Human Sexual Anatomy & Physiology (Part 1)
... – Absence of receptors for this hormone • In an XY male, defeminization does not occur but masculanization does • Person is born with both sets of internal sex organs ...
... – Absence of receptors for this hormone • In an XY male, defeminization does not occur but masculanization does • Person is born with both sets of internal sex organs ...
Chapter 45 Student Guided Notes
... The anterior pituitary is an endocrine gland that synthesizes and secretes hormones. ○ Secretion of each hormone by the anterior pituitary is regulated by one or more signals from the hypothalamus. ...
... The anterior pituitary is an endocrine gland that synthesizes and secretes hormones. ○ Secretion of each hormone by the anterior pituitary is regulated by one or more signals from the hypothalamus. ...
The Endocrine System
... A steroid hormone will: Diffuse through membrane of target cells Enter the nucleus Bind to a specific protein in the nucleus Bind to specific sites on the cell’s DNA Activate genes synthesis of new ...
... A steroid hormone will: Diffuse through membrane of target cells Enter the nucleus Bind to a specific protein in the nucleus Bind to specific sites on the cell’s DNA Activate genes synthesis of new ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary, influenced by levels of hormones in the blood. Neurosecre ...
... diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary, influenced by levels of hormones in the blood. Neurosecre ...
Endocrinology: Endocrine System Function Nervous vs. Endocrine
... – Secrete products into the interstitial fluid ...
... – Secrete products into the interstitial fluid ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • Specific actions of chemical messengers are at the level of the target cell • These two systems interact and regulate each other ...
... • Specific actions of chemical messengers are at the level of the target cell • These two systems interact and regulate each other ...
endocrine glands - Catawba County Schools
... stimulates production of milk after childbirth THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE – TSH stimulates thyroxine ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE – ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE – FSH stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in ...
... stimulates production of milk after childbirth THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE – TSH stimulates thyroxine ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE – ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE – FSH stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in ...
Chapt15 Lecture 13ed Pt 2
... 3. Each type of hypothalamic hormone either stimulates or inhibits production and secretion of an anterior pituitary hormone. ...
... 3. Each type of hypothalamic hormone either stimulates or inhibits production and secretion of an anterior pituitary hormone. ...
HUBS 191 MODULE 5 NOTES MODULE 5 : ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... - endocrine cells are sensitive to the physiological changes produced by their target cells - secretion by many endocrine glands is regulated by hormone produced by another gland eg secretion by anterior pituitary can be regulated by releasing hormones/inhibiting hormones secreted by hypothalamus - ...
... - endocrine cells are sensitive to the physiological changes produced by their target cells - secretion by many endocrine glands is regulated by hormone produced by another gland eg secretion by anterior pituitary can be regulated by releasing hormones/inhibiting hormones secreted by hypothalamus - ...
Anterior Pituitary
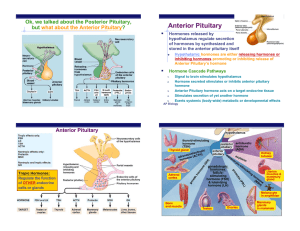
... Ok, we talked about the Posterior Pituitary, but what about the Anterior Pituitary? ...
... Ok, we talked about the Posterior Pituitary, but what about the Anterior Pituitary? ...
The Endocrine System
... Diabetic neuropathies are a family of nerve disorders caused by diabetes. People with diabetes can develop nerve damage throughout the body. Symptoms include pain, tingling, or numbness-loss of feeling-in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. This can result in wounds that are slow to heal. ...
... Diabetic neuropathies are a family of nerve disorders caused by diabetes. People with diabetes can develop nerve damage throughout the body. Symptoms include pain, tingling, or numbness-loss of feeling-in the hands, arms, feet, and legs. This can result in wounds that are slow to heal. ...
Breaking Dogma on the Hypothalamic
... the evolution of a complex pituitary with dual developmental origin along with the more highly developed tripartite brain added another layer of control leading to the neuroendocrine control of many complex physiological functions such as growth, reproduction, development and metabolism among others ...
... the evolution of a complex pituitary with dual developmental origin along with the more highly developed tripartite brain added another layer of control leading to the neuroendocrine control of many complex physiological functions such as growth, reproduction, development and metabolism among others ...
Chapter 9
... Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to pr ...
... Releasing hormones: GHRH. Growth hormone-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release growth hormone. TRH. Thyroid-releasing hormone. Causes the anterior pituitary to release thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). CRH. Corticotropin-releasing hormone. Causes anterior pituitary to pr ...
Chapter 18 - Endocrine
... – Ring structures = steroids – Polypeptides = ACTH, TRH, FSH, LH, oxytocin, insulin, etc. – Monoamines = Dopamine, Thryoxine (T3/T4) ...
... – Ring structures = steroids – Polypeptides = ACTH, TRH, FSH, LH, oxytocin, insulin, etc. – Monoamines = Dopamine, Thryoxine (T3/T4) ...
File
... Paracrines: locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them ...
... Paracrines: locally acting chemicals that affect cells other than those that secrete them ...
Endocrine System Lecture
... •Ductless: hormones secreted directly into bloodstream as the blood circulates through the gland •Secretions are carried to all areas of the body where they have a special influence cells, tissues and organs ...
... •Ductless: hormones secreted directly into bloodstream as the blood circulates through the gland •Secretions are carried to all areas of the body where they have a special influence cells, tissues and organs ...
Endocrine System Quiz Quiz # 2 Fall 2008
... • For a patient who presents with disturbances of plasma levels of sodium and potassium, which of the following hormones is most likely involved: • A) insulin • B) aldosterone • C) PTH ...
... • For a patient who presents with disturbances of plasma levels of sodium and potassium, which of the following hormones is most likely involved: • A) insulin • B) aldosterone • C) PTH ...
File
... and are water soluble eg. insulin, growth hormone, epinepherine - do NOT enter target cells but “land” on receptors on the cell surface ...
... and are water soluble eg. insulin, growth hormone, epinepherine - do NOT enter target cells but “land” on receptors on the cell surface ...
The Endocrine System
... • The pituitary gland’s secretions are regulated by both the nervous system and the hypothalamus. • Anterior Pituitary secretes: Growth Hormone (GH) – stimulates cells to increase in size. Prolactin (PRL) – stimulates & sustains milk production. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) – controls thyroi ...
... • The pituitary gland’s secretions are regulated by both the nervous system and the hypothalamus. • Anterior Pituitary secretes: Growth Hormone (GH) – stimulates cells to increase in size. Prolactin (PRL) – stimulates & sustains milk production. Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) – controls thyroi ...
Hormones 101
... Hormones act as the body’s messengers. They are secreted into the bloodstream and control most major bodily functions. Hormones are vital to a person’s health, however, as you age, hormone production progressively decreases. Synthetic hormones are often prescribed by doctors in an attempt to restore ...
... Hormones act as the body’s messengers. They are secreted into the bloodstream and control most major bodily functions. Hormones are vital to a person’s health, however, as you age, hormone production progressively decreases. Synthetic hormones are often prescribed by doctors in an attempt to restore ...
(12) Endocrine System
... effects on same target cell • Response of target cell to same second messenger can differ in different cells ...
... effects on same target cell • Response of target cell to same second messenger can differ in different cells ...
Introduction to Anatomy and Physiology II BY 32
... • Neural: stimulation from the nervous system via neurotransmitters. ...
... • Neural: stimulation from the nervous system via neurotransmitters. ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Releasing Factors (hormones) stimulate secretion by Anterior Pituitary Inhibiting Factors (hormones) are antagonistic to Releasing Nervous tissue carries hormones to ...
... Releasing Factors (hormones) stimulate secretion by Anterior Pituitary Inhibiting Factors (hormones) are antagonistic to Releasing Nervous tissue carries hormones to ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.