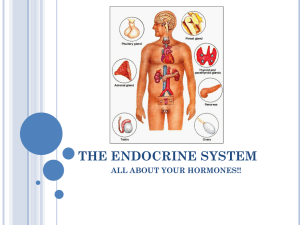
The Human Endocrine System: The Glands and Their Hormones
... Negative feedback example – blood sugar levels increase after eating cake, which makes insulin levels rise in order to lower the blood sugar levels back to normal (like a thermostat) Positive feedback example – labor contractions begin and strengthen over time, continuously, until the baby is born H ...
... Negative feedback example – blood sugar levels increase after eating cake, which makes insulin levels rise in order to lower the blood sugar levels back to normal (like a thermostat) Positive feedback example – labor contractions begin and strengthen over time, continuously, until the baby is born H ...
Notes
... have a 4 carbon ring structure with different side groups. ex. Cortisol, progesterone, testosterone. - made in the rough ER they have to be carried in the blood by a protein carrier because they are fat soluble. - They work by binding to receptors, entering the nucleus and binding to a specific part ...
... have a 4 carbon ring structure with different side groups. ex. Cortisol, progesterone, testosterone. - made in the rough ER they have to be carried in the blood by a protein carrier because they are fat soluble. - They work by binding to receptors, entering the nucleus and binding to a specific part ...
SSN HISTO
... 1) The Blood Supply of the Adrenals The arteries supplying the adrenal gland break up into a fine network of small vessels, called the capsular plexus, in the connective tissue capsule surrounding the whole gland. This plexus feeds both the cortex and the medulla: a) Cortex The vessels of the plexus ...
... 1) The Blood Supply of the Adrenals The arteries supplying the adrenal gland break up into a fine network of small vessels, called the capsular plexus, in the connective tissue capsule surrounding the whole gland. This plexus feeds both the cortex and the medulla: a) Cortex The vessels of the plexus ...
Endocrine System
... – Negative feedback system (levels of hormones increase until signals are sent to glands to stop secretion of that hormone) • Endocrine glands: – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas – sugar metabolism – Gonads ...
... – Negative feedback system (levels of hormones increase until signals are sent to glands to stop secretion of that hormone) • Endocrine glands: – Pituitary – “master gland,” growth hormone – Thyroid – metabolic rate – Adrenal – salt and carbohydrate metabolism – Pancreas – sugar metabolism – Gonads ...
Document
... messengers (cAMP). (Hormones that can not penetrate the membrane). Act on the genetic apparatus of the cell (nucleus, DNA) and promote the synthesis of enzymes (Steroid and thyroid hormones). ...
... messengers (cAMP). (Hormones that can not penetrate the membrane). Act on the genetic apparatus of the cell (nucleus, DNA) and promote the synthesis of enzymes (Steroid and thyroid hormones). ...
Chapter 18 Essays
... 8. Give a step-by-step, real-life example (i.e. for a specific hormone) showing how a receptor, a G-protein and a second messenger are involved in a hormone’s effect on a target cell’s metabolic activity. The best answers will include a diagram (as in Spotlight 18-3) and an explanation of the diagra ...
... 8. Give a step-by-step, real-life example (i.e. for a specific hormone) showing how a receptor, a G-protein and a second messenger are involved in a hormone’s effect on a target cell’s metabolic activity. The best answers will include a diagram (as in Spotlight 18-3) and an explanation of the diagra ...
I can File
... hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, and describe how they maintain homeostasis through feedback ...
... hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrine, aldosterone, and describe how they maintain homeostasis through feedback ...
Endocrinology - You Can Do It! | Physical Therapy Students
... Control of ADH secretion: High osmolarity stimulates ADH . When we have high osmolarity water will leave the osmoreceptors so they will shrink this shrinking will stimulate the hypothalamus to produce ADH that will be secreted from the ...
... Control of ADH secretion: High osmolarity stimulates ADH . When we have high osmolarity water will leave the osmoreceptors so they will shrink this shrinking will stimulate the hypothalamus to produce ADH that will be secreted from the ...
Hypothalamus - pituitary
... • Secretion by the anterior pituitary is controlled by hormones called hypothalamic releasing hormones and inhibitory hormones conducted to the anterior pituitary through hypothalamic hypophysial portal vessels . • Posterior pituitary secrets two hormones, which are synthesized within cell bodies of ...
... • Secretion by the anterior pituitary is controlled by hormones called hypothalamic releasing hormones and inhibitory hormones conducted to the anterior pituitary through hypothalamic hypophysial portal vessels . • Posterior pituitary secrets two hormones, which are synthesized within cell bodies of ...
013368718X_CH34_529-544.indd
... The hypothalamus controls the secretions of the pituitary gland and is the link between the central nervous system and the endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the posterior pituitary through neurosecretory cells. The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones that control the secretions of the ...
... The hypothalamus controls the secretions of the pituitary gland and is the link between the central nervous system and the endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the posterior pituitary through neurosecretory cells. The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones that control the secretions of the ...
Hormones Trigger Changes in Target Cells
... Hormones Trigger Changes in Target Cells • There are two general mechanisms by which hormones trigger changes in target cells. • In the first mechanism, – Hormones bring about changes without ever entering their target cells. – These hormones are protein hormones – Example: insulin ...
... Hormones Trigger Changes in Target Cells • There are two general mechanisms by which hormones trigger changes in target cells. • In the first mechanism, – Hormones bring about changes without ever entering their target cells. – These hormones are protein hormones – Example: insulin ...
A1984SK79600001
... who with Geoffrey Harris had done so much to establish the neurovascular concept of pituitary control, joined us at the end of the summer. He immediately designed a head-holder so much better than our original model that we adopted it and made him a coauthor of the atlas publication. (An improved ve ...
... who with Geoffrey Harris had done so much to establish the neurovascular concept of pituitary control, joined us at the end of the summer. He immediately designed a head-holder so much better than our original model that we adopted it and made him a coauthor of the atlas publication. (An improved ve ...
34.2 packet - Biology Daily Summaries
... The hypothalamus controls the secretions of the pituitary gland and is the link between the central nervous system and the endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the posterior pituitary through neurosecretory cells. The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones that control the secretions of the ...
... The hypothalamus controls the secretions of the pituitary gland and is the link between the central nervous system and the endocrine system. The hypothalamus controls the posterior pituitary through neurosecretory cells. The hypothalamus produces releasing hormones that control the secretions of the ...
Pituitary Disorders
... Where is it located??? Name its’ 3 parts or sections. What hormones are secreted by the pituitary gland??? ...
... Where is it located??? Name its’ 3 parts or sections. What hormones are secreted by the pituitary gland??? ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... Which organs are responsible for most of the metabolism or excretion of hormones? Give two examples of hormones that are secreted in inactive forms, and are converted to the active form in the target tissue. Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond t ...
... Which organs are responsible for most of the metabolism or excretion of hormones? Give two examples of hormones that are secreted in inactive forms, and are converted to the active form in the target tissue. Since all hormones are delivered to all regions of the body, why doesn’t each cell respond t ...
Chapter 11
... Steroid hormones – link to cell, bind to nucleus, activate genes to make specific proteins ...
... Steroid hormones – link to cell, bind to nucleus, activate genes to make specific proteins ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... hypothalamus sends hormone to anterior lobe of pituitary stimulates pituitary to secrete corticotrophin (adrenocorticotropic hormone; ACTH) blood carries ACTH to target cells in adrenal ...
... hypothalamus sends hormone to anterior lobe of pituitary stimulates pituitary to secrete corticotrophin (adrenocorticotropic hormone; ACTH) blood carries ACTH to target cells in adrenal ...
9b-9c-9i LN - Walnut High School
... – What is the function of the pituitary gland? • The pituitary gland secretes nine hormones that directly regulate many body functions and controls the actions of several other endocrine glands. – The _______________ ________ is a structure at the base of the skull. – The gland is divided into two p ...
... – What is the function of the pituitary gland? • The pituitary gland secretes nine hormones that directly regulate many body functions and controls the actions of several other endocrine glands. – The _______________ ________ is a structure at the base of the skull. – The gland is divided into two p ...
bio12_sm_10_5
... cells. 2. Steroids affect DNA by binding to receptors in the nucleus. This hormone-receptor complex then binds to certain regulatory elements of genes and activates transcription. 3. Synthetic hormones are human-designed chemicals that mimic the effects of natural hormones. 4. The names of many ster ...
... cells. 2. Steroids affect DNA by binding to receptors in the nucleus. This hormone-receptor complex then binds to certain regulatory elements of genes and activates transcription. 3. Synthetic hormones are human-designed chemicals that mimic the effects of natural hormones. 4. The names of many ster ...
Hypophysiotropic Centers in the Brain of Amphibians and Fish Many
... the histochemical properties of particular Many experiments have been carried cellular substances, e.g., hormones and out to establish the relation between carrier proteins in the neurosecretory cell. hypothalamic neurosecretory processes Bargmann (1949) selectively stained such and certain pituitar ...
... the histochemical properties of particular Many experiments have been carried cellular substances, e.g., hormones and out to establish the relation between carrier proteins in the neurosecretory cell. hypothalamic neurosecretory processes Bargmann (1949) selectively stained such and certain pituitar ...
The Endocrine System
... Endocrine – gland that secretes its product into the blood without the use of ducts ...
... Endocrine – gland that secretes its product into the blood without the use of ducts ...
Reproductive System - Claremont Secondary School
... D. is when the endometrium begins to degenerate and menstrual flow occurs. 22. What are the sources of the four hormones that regulate the ovarian and uterine cycles? A. Uterus and the ovaries. B. Anterior pituitary gland and the ovaries. C. Anterior and posterior pituitary gland and the ovaries. D. ...
... D. is when the endometrium begins to degenerate and menstrual flow occurs. 22. What are the sources of the four hormones that regulate the ovarian and uterine cycles? A. Uterus and the ovaries. B. Anterior pituitary gland and the ovaries. C. Anterior and posterior pituitary gland and the ovaries. D. ...
The Endocrine System
... There are three different kinds of molecules that could be hormones: Protein/Peptide hormones Anime (derived from amino acids) ...
... There are three different kinds of molecules that could be hormones: Protein/Peptide hormones Anime (derived from amino acids) ...
The Endocrine system - Aurora City Schools
... Hormones- chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of your body’s functions ...
... Hormones- chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate many of your body’s functions ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.