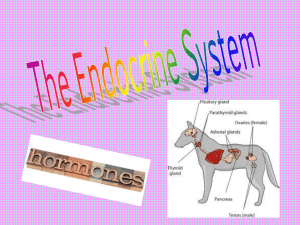
The Endocrine System: An Overview Endocrine - dr
... Signals most body cells to take up glucose from the blood Lowers blood sugar ...
... Signals most body cells to take up glucose from the blood Lowers blood sugar ...
File
... 10) Oxytocin inducing the uterus to contract during labor is an example of positive feedback mechanism; therefore A) increased secretion of oxytocin would decrease uterine contractions. B) increased secretion of oxytocin would increase uterine contractions. C) decreased secretion of oxytocin would ...
... 10) Oxytocin inducing the uterus to contract during labor is an example of positive feedback mechanism; therefore A) increased secretion of oxytocin would decrease uterine contractions. B) increased secretion of oxytocin would increase uterine contractions. C) decreased secretion of oxytocin would ...
Thyroid Gland
... Disorders Related to the Pancreas Diabetes Mellitus – results from insulin deficiency, blood sugar rises (hypoglycemia); excess excreted in urine. Type I – insulin dependent diabetes mellitus or juvenile onset diabetes, often caused by inherited immune disorder that destroys pancreatic cells Type I ...
... Disorders Related to the Pancreas Diabetes Mellitus – results from insulin deficiency, blood sugar rises (hypoglycemia); excess excreted in urine. Type I – insulin dependent diabetes mellitus or juvenile onset diabetes, often caused by inherited immune disorder that destroys pancreatic cells Type I ...
Endocrine Disorders
... which is Xanthine derivative inhibits phosphodiesterase activity therefore causes prolonged hormonal action. Subgroup (B) They act by increasing cGMP level inside the cells through activation of guanylate cyclase. It includes one hormone only called atrial natruretic factor (ANF) which is produced b ...
... which is Xanthine derivative inhibits phosphodiesterase activity therefore causes prolonged hormonal action. Subgroup (B) They act by increasing cGMP level inside the cells through activation of guanylate cyclase. It includes one hormone only called atrial natruretic factor (ANF) which is produced b ...
Practice Exam 3 10/31/10 1) The site of ovulation in mares. A
... 29) Mares differ from other domestic species in that they A) ovulate a secondary oocyte B) process a suburethral diverticulum C) ovulate from the ovulation fossa of their inverted cortex D) all of the above 30) Which of the following is not an important pathway of control between endocrine glands? A ...
... 29) Mares differ from other domestic species in that they A) ovulate a secondary oocyte B) process a suburethral diverticulum C) ovulate from the ovulation fossa of their inverted cortex D) all of the above 30) Which of the following is not an important pathway of control between endocrine glands? A ...
CHAPTER 36
... the nucleus are the following: They activate the genetic mechanisms for the formation of many types of intracellular proteins—probably 100 or more. Many of these are enzymes that promote enhanced intracellular metabolic activity in virtually all cells of the body. ...
... the nucleus are the following: They activate the genetic mechanisms for the formation of many types of intracellular proteins—probably 100 or more. Many of these are enzymes that promote enhanced intracellular metabolic activity in virtually all cells of the body. ...
Endocrine System - Killingly Public Schools
... Endocrine System • Hormones – chemicals produced in response to specific stimuli that stimulate reactions in specific body organs and tissues – released directly into the bloodstream, interact with receptors causing the target tissue to perform a specific function ...
... Endocrine System • Hormones – chemicals produced in response to specific stimuli that stimulate reactions in specific body organs and tissues – released directly into the bloodstream, interact with receptors causing the target tissue to perform a specific function ...
Neural Anatomy and Images
... nmlf: nucleus of the medio-longitudinal fasciculus npc: nucleus of the posterior commissure npoc: nucleus of the post-optic commissure oc: optic chiasma on: optic nerve pc: posterior commissure poc: post-optic commissure r: rhombomere rb: Rohon-Beard neurons sm: stria medullaris (habenular afferents ...
... nmlf: nucleus of the medio-longitudinal fasciculus npc: nucleus of the posterior commissure npoc: nucleus of the post-optic commissure oc: optic chiasma on: optic nerve pc: posterior commissure poc: post-optic commissure r: rhombomere rb: Rohon-Beard neurons sm: stria medullaris (habenular afferents ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System
... • Overview: The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators • Hormone definition: a chemical signal secreted into the circulatory system and communicates regulatory messages within the body ...
... • Overview: The Body’s Long-Distance Regulators • Hormone definition: a chemical signal secreted into the circulatory system and communicates regulatory messages within the body ...
Breaking Dogma on the Hypothalamic
... the evolution of a complex pituitary with dual developmental origin along with the more highly developed tripartite brain added another layer of control leading to the neuroendocrine control of many complex physiological functions such as growth, reproduction, development and metabolism among others ...
... the evolution of a complex pituitary with dual developmental origin along with the more highly developed tripartite brain added another layer of control leading to the neuroendocrine control of many complex physiological functions such as growth, reproduction, development and metabolism among others ...
Endocrine System
... Regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic, and homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.20 ...
... Regulates or supports a variety of important cardiovascular, metabolic, immunologic, and homeostatic functions including water balance People with adrenal insufficiency: these stresses can cause hypotension, shock and death: must give glucocorticoids, eg for surgery or if have infection, etc.20 ...
Posterior Pituitary & Pineal Glands
... osmolarity (concentration of solutes in blood) which is detected by the osmoreceptors (neurons connected to blood vessels) which relay into the hypothalamus If there is a high concentration of solutes, ADH is produced and secreted out of neurons in the bloodstream If the concentration is low, ADH is ...
... osmolarity (concentration of solutes in blood) which is detected by the osmoreceptors (neurons connected to blood vessels) which relay into the hypothalamus If there is a high concentration of solutes, ADH is produced and secreted out of neurons in the bloodstream If the concentration is low, ADH is ...
Lesson 2.3: Chemical Communication Preface While the nervous
... A protein hormone that is produced especially by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and that promotes an increase in the sugar content of the blood by increasing the rate of breakdown of glycogen in the liver. Any one of the many circulating chemical signals found in all multicellular organisms tha ...
... A protein hormone that is produced especially by the pancreatic islets of Langerhans and that promotes an increase in the sugar content of the blood by increasing the rate of breakdown of glycogen in the liver. Any one of the many circulating chemical signals found in all multicellular organisms tha ...
BIOLOGY 120 TAKE HOME EXAM
... 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as __________________. 4. Parathyroid hormone functions by in ...
... 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as __________________. 4. Parathyroid hormone functions by in ...
Sex Hormones
... • Most look female at birth but a penis develops during adolescence and puberty. • Most then accept a male gender identity. – Brain is exposed to testosterone during early development. ...
... • Most look female at birth but a penis develops during adolescence and puberty. • Most then accept a male gender identity. – Brain is exposed to testosterone during early development. ...
Basal nuclei
... that the spinal cord does for the rest of the body Reception and integration of all synaptic input from spinal cord Relaying sensory information to cerebellum, thalamus, and to different portions of the brainstem & arousal and activation of cerebral cortex Regulation of muscle reflexes involved with ...
... that the spinal cord does for the rest of the body Reception and integration of all synaptic input from spinal cord Relaying sensory information to cerebellum, thalamus, and to different portions of the brainstem & arousal and activation of cerebral cortex Regulation of muscle reflexes involved with ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... c. This positive feedback mechanism increases intensity; such positive feedback does not maintain homeostasis. d. Oxytocin also may play a role in the propulsion of semen through the male reproductive tract. B. Anterior Pituitary 1. Stimulation by the hypothalamus controls the release of anterior pi ...
... c. This positive feedback mechanism increases intensity; such positive feedback does not maintain homeostasis. d. Oxytocin also may play a role in the propulsion of semen through the male reproductive tract. B. Anterior Pituitary 1. Stimulation by the hypothalamus controls the release of anterior pi ...
Central Nervous System Sensory neurons transmit impulses from the
... What is the name of this chemical? Hormone 2. The organs and tissues that the chemical is transported to by the blood is made up of what kind of cells? Target cells 3. What do hormones attach to on these cells? Receptors ...
... What is the name of this chemical? Hormone 2. The organs and tissues that the chemical is transported to by the blood is made up of what kind of cells? Target cells 3. What do hormones attach to on these cells? Receptors ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 10
... E. Thymosin helps in the development of T cells in the thymus gland. Erythropoietin is secreted by the kidneys in response to reduced oxygen levels in the blood. Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the placenta; its function is similar to LH. Melatonin is produced by the pineal body, and is ...
... E. Thymosin helps in the development of T cells in the thymus gland. Erythropoietin is secreted by the kidneys in response to reduced oxygen levels in the blood. Human chorionic gonadotropin is produced by the placenta; its function is similar to LH. Melatonin is produced by the pineal body, and is ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system
... is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. The hormone calcitonin is also produced and controls calcium ...
... is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. The hormone calcitonin is also produced and controls calcium ...
Chapter 20: Endocrine System
... Hormones are chemicals that influence metabolism of cells, the growth and development of body parts, and homeostasis. Hormones can be classified as peptides or steroids. ...
... Hormones are chemicals that influence metabolism of cells, the growth and development of body parts, and homeostasis. Hormones can be classified as peptides or steroids. ...
Hormone review
... Gonadotropic Hormones (FSH and LH) ovaries and testes sex hormones; controls gamete production Negative Feedback Inhibition Hormone secretions by glands that are under the control of the hypothalamus are controlled by negative feedback. When the hormone levels are high, they inhibit the hypothal ...
... Gonadotropic Hormones (FSH and LH) ovaries and testes sex hormones; controls gamete production Negative Feedback Inhibition Hormone secretions by glands that are under the control of the hypothalamus are controlled by negative feedback. When the hormone levels are high, they inhibit the hypothal ...
C. Pancreas
... This positive feedback mechanism increases intensity; such positive feedback does not maintain homeostasis. d. Oxytocin also may play a role in the propulsion of semen through the male reproductive tract. B. Anterior Pituitary 1. Stimulation by the hypothalamus controls the release of anterior pitui ...
... This positive feedback mechanism increases intensity; such positive feedback does not maintain homeostasis. d. Oxytocin also may play a role in the propulsion of semen through the male reproductive tract. B. Anterior Pituitary 1. Stimulation by the hypothalamus controls the release of anterior pitui ...
M3 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... • the body’s “slow” chemical communication system • a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream • Act on brain to influence our growth/emotions/moti vations/mood. ...
... • the body’s “slow” chemical communication system • a set of glands that secrete hormones into the bloodstream • Act on brain to influence our growth/emotions/moti vations/mood. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.