Endocrine Virtual Lab! AP Biology
... the hypothalamus secretes TRH, which travels to the pituitary gland to release TSH; TSH travels to the thyroid gland (the target organ) and stimulates the release of thyroid hormone. It is important to note that the hypothalamic releasing hormones are only required for the synthesis and release of t ...
... the hypothalamus secretes TRH, which travels to the pituitary gland to release TSH; TSH travels to the thyroid gland (the target organ) and stimulates the release of thyroid hormone. It is important to note that the hypothalamic releasing hormones are only required for the synthesis and release of t ...
The Endocrine System
... Hypothalamus (brain) – several releasing and inhibiting hormones that affect the hormone secretions of the anterior pituitary Controls temperature, appetite, and thirst Atria (heart) – secretes atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH) that regulates fluid and electrolyte homeostasis ...
... Hypothalamus (brain) – several releasing and inhibiting hormones that affect the hormone secretions of the anterior pituitary Controls temperature, appetite, and thirst Atria (heart) – secretes atrial natriuretic hormone (ANH) that regulates fluid and electrolyte homeostasis ...
Typical disorders of the endocrine system 1. Choose the correct
... aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insufficiency which hormones can occur in the body after the sudden cancellation of long-term corticos ...
... aldosteronism (Conn's syndrome). 37. Excessive production of ACTH leads to increased secretion of: + a) androgenic corticosteroids; b) norepinephrine; c) insulin; d) epinephrine; + e) cortisol. 38. Insufficiency which hormones can occur in the body after the sudden cancellation of long-term corticos ...
Endocrine System
... 1) Stimulate most cells, target bone & skeletal muscle 2) Promote protein synthesis & to use of fats for fuel ii. Metabolic action 1) Stimulates liver, skel. muscle, bone, & cartilage to make insulin-like growth factors 2) Directly promote lipolysis & inhibits glucose uptake c. Thyroid Stimulating H ...
... 1) Stimulate most cells, target bone & skeletal muscle 2) Promote protein synthesis & to use of fats for fuel ii. Metabolic action 1) Stimulates liver, skel. muscle, bone, & cartilage to make insulin-like growth factors 2) Directly promote lipolysis & inhibits glucose uptake c. Thyroid Stimulating H ...
Hormones Gone Wild KEY
... Lincoln's pituitary tumor seems to have caused hypothyroidism, which means that the thyroids are not producing enough hormones. This can lead to lethargy (being tired and sluggish) and weight gain, two of his symptoms. This is not really affecting a particular system as it is his entire body, as his ...
... Lincoln's pituitary tumor seems to have caused hypothyroidism, which means that the thyroids are not producing enough hormones. This can lead to lethargy (being tired and sluggish) and weight gain, two of his symptoms. This is not really affecting a particular system as it is his entire body, as his ...
The thyroid hormones
... a bony structure, the sella turcica, located at the base of the skull. The gland is a small organ about I cm long; it weighs 500 mg and is divided into two parts, anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis). ...
... a bony structure, the sella turcica, located at the base of the skull. The gland is a small organ about I cm long; it weighs 500 mg and is divided into two parts, anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis). ...
Document
... messengers is to maintain homeostasis and promote permanent structural changes. Hormones travel in the bloodstream to target tissues. The major components of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, and reproductive organs (gonads). The pancreas is also p ...
... messengers is to maintain homeostasis and promote permanent structural changes. Hormones travel in the bloodstream to target tissues. The major components of the endocrine system are the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, and reproductive organs (gonads). The pancreas is also p ...
Classification of Hormones Lecture 1
... messenger, the hormone itself being the first messenger. • Most peptide hormones like insulin, glucagon, and hormones of the pituitary gland belong to this group. ...
... messenger, the hormone itself being the first messenger. • Most peptide hormones like insulin, glucagon, and hormones of the pituitary gland belong to this group. ...
Lecture 17. The main methods in endocrinology
... a bony structure, the sella turcica, located at the base of the skull. The gland is a small organ about I cm long; it weighs 500 mg and is divided into two parts, anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis). ...
... a bony structure, the sella turcica, located at the base of the skull. The gland is a small organ about I cm long; it weighs 500 mg and is divided into two parts, anterior (adenohypophysis) and posterior (neurohypophysis). ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM WEBQUEST
... The endocrine system is a complex network of glands, hormones and receptors. It provides the key communication and control link between the nervous system and bodily functions such as reproduction, immunity, metabolism and behavior. In nearly all complex multicellular animals, there are two main sys ...
... The endocrine system is a complex network of glands, hormones and receptors. It provides the key communication and control link between the nervous system and bodily functions such as reproduction, immunity, metabolism and behavior. In nearly all complex multicellular animals, there are two main sys ...
Molecular Involvement of the Pit-2 Gene in Anterior Pituitary Cell
... activation of the pzt-l gene and persists into the mature animal. The pit-1 gene is subject to autoregulation by its own product, and regulatory regions of the gene contain response elements conferring activation by retinoic acid, vitamin D3 derivatives, cyclic AMP signaling pathways, and pituitary- ...
... activation of the pzt-l gene and persists into the mature animal. The pit-1 gene is subject to autoregulation by its own product, and regulatory regions of the gene contain response elements conferring activation by retinoic acid, vitamin D3 derivatives, cyclic AMP signaling pathways, and pituitary- ...
Lecture 1. Introduction
... Hormones (modern, broad definition): any substance that is released by a cell and acts on another cell (to regulate its function). The means of intercellular communication. This definition includes: - Gap junctions: direct flow of various chemicals from one cell to another - Autocrines - Paracrines ...
... Hormones (modern, broad definition): any substance that is released by a cell and acts on another cell (to regulate its function). The means of intercellular communication. This definition includes: - Gap junctions: direct flow of various chemicals from one cell to another - Autocrines - Paracrines ...
Endocrine System Endocrine Vs Nervous System
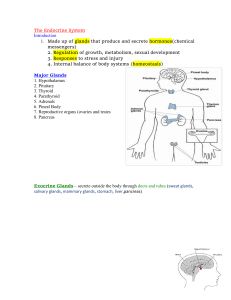
... The pituitary contains two lobes. Hormones released by the posterior lobe are synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus. Unlike the posterior lobe, the anterior lobe produces the hormones that it releases. Refer to the diagram below as you read about the hypothalamus, pituitary, and each of the gla ...
... The pituitary contains two lobes. Hormones released by the posterior lobe are synthesized by neurons in the hypothalamus. Unlike the posterior lobe, the anterior lobe produces the hormones that it releases. Refer to the diagram below as you read about the hypothalamus, pituitary, and each of the gla ...
• Main Function: It releases hormones into the blood to It releases
... located in the brain and controls the release of hormones from the pituitary p yg gland. It is an important link between the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
... located in the brain and controls the release of hormones from the pituitary p yg gland. It is an important link between the endocrine and nervous systems. ...
Human Endocrine Glands Section 39-2 pgs 1003-1008
... This is the feeling you get when you are excited or frightened. ...
... This is the feeling you get when you are excited or frightened. ...
The Endocrine System and Homeostasis
... activates specific genes, causing changes in the cell. EXAMPLES: Steroid hormones, such as testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol. • Water Soluble (protein or protein-related hormones): these hormones cannot diffuse across the cell membrane. EXAMPLES: Epinephrine, human growth hormone, thyroxine, and ...
... activates specific genes, causing changes in the cell. EXAMPLES: Steroid hormones, such as testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol. • Water Soluble (protein or protein-related hormones): these hormones cannot diffuse across the cell membrane. EXAMPLES: Epinephrine, human growth hormone, thyroxine, and ...
CH 3 Practice Test
... somatic nervous system b. sympathetic nervous system c. endocrine system d. parasympathetic nervous system e. reflexive nervous system ...
... somatic nervous system b. sympathetic nervous system c. endocrine system d. parasympathetic nervous system e. reflexive nervous system ...
Chapter 15: Endocrine System
... Parathyroid glands, page 552 •Tiny glands embedded in the posterior aspect of the thyroid ...
... Parathyroid glands, page 552 •Tiny glands embedded in the posterior aspect of the thyroid ...
The Endocrine System and Homeostasis
... chemicals that affect the hypothalamus’ nerve activity by negative feedback. The pituitary releases hormones which stimulate other glands to release hormones that either increase or decrease cell processes ...
... chemicals that affect the hypothalamus’ nerve activity by negative feedback. The pituitary releases hormones which stimulate other glands to release hormones that either increase or decrease cell processes ...
xCh15 endocrine sys
... Hypothalamus – major link between nervous and endocrine system Hypothalamus secretes 9 hormones, the pituitary secretes 7. Together these hormones regulate virtually all aspects of growth, development, metabolism, and homeostasis ...
... Hypothalamus – major link between nervous and endocrine system Hypothalamus secretes 9 hormones, the pituitary secretes 7. Together these hormones regulate virtually all aspects of growth, development, metabolism, and homeostasis ...
The Endocrine System
... Location: base of the brain, (attached to hypothalamus) *Often called the “master gland” because of its great influence on the body organs Anterior Pituitary Hormones Prolactin or PRL - PRL stimulates milk production from a woman's breasts after childbirth Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth ...
... Location: base of the brain, (attached to hypothalamus) *Often called the “master gland” because of its great influence on the body organs Anterior Pituitary Hormones Prolactin or PRL - PRL stimulates milk production from a woman's breasts after childbirth Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.