab 2
... thyroid gland. – Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): Regulate the endocrine activity of the cortex portion of the adrenal gland – Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and – Luteinizing hormone (LH): Both regulate gamete production and hormonal activity of the gonads (ovaries and testes). ...
... thyroid gland. – Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH): Regulate the endocrine activity of the cortex portion of the adrenal gland – Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and – Luteinizing hormone (LH): Both regulate gamete production and hormonal activity of the gonads (ovaries and testes). ...
A Closer Look at Some Hormones 1. Melatonin $ produced by
... with normal body proportions. Genetic dwarfism is totally different. Pituitary dwarfism may result from a pituitary tumour or no pituitary gland at all. Puberty may be delayed or never occur at all. (See picture page 429) Treatment today is with genetically engineered bacteria that will ...
... with normal body proportions. Genetic dwarfism is totally different. Pituitary dwarfism may result from a pituitary tumour or no pituitary gland at all. Puberty may be delayed or never occur at all. (See picture page 429) Treatment today is with genetically engineered bacteria that will ...
endocrine disorders goiter
... hypothalamus • 2 parts : Neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis Indirectly controls : ...
... hypothalamus • 2 parts : Neurohypophysis Adenohypophysis Indirectly controls : ...
I-Introduction
... Classic definition: Hormones are chemical substances produced by specialized tissues (endocrine glands) and secreted into the blood stream, where they are carried to target organs Broader definition: Hormone are chemicals, non-nutrients, intracellular messengers that are effective at micromolar ...
... Classic definition: Hormones are chemical substances produced by specialized tissues (endocrine glands) and secreted into the blood stream, where they are carried to target organs Broader definition: Hormone are chemicals, non-nutrients, intracellular messengers that are effective at micromolar ...
Comparative Vertebrate Physiology
... DAG activates protein kinases, IP3 triggers Ca++ release from ER Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
... DAG activates protein kinases, IP3 triggers Ca++ release from ER Ca++ activates channels on plasma membrane or binds to calmodulin which activates metabolism ...
1 Chapter 2: The Endocrine System Chemical Communication
... A collection of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) at the base of the brain which receives projections from higher brain sites Neurosecretory cells – in hypothalamus, function as endocrine glands but are neurons and therefore produce neurohormones which are released into blood vessels in the anterior pit ...
... A collection of neuronal cell bodies (nuclei) at the base of the brain which receives projections from higher brain sites Neurosecretory cells – in hypothalamus, function as endocrine glands but are neurons and therefore produce neurohormones which are released into blood vessels in the anterior pit ...
HARMONES IN ANIMALS NOTES
... • It is considered to be master gland as it secretes many hormones to regulate the organs as well as the other glands. • Different hormones secreted by this gland include Growth hormone, TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, MSH, Vasopressin and Oxytocin. The hypothalamus: • It is a neuro-endocrine part of the brain. ...
... • It is considered to be master gland as it secretes many hormones to regulate the organs as well as the other glands. • Different hormones secreted by this gland include Growth hormone, TSH, FSH, LH, ACTH, MSH, Vasopressin and Oxytocin. The hypothalamus: • It is a neuro-endocrine part of the brain. ...
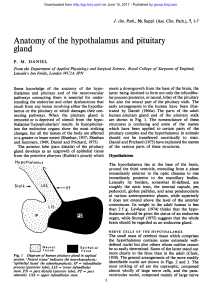
Anatomy of the hypothalamus and pituitary
... of both afferent and efferent non-myelinated nerve Many small arterial twigs from the ring pass into the fibres connect the hypothalamic nerve cells with the pituitary stalk (Figs. 4, 6). The venous drainage various parts of the cerebral hemispheres, brain enters into fairly large veins running in t ...
... of both afferent and efferent non-myelinated nerve Many small arterial twigs from the ring pass into the fibres connect the hypothalamic nerve cells with the pituitary stalk (Figs. 4, 6). The venous drainage various parts of the cerebral hemispheres, brain enters into fairly large veins running in t ...
AP Biology, Chapter 45 Hormones and the Endocrine System The
... LH: triggers ovulation, development of follicle into corpus luteum, stimulates testosterone production in males Thyroid Regulation: A Hormone Cascade Pathway Intro 14. List the hormones the thyroid gland produces and their actions. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine control the metabolism of glucose Cal ...
... LH: triggers ovulation, development of follicle into corpus luteum, stimulates testosterone production in males Thyroid Regulation: A Hormone Cascade Pathway Intro 14. List the hormones the thyroid gland produces and their actions. Thyroxine and triiodothyronine control the metabolism of glucose Cal ...
hormone - Daniela Sartori
... Subsequent exposure to this hormone produces a lesser response Due to decrease in # of receptors on targets Most peptide hormones have pulsatile secretion which prevents downregulation ...
... Subsequent exposure to this hormone produces a lesser response Due to decrease in # of receptors on targets Most peptide hormones have pulsatile secretion which prevents downregulation ...
The Hormones of the Human
... release of estrogens from the ovarian follicle. A high level of estrogen, in turn, suppresses the further production of FSH. 2. Antagonistic pairs of hormones. Example: Insulin causes the level of blood sugar (glucose) to drop when it has risen. Glucagon causes it to rise when it has fallen. 3. Hor ...
... release of estrogens from the ovarian follicle. A high level of estrogen, in turn, suppresses the further production of FSH. 2. Antagonistic pairs of hormones. Example: Insulin causes the level of blood sugar (glucose) to drop when it has risen. Glucagon causes it to rise when it has fallen. 3. Hor ...
Chapter 18
... Cyclic-AMP can activate enzymes specific to a cell. Thus, one hormone can have effect on many different types of cells. Other second messengers are Ca++ and cyclic-GMP. Thyroid and steroid hormones have effects directly on the nucleus or indirectly through cytosol. These hormones affect protein synt ...
... Cyclic-AMP can activate enzymes specific to a cell. Thus, one hormone can have effect on many different types of cells. Other second messengers are Ca++ and cyclic-GMP. Thyroid and steroid hormones have effects directly on the nucleus or indirectly through cytosol. These hormones affect protein synt ...
Slide 1 - AccessMedicine
... Regulation of thyroid hormone synthesis. Left. Thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feed back to inhibit hypothalamic production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and pituitary production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates thyroid gland production of T4 and T3. Right. Thyroid follicles ...
... Regulation of thyroid hormone synthesis. Left. Thyroid hormones T4 and T3 feed back to inhibit hypothalamic production of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and pituitary production of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). TSH stimulates thyroid gland production of T4 and T3. Right. Thyroid follicles ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.