Class PowerPoint - Franklin College
... that regulate sodium levels in the blood (Aldosterone), sex hormones (low levels), and glucocorticoids (cortisol) which plays an important role in managing long-term stress. • Effects of Cortisol - increases blood glucose levels, increases blood lipids, increases blood pressure, suppresses the immun ...
... that regulate sodium levels in the blood (Aldosterone), sex hormones (low levels), and glucocorticoids (cortisol) which plays an important role in managing long-term stress. • Effects of Cortisol - increases blood glucose levels, increases blood lipids, increases blood pressure, suppresses the immun ...
The Endocrine System
... – 4 trophic hormones—they control the activity of other endocrine glands – 2 growth hormones ...
... – 4 trophic hormones—they control the activity of other endocrine glands – 2 growth hormones ...
Slide 1
... the “checks and balances” system via the negative feedback mechanisms Located in the cerebrum Anterior lobe: glandular tissue; makes hormones – Tropic hormones: stimulate other endocrine glands to make their hormones; thyrotropic, adrenocorticotropic, and two gonadotropic hormones – NonTropic hormon ...
... the “checks and balances” system via the negative feedback mechanisms Located in the cerebrum Anterior lobe: glandular tissue; makes hormones – Tropic hormones: stimulate other endocrine glands to make their hormones; thyrotropic, adrenocorticotropic, and two gonadotropic hormones – NonTropic hormon ...
Endocrine System
... 1. Blood level of hormone falls 2. Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... 1. Blood level of hormone falls 2. Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
Endocrine Notes
... 1. Blood level of hormone falls 2. Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
... 1. Blood level of hormone falls 2. Brain gets message and sends out hormone to stimulate gland 3. Gland stimulates more hormone 4. When blood levels of hormone increase, the brain hormones stop ...
Structure-Function II
... The hypothalamus, like the thalamus, is comprised of many distinct (and some not-so-distinct) nuclei. The hypothalamus performs many “primitive” functions. In particular, in response to the needs of the organism, it: ...
... The hypothalamus, like the thalamus, is comprised of many distinct (and some not-so-distinct) nuclei. The hypothalamus performs many “primitive” functions. In particular, in response to the needs of the organism, it: ...
Slide 1
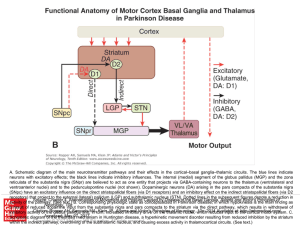
... A. Schematic diagram of the main neurotransmitter pathways and their effects in the cortical–basal ganglia–thalamic circuits. The blue lines indicate neurons with excitatory effects; the black lines indicate inhibitory influences. The internal (medial) segment of the globus pallidus (MGP) and the zo ...
... A. Schematic diagram of the main neurotransmitter pathways and their effects in the cortical–basal ganglia–thalamic circuits. The blue lines indicate neurons with excitatory effects; the black lines indicate inhibitory influences. The internal (medial) segment of the globus pallidus (MGP) and the zo ...
The Endocrine System Chapter 10
... all endocrine cells, tissues, and endocrine glands (organs) of the body Many different organs have some endocrine cells/tissues within their structure, but the organ’s primary function is not endocrine (ie: heart, kidney, digestive organs, pancreas hypothalamus, gonads, thymus) Some organs are p ...
... all endocrine cells, tissues, and endocrine glands (organs) of the body Many different organs have some endocrine cells/tissues within their structure, but the organ’s primary function is not endocrine (ie: heart, kidney, digestive organs, pancreas hypothalamus, gonads, thymus) Some organs are p ...
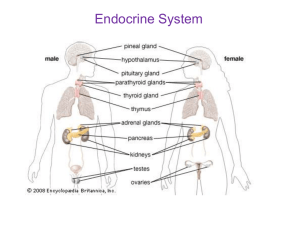
Glands of the Endocrine System
... Target cell- receives the message – Receptor for hormone – Hormone creates a response ...
... Target cell- receives the message – Receptor for hormone – Hormone creates a response ...
File - BINZHOU MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
... Inferior cerebellar peduncle -connect with medulla and with ...
... Inferior cerebellar peduncle -connect with medulla and with ...
Endocrine_System__part_1__Feb_28__studen
... • The study of hormones • Like nervous system- helps control the body and aid in communication • Hormone- chemical messenger, travels through the bloodstream to target cells, effective at very low concentration ...
... • The study of hormones • Like nervous system- helps control the body and aid in communication • Hormone- chemical messenger, travels through the bloodstream to target cells, effective at very low concentration ...
The Hypothalamo-Pituitary- Adrenal Axis
... TSH: thyroid stimulating hormone GH: growth hormone **Please see Figures 10.7-10.9 in text** ...
... TSH: thyroid stimulating hormone GH: growth hormone **Please see Figures 10.7-10.9 in text** ...
ch_45 endocrine system
... What does this tell you about these hormones? How could these hormones have different effects? same gene family gene duplication? ...
... What does this tell you about these hormones? How could these hormones have different effects? same gene family gene duplication? ...
The Human brain
... • Has bundles of neurons connecting the lower portion of the brain with spinal cord. • Contains reflex centers for vision and hearing. ...
... • Has bundles of neurons connecting the lower portion of the brain with spinal cord. • Contains reflex centers for vision and hearing. ...
Hormone-relationships
... 1. corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH): stimulates production and release of ACTH 2. thyroid releasing hormone (TRH): stimulates the production and release of TSH 3. somatostatin (Growth Hormone inhibiting Factor): inhibits the production and release of growth hormone 4. growth hormone releasing h ...
... 1. corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH): stimulates production and release of ACTH 2. thyroid releasing hormone (TRH): stimulates the production and release of TSH 3. somatostatin (Growth Hormone inhibiting Factor): inhibits the production and release of growth hormone 4. growth hormone releasing h ...
Chapter 9: The endocrine system
... Hormones of the anterior pituitary: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) • TSH influences the growth of and hormone release from the thyroid gland • The thyroid gland releases thyroid hormones, which contain amino acid-like molecules bound to iodine atoms and also calcitonin, which regulates calcium d ...
... Hormones of the anterior pituitary: Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) • TSH influences the growth of and hormone release from the thyroid gland • The thyroid gland releases thyroid hormones, which contain amino acid-like molecules bound to iodine atoms and also calcitonin, which regulates calcium d ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Coastal Bend College
... we call hormones • What are hormones? • Hormones are a chemical product of a gland that exerts its effect in an organ at a distant site. • The chemical is carried by the blood system to the distant organ ...
... we call hormones • What are hormones? • Hormones are a chemical product of a gland that exerts its effect in an organ at a distant site. • The chemical is carried by the blood system to the distant organ ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... Autonomic nervous system Secretion of pituitary hormones Organization of body metabolism Availability of energy foods such as glucose sleep & wakefulness Temperature, thirst & water regulation Hunger & Appetite Behavior - fear, rage, sexual desire Growth Sexual reproduction ...
... Autonomic nervous system Secretion of pituitary hormones Organization of body metabolism Availability of energy foods such as glucose sleep & wakefulness Temperature, thirst & water regulation Hunger & Appetite Behavior - fear, rage, sexual desire Growth Sexual reproduction ...
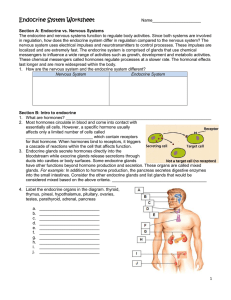
Endocrine System Worksheet
... 4. What hormones stimulate the testes and ovaries to function? _______________________________ 5. In females, which hormone promotes the maturation of the reproductive organs and the development of secondary sex characteristics? __________________________ 6. In males, which hormone promotes the matu ...
... 4. What hormones stimulate the testes and ovaries to function? _______________________________ 5. In females, which hormone promotes the maturation of the reproductive organs and the development of secondary sex characteristics? __________________________ 6. In males, which hormone promotes the matu ...
chapter summary
... which transports them to specific target sites where they regulate or direct a particular function by altering protein activity within the target cells. •Even though hormones are able to reach all tissues via the blood, they exert their effects only at their target cells because these cells alone ha ...
... which transports them to specific target sites where they regulate or direct a particular function by altering protein activity within the target cells. •Even though hormones are able to reach all tissues via the blood, they exert their effects only at their target cells because these cells alone ha ...
Endocrine Review Package
... This flow diagram shows the balancing effect of insulin and glucagon on blood sugar levels. Study it carefully and answer the related questions. Also use page 341 in Nelson 1) What are the specialized cells that ...
... This flow diagram shows the balancing effect of insulin and glucagon on blood sugar levels. Study it carefully and answer the related questions. Also use page 341 in Nelson 1) What are the specialized cells that ...
films/media suggestions
... that regulate the conversion of fat into glucose, sodium and potassium balance, and male secondary sexual characteristics. 7. Prolactin stimulates milk production in mammary glands. 8. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) initiates color changes in the skin of amphibians and reptiles; its role in th ...
... that regulate the conversion of fat into glucose, sodium and potassium balance, and male secondary sexual characteristics. 7. Prolactin stimulates milk production in mammary glands. 8. Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) initiates color changes in the skin of amphibians and reptiles; its role in th ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.