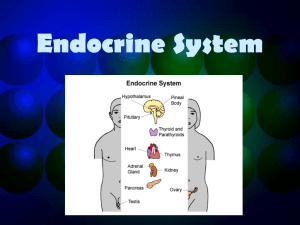
Endocrine System Video Guide
... 12. Glucagon stimulates the break down of ___________ into ______________. 13. If there is no insulin, sugars can’t be used by cells and the cells will start using their own proteins and lipids for energy. Sugar levels in the blood ____________ and cause a condition known as __________________ melli ...
... 12. Glucagon stimulates the break down of ___________ into ______________. 13. If there is no insulin, sugars can’t be used by cells and the cells will start using their own proteins and lipids for energy. Sugar levels in the blood ____________ and cause a condition known as __________________ melli ...
Biology 30 Notes October 8 - Endocrine System Pituitary Gland
... cycle. Corpus Luteum – yellowish gland like structure that develops from a follicle that has matured and released its egg (ovum), it produces progesterone and some estrogen, if pregnancy doesn’t occur it degenerates. In the testes, stimulates the release of testosterone. PRL - Prolactin Stimulates m ...
... cycle. Corpus Luteum – yellowish gland like structure that develops from a follicle that has matured and released its egg (ovum), it produces progesterone and some estrogen, if pregnancy doesn’t occur it degenerates. In the testes, stimulates the release of testosterone. PRL - Prolactin Stimulates m ...
Human Endocrine System
... •The gonads (testes and ovaries) are endocrine glands. •The testes secrete testosterone, which stimulates the growth of male sex organs, sex characteristics, and production of sperm. •The ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone. •Estrogen influences the development of the female sex characteristic ...
... •The gonads (testes and ovaries) are endocrine glands. •The testes secrete testosterone, which stimulates the growth of male sex organs, sex characteristics, and production of sperm. •The ovaries secrete estrogen and progesterone. •Estrogen influences the development of the female sex characteristic ...
Physiology is an Integrated Science
... posterior pituitary is a neural extension of the hypothalamus hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract 2 hormones are made in the hypothalamus, released from the posterior pituitary : antidiuretic hormone ADH oxytocin ...
... posterior pituitary is a neural extension of the hypothalamus hypothalamic-hypophyseal tract 2 hormones are made in the hypothalamus, released from the posterior pituitary : antidiuretic hormone ADH oxytocin ...
Practice Quiz
... a. She grows abnormally tall b. Plasma levels of IGF-1 will be high. c. Plasma levels of GHRH will be high d. Bones of the face, hands, and feet will ...
... a. She grows abnormally tall b. Plasma levels of IGF-1 will be high. c. Plasma levels of GHRH will be high d. Bones of the face, hands, and feet will ...
Endocrine System
... • Later, when blood glucose levels begin to fall, glucagon is secreted by the pancreas and acts on hepatocytes (liver cells) to activate the enzymes that depolymerize (break apart) glycogen and release glucose back into the blood stream so it can go where it is needed in the body’s cells for mitocho ...
... • Later, when blood glucose levels begin to fall, glucagon is secreted by the pancreas and acts on hepatocytes (liver cells) to activate the enzymes that depolymerize (break apart) glycogen and release glucose back into the blood stream so it can go where it is needed in the body’s cells for mitocho ...
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction (p. 293) A. The
... Its endocrine portions are the islets of Langerhans that include two cell types-alpha cells that secrete glucagon, and beta cells that secrete insulin. ...
... Its endocrine portions are the islets of Langerhans that include two cell types-alpha cells that secrete glucagon, and beta cells that secrete insulin. ...
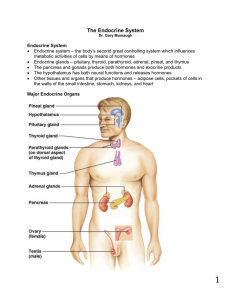
The Endocrine System
... during childbirth and causes milk letdown during breast-feeding. Each endocrine gland plays a distinct role in the body, but these actions overlap and therefore affect each other. ...
... during childbirth and causes milk letdown during breast-feeding. Each endocrine gland plays a distinct role in the body, but these actions overlap and therefore affect each other. ...
Endocrine System
... The activated enzyme activates another molecule, called a second messenger, which causes changes in the cell based on the hormone message • Examples: insulin, thyroid hormones This guide was created by Rohit Ramkumar, Amy Shen, and Jin Yu. To learn more about the student authors, http://www.ck12.or ...
... The activated enzyme activates another molecule, called a second messenger, which causes changes in the cell based on the hormone message • Examples: insulin, thyroid hormones This guide was created by Rohit Ramkumar, Amy Shen, and Jin Yu. To learn more about the student authors, http://www.ck12.or ...
Endocrine System
... Types of Glands • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells ot ...
... Types of Glands • Endocrine glands: secrete hormones in small amounts directly into the bloodstream. • Specific hormones effect specific body parts. • They travel through the bloodstream until they reach their target cells (they cell that the hormone acts on) • Hormones do NOT affect other cells ot ...
22 - PUE
... 13. One at the anterior part of each kidney. 14. Leydig cells or interstitial cells. 15. Atrial natriuretic factor. 16. Progesterone 17. Secretin acts on the exocrine pancreas and stimulates secretion of water and bicarbonate ions 18. Cholecystokinin. 19. Steroids. 20. Erythropoiesis. ...
... 13. One at the anterior part of each kidney. 14. Leydig cells or interstitial cells. 15. Atrial natriuretic factor. 16. Progesterone 17. Secretin acts on the exocrine pancreas and stimulates secretion of water and bicarbonate ions 18. Cholecystokinin. 19. Steroids. 20. Erythropoiesis. ...
Endocrine System Notes
... appearance, behavior, growth, reproduction, and fluid balance. Most hormones are produced endocrine by _______________ glands. ...
... appearance, behavior, growth, reproduction, and fluid balance. Most hormones are produced endocrine by _______________ glands. ...
The endocrine system helps regulate body conditions
... control growth, sexual development, and water absorption. The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that controls the pituitary gland. The pineal gland regulates sleep, body temperature, reproduction, and aging. The thyroid gland produces hormones for growth and metabolism. The thymus helps ...
... control growth, sexual development, and water absorption. The hypothalamus is the part of the brain that controls the pituitary gland. The pineal gland regulates sleep, body temperature, reproduction, and aging. The thyroid gland produces hormones for growth and metabolism. The thymus helps ...
Motivation
... Lean people are more sensitive to insulin so more carbohydrate is used and does not become fat. ...
... Lean people are more sensitive to insulin so more carbohydrate is used and does not become fat. ...
endocrine glands
... Gonadotropins – Are hormones capable of promoting growth and function of the gonads, which include the ovaries and testes. Two Major Gonadotropins secreted from the Anterior Pituitary: 1. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) 2. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Note: LH and FSH are released from anterior pitui ...
... Gonadotropins – Are hormones capable of promoting growth and function of the gonads, which include the ovaries and testes. Two Major Gonadotropins secreted from the Anterior Pituitary: 1. Luteinizing Hormone (LH) 2. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Note: LH and FSH are released from anterior pitui ...
Normal pituitary Magnetic resonance scan
... Hypothalamus-Pituitary: Anatomy Hypothalamus: nervous tissue below thalamus Pituitary: small outgrowth of the forebrain, size of half a pea • Two functional parts – Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary) • Rathke’s pouch – ectoderm above mouth ...
... Hypothalamus-Pituitary: Anatomy Hypothalamus: nervous tissue below thalamus Pituitary: small outgrowth of the forebrain, size of half a pea • Two functional parts – Adenohypophysis (anterior pituitary) • Rathke’s pouch – ectoderm above mouth ...
The Endocrine System
... o Regulate the metabolic function of other cells o Have lag times ranging from seconds to hours o Tend to have prolonged effects Hormones circulate to all tissues but only activate cells referred to as target cells o In general, hormones regulate body growth, the use of foods and energy, resistanc ...
... o Regulate the metabolic function of other cells o Have lag times ranging from seconds to hours o Tend to have prolonged effects Hormones circulate to all tissues but only activate cells referred to as target cells o In general, hormones regulate body growth, the use of foods and energy, resistanc ...
Chapter 37: The Endocrine System
... The islets of Langerhans are clusters of endocrine cells found in the pancreas; they stain lighter than surrounding cells. (credit: modification of work by Muhammad T. Tabiin, Christopher P. White, Grant Morahan, and Bernard E. Tuch; scale-bar data from ...
... The islets of Langerhans are clusters of endocrine cells found in the pancreas; they stain lighter than surrounding cells. (credit: modification of work by Muhammad T. Tabiin, Christopher P. White, Grant Morahan, and Bernard E. Tuch; scale-bar data from ...
Exam 3 Practice Exam
... A) non-water soluble hormones bind to receptors on cell membranes B) water-soluble hormones bind to receptors in the cell nucleus C) hormones such as steroids and T3 are able to affect nuclear function and gene transcription D) GH and prolactin cause molecular synthesis by directly acting on mitocho ...
... A) non-water soluble hormones bind to receptors on cell membranes B) water-soluble hormones bind to receptors in the cell nucleus C) hormones such as steroids and T3 are able to affect nuclear function and gene transcription D) GH and prolactin cause molecular synthesis by directly acting on mitocho ...
Homeostasis Unit Review Homeostasis and Feedback Loops 1
... 8. Is the descending end of the loop of Henle permeable to water? 9. As you move to the center of the medulla, does it become increasingly hypertonic or hypotonic? 10. Is the ascending end of the loop of Henle permeable to water? 11. Why does drinking alcohol make you have to pee often? 12. What ...
... 8. Is the descending end of the loop of Henle permeable to water? 9. As you move to the center of the medulla, does it become increasingly hypertonic or hypotonic? 10. Is the ascending end of the loop of Henle permeable to water? 11. Why does drinking alcohol make you have to pee often? 12. What ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.