Endocrine System Study Guide Anatomy
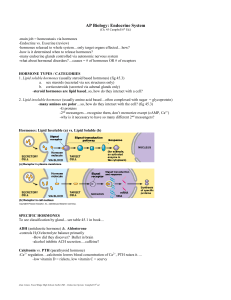
... Adrenaline - emergency situation, the "fight or flight" hormone will increase the heart rate and blood pressure Chemicals –how Hormones are classified Epinephrine – causes heart rate increase and mental alertness improvement FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone LH – Luteinizing Hormone FSH & LH - two ...
... Adrenaline - emergency situation, the "fight or flight" hormone will increase the heart rate and blood pressure Chemicals –how Hormones are classified Epinephrine – causes heart rate increase and mental alertness improvement FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone LH – Luteinizing Hormone FSH & LH - two ...
Thalamus, Hypothalamus, Prethalamus, and Epithalamus
... with posterior pituitary through synaptic transmission and communicates with anterior pituitary through soluble humoral oral factors (hormones). Below is a list of hormones the hypothalamus secretes, their effect on the pituitary gland, and brief descriptions of physiological effects of the pituitar ...
... with posterior pituitary through synaptic transmission and communicates with anterior pituitary through soluble humoral oral factors (hormones). Below is a list of hormones the hypothalamus secretes, their effect on the pituitary gland, and brief descriptions of physiological effects of the pituitar ...
Homeostasis test
... the water potential of the blood becomes less negative. this triggers the pituitary to secrete less ADH this decreases the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule to water – which means less water is reabsorbed and more dilute urine is produced A certain student (mentioning no names) wish ...
... the water potential of the blood becomes less negative. this triggers the pituitary to secrete less ADH this decreases the permeability of the distal convoluted tubule to water – which means less water is reabsorbed and more dilute urine is produced A certain student (mentioning no names) wish ...
The Urinary System
... Nitrogenous waste: • urea • uric acid • creatinine Ions: • sodium • potassium • sulfate • phosphate From the original 1800 g NaCl, only 10 g appears in the urine ...
... Nitrogenous waste: • urea • uric acid • creatinine Ions: • sodium • potassium • sulfate • phosphate From the original 1800 g NaCl, only 10 g appears in the urine ...
The Endocrine System - APBIOSTUDENTS
... secretory neurons (neurons that make hormones rather than neurotransmitters). These hormones are stored in the axon terminals of the secretory hormones and are released when neuron is excited (action potential). Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) affects certain kidney cells. The hormone causes these cell ...
... secretory neurons (neurons that make hormones rather than neurotransmitters). These hormones are stored in the axon terminals of the secretory hormones and are released when neuron is excited (action potential). Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) affects certain kidney cells. The hormone causes these cell ...
Endocrine System booklet
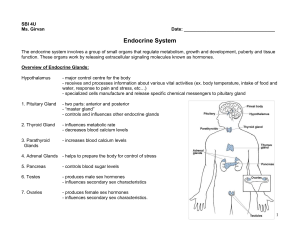
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
... Endocrine System The endocrine system involves a group of small organs that regulate metabolism, growth and development, puberty and tissue function. These organs work by releasing extracellular signaling molecules known as hormones. Overview of Endocrine Glands: Hypothalamus ...
The Divided Brain
... The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen is required for the development of secondary sex characteristics and for the development of eggs. Progesterone prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg. ...
... The ovaries produce estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen is required for the development of secondary sex characteristics and for the development of eggs. Progesterone prepares the uterus for a fertilized egg. ...
The Endocrine System
... body, they are still considered to be one system because they have similar functions, similar mechanisms of influence, and many important interrelationships. • Hormones are your body's chemical messengers. They travel in your bloodstream to tissues or organs. They work slowly, over time, and affect ...
... body, they are still considered to be one system because they have similar functions, similar mechanisms of influence, and many important interrelationships. • Hormones are your body's chemical messengers. They travel in your bloodstream to tissues or organs. They work slowly, over time, and affect ...
Chapter 7
... • Receptor must be activated by binding to hormone before binding to specific region of DNA called HRE (hormone responsive element). – Located adjacent to gene that will be transcribed. ...
... • Receptor must be activated by binding to hormone before binding to specific region of DNA called HRE (hormone responsive element). – Located adjacent to gene that will be transcribed. ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... • Hormones released by one gland travel to another and cause release of a second hormone HORMONE EFFECTS • In order for a target cell/tissue to respond to a hormone, the cell(s) must have a _____________________________ to detect its presence – Like _____________________________, these receptors are ...
... • Hormones released by one gland travel to another and cause release of a second hormone HORMONE EFFECTS • In order for a target cell/tissue to respond to a hormone, the cell(s) must have a _____________________________ to detect its presence – Like _____________________________, these receptors are ...
Endocrine System
... Maintains homeostasis internally Responds to environmental changes Growth and development Reproduction ...
... Maintains homeostasis internally Responds to environmental changes Growth and development Reproduction ...
1 General Overview of the Endocrine System Questions to be
... the testes where it stimulates production and secretion of testosterone into the general circulation, which travels throughout the body to affect muscle growth, secondary sex characteristics, sexual behavior, etc. ...
... the testes where it stimulates production and secretion of testosterone into the general circulation, which travels throughout the body to affect muscle growth, secondary sex characteristics, sexual behavior, etc. ...
Chapter 30
... • The CNS regulates the body’s hormones through a chain of command. • For example, the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland with thyrotropic-releasing hormone (TRH). • This causes the pituitary to release or thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). • TSH then causes the thyroid gland to release thyroi ...
... • The CNS regulates the body’s hormones through a chain of command. • For example, the hypothalamus controls the pituitary gland with thyrotropic-releasing hormone (TRH). • This causes the pituitary to release or thyroidstimulating hormone (TSH). • TSH then causes the thyroid gland to release thyroi ...
FEMALE HORMONES and their activity
... Testosterone is responsible for much more than defining sexual characteristics in men or influencing sex drive. Testosterone is essential for life since it helps to regulate basic metabolism. Testosterone also facilitates protein synthesis and the building of body tissues. Testosterone is produced b ...
... Testosterone is responsible for much more than defining sexual characteristics in men or influencing sex drive. Testosterone is essential for life since it helps to regulate basic metabolism. Testosterone also facilitates protein synthesis and the building of body tissues. Testosterone is produced b ...
CMM/BIO4350
... TSH, sympathetic activity, CART, somatic motor) describe regulation of feeding in 2-6 sentences. You can use a diagram as part of your answer. 4 MARKS When you have been eating more for sustained periods of time you will have more fat and this will increase the amount of leptin released from the fat ...
... TSH, sympathetic activity, CART, somatic motor) describe regulation of feeding in 2-6 sentences. You can use a diagram as part of your answer. 4 MARKS When you have been eating more for sustained periods of time you will have more fat and this will increase the amount of leptin released from the fat ...
The Endocrine System - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... Regulate levels of electrolytes and water in extracellular fluid 95% are aldosterone Sodium reabsorption Potassium excretion ...
... Regulate levels of electrolytes and water in extracellular fluid 95% are aldosterone Sodium reabsorption Potassium excretion ...
Endokrin Sistem - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... Regulate levels of electrolytes and water in extracellular fluid 95% are aldosterone Sodium reabsorption Potassium excretion ...
... Regulate levels of electrolytes and water in extracellular fluid 95% are aldosterone Sodium reabsorption Potassium excretion ...
Chapter 25 The Endocrine Glands
... Adrenal medullary tumors secrete catecholamines. Produce pronounced cardiovascular effects. May cause cerebral hemorrhage from high blood pressure. Treated by removal of tumor. Pancreatic Islets See Chapter 22. The Gonads FUNCTION Production of sex hormones: controlled by FSH and LH. Production of g ...
... Adrenal medullary tumors secrete catecholamines. Produce pronounced cardiovascular effects. May cause cerebral hemorrhage from high blood pressure. Treated by removal of tumor. Pancreatic Islets See Chapter 22. The Gonads FUNCTION Production of sex hormones: controlled by FSH and LH. Production of g ...
Microsoft Word 97
... If some glands do not have tubes connecting them to other body areas, how do their secretions move about? ...
... If some glands do not have tubes connecting them to other body areas, how do their secretions move about? ...
Document
... thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood D. a blood study that gives the direct measurement of the amount of thyroxine in the blood ...
... thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood D. a blood study that gives the direct measurement of the amount of thyroxine in the blood ...
The Endocrine System - Highland 4U Biology with Mr. Byrnes
... • Exercises control over other endocrine glands, but is actually controlled itself by the hypothalamus • Small, sphere-like organ at the base of the brain • Connected to the hypothalamus (p376) • Produces and stores hormones ...
... • Exercises control over other endocrine glands, but is actually controlled itself by the hypothalamus • Small, sphere-like organ at the base of the brain • Connected to the hypothalamus (p376) • Produces and stores hormones ...
Thyroid and antithyroid hormones
... T3 and T4 are synthesized in the thyroid gland. Inorganic iodine is trapped with great avidity by the gland, oxidized and attached to tyrosine. Combination of mono- and/ordi-iodinated tyrosine forms T3 and T4. The thyroxine peroxidase is important both in the initial oxidation and the final combina ...
... T3 and T4 are synthesized in the thyroid gland. Inorganic iodine is trapped with great avidity by the gland, oxidized and attached to tyrosine. Combination of mono- and/ordi-iodinated tyrosine forms T3 and T4. The thyroxine peroxidase is important both in the initial oxidation and the final combina ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.