Student Academic Learning Services The Endocrine System Quiz
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
BIOL242pituitaryOCT2012
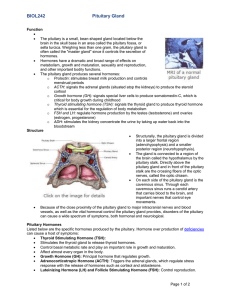
... Because of the close proximity of the pituitary gland to major intracranial nerves and blood vessels, as well as the vital hormonal control the pituitary gland provides, disorders of the pituitary can cause a wide spectrum of symptoms, both hormonal and neurological. Pituitary Hormones Listed belo ...
... Because of the close proximity of the pituitary gland to major intracranial nerves and blood vessels, as well as the vital hormonal control the pituitary gland provides, disorders of the pituitary can cause a wide spectrum of symptoms, both hormonal and neurological. Pituitary Hormones Listed belo ...
Chapter 20 - mwsu-wiki
... - composed of 2 lobes on either side of the trachea and inferior to the thyroid cartilage - joined by the isthmus - which crosses the anterior surface of the trachea and larynx at the cridoid cartilage - composed of follicles - follicular cells that surround a viscous substance called colloid - Acet ...
... - composed of 2 lobes on either side of the trachea and inferior to the thyroid cartilage - joined by the isthmus - which crosses the anterior surface of the trachea and larynx at the cridoid cartilage - composed of follicles - follicular cells that surround a viscous substance called colloid - Acet ...
Document
... body, stimulating actions in other endocrine glands The endocrine system is involved in the fight-or-flight response Too much stress may also suppress the process of neurogenesis in the hippocampus In times of stress, the hypothalamus sends signals along two pathways… the autonomic and through the p ...
... body, stimulating actions in other endocrine glands The endocrine system is involved in the fight-or-flight response Too much stress may also suppress the process of neurogenesis in the hippocampus In times of stress, the hypothalamus sends signals along two pathways… the autonomic and through the p ...
Lecture 046 - Animal Hormones
... conversion of Pfr Pr in dark inhibits response, & stimulates other responses: growth in height ...
... conversion of Pfr Pr in dark inhibits response, & stimulates other responses: growth in height ...
Endocrine System
... effects and targets: 1) amino acid uptake and protein synthesis are stimulated; 2) long bone extension (height growth) is stimulated indirectly, by stimulating the release of growth factors from the liver. Overproduction leads to giantism – height, but also pronounced brow ridges and other effects. ...
... effects and targets: 1) amino acid uptake and protein synthesis are stimulated; 2) long bone extension (height growth) is stimulated indirectly, by stimulating the release of growth factors from the liver. Overproduction leads to giantism – height, but also pronounced brow ridges and other effects. ...
Ch45endocrine
... Regulation by chemical messengers Neurotransmitters released by neurons Hormones release by endocrine glands endocrine gland ...
... Regulation by chemical messengers Neurotransmitters released by neurons Hormones release by endocrine glands endocrine gland ...
Jenny Yin Endocrine System Maintain homeostasis Local Hormones
... ● The Hypothalamus Controls the Secretions of the Pituitary Gland ● Hypothalamic Hormones Control the Anterior Pituitary ● The Anterior Pituitary Produces and Releases a Variety of Hormones ● The Posterior Pituitary Releases Hormones Produced by Cells in the Hypothalamus ● The Thyroid and Parathyroi ...
... ● The Hypothalamus Controls the Secretions of the Pituitary Gland ● Hypothalamic Hormones Control the Anterior Pituitary ● The Anterior Pituitary Produces and Releases a Variety of Hormones ● The Posterior Pituitary Releases Hormones Produced by Cells in the Hypothalamus ● The Thyroid and Parathyroi ...
Student Academic Learning Services The
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
... 6. Being lipid soluble, steroids can do all the following EXCEPT: A) B) C) D) ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... prostaglandins--steroids that are secreted by different parts of the body, act on cells close to them (local hormones) a. a. act by modifying effects of other hormones by inhibiting or stimulating formation of cAMP, not true hormones ...
... prostaglandins--steroids that are secreted by different parts of the body, act on cells close to them (local hormones) a. a. act by modifying effects of other hormones by inhibiting or stimulating formation of cAMP, not true hormones ...
EndocrineSystemQuiz
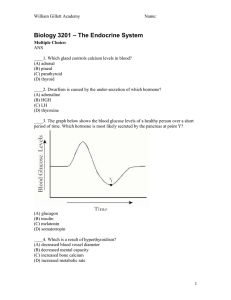
... (A) Decreases the activity of the thymus (B) Decreases the activity of the thyroid (C) Increases the activity of the thymus (D) Increases the activity of the thyroid ____19. How does insulin affect blood in a normal human body? (A) Decreases calcium levels (B) Decreases glucose levels (C) Increases ...
... (A) Decreases the activity of the thymus (B) Decreases the activity of the thyroid (C) Increases the activity of the thymus (D) Increases the activity of the thyroid ____19. How does insulin affect blood in a normal human body? (A) Decreases calcium levels (B) Decreases glucose levels (C) Increases ...
CASE 33
... portal system, one of only two portal systems in the body. Capillaries in the median eminence of the hypothalamus and in the infundibular stem converge to form portal vessels that travel to the anterior lobe, where they branch into a second set of capillaries that supply the anterior pituitary. Thus ...
... portal system, one of only two portal systems in the body. Capillaries in the median eminence of the hypothalamus and in the infundibular stem converge to form portal vessels that travel to the anterior lobe, where they branch into a second set of capillaries that supply the anterior pituitary. Thus ...
8.2 Major Endocrine Organs
... • adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH) - Tropin – release of steroid hormones from adrenal cortex ...
... • adrenocorticotropin hormone (ACTH) - Tropin – release of steroid hormones from adrenal cortex ...
Animal Hormones
... adrenal glands • located on top of kidneys • two parts • adrenal medulla –produces epinephrine & norepinephrine –derived from nervous tissue –under nervous system control –mediates the “fight-or-flight” response ...
... adrenal glands • located on top of kidneys • two parts • adrenal medulla –produces epinephrine & norepinephrine –derived from nervous tissue –under nervous system control –mediates the “fight-or-flight” response ...
Endocrine PP - Laura Banks
... • Luteinizing (LH)• Thyroid-stimulating (TSH)- stimulates the thyroid to release its hormones • Adrenocorticotrophic (ACTH)- stimulates the adrenal glands to release their hormones ...
... • Luteinizing (LH)• Thyroid-stimulating (TSH)- stimulates the thyroid to release its hormones • Adrenocorticotrophic (ACTH)- stimulates the adrenal glands to release their hormones ...
Hormonal
... Interact only with target cells – cells with receptors for the specific hormone Peptide Amino acids, peptides, proteins Steroid Derived from cholesterol; therefore are lipid soluble and can pass through the plasma membrane How Hormones Function Peptide Bind to receptors on the plasma membrane (cell ...
... Interact only with target cells – cells with receptors for the specific hormone Peptide Amino acids, peptides, proteins Steroid Derived from cholesterol; therefore are lipid soluble and can pass through the plasma membrane How Hormones Function Peptide Bind to receptors on the plasma membrane (cell ...
Printable - Georgia CTAE | Home
... characterized by extreme weakness, loss of weight, low blood pressure, gastrointestinal disturbances, and brownish pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes ...
... characterized by extreme weakness, loss of weight, low blood pressure, gastrointestinal disturbances, and brownish pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes ...
Ch 45: Chemical Signals in Animals / Endocrine System
... environment at a constant level (or between narrow limits), including: -blood pH -oxygen / CO2 levels -blood glucose -body temperature -water balance ...
... environment at a constant level (or between narrow limits), including: -blood pH -oxygen / CO2 levels -blood glucose -body temperature -water balance ...
Ch 45: Chemical Signals in Animals / Endocrine System
... environment at a constant level (or between narrow limits), including: -blood pH -oxygen / CO2 levels -blood glucose -body temperature -water balance ...
... environment at a constant level (or between narrow limits), including: -blood pH -oxygen / CO2 levels -blood glucose -body temperature -water balance ...
Chapter 41 Endocrine System
... 1. Human growth hormone (hGH) stimulates body growth by promoting cell division, protein synthesis, and bone growth. Disorders associated with improper levels of hGH are pituitary dwarfism, giantism, and acromegaly. 2. Lactogenic hormone (LTH) or Prolactin (PRL) causes the mammary glands to produce ...
... 1. Human growth hormone (hGH) stimulates body growth by promoting cell division, protein synthesis, and bone growth. Disorders associated with improper levels of hGH are pituitary dwarfism, giantism, and acromegaly. 2. Lactogenic hormone (LTH) or Prolactin (PRL) causes the mammary glands to produce ...
Structure of the Brain
... - Tegmentum (includes the root of the 3rd and 4th cranial nerves, contains part of the reticular formation. It serves as a go between for the forebrain and hindbrain) - Substancia nigra ( gives rise to dopamine containing path) - Superior and inferior colliculus (important routes for sensory informa ...
... - Tegmentum (includes the root of the 3rd and 4th cranial nerves, contains part of the reticular formation. It serves as a go between for the forebrain and hindbrain) - Substancia nigra ( gives rise to dopamine containing path) - Superior and inferior colliculus (important routes for sensory informa ...
Use the completed feedback mechanism to answer the
... f. If someone does not respond to insulin what can they do to ensure that their blood sugar does not get too high? g. If someone does not produce insulin what can they do to ensure that their blood sugar does not get too high? h. Think evolutionarily, why does your body work to store sugar at the po ...
... f. If someone does not respond to insulin what can they do to ensure that their blood sugar does not get too high? g. If someone does not produce insulin what can they do to ensure that their blood sugar does not get too high? h. Think evolutionarily, why does your body work to store sugar at the po ...
Negative Feedback Regulation of Hypothalamus and
... It is intended for students that are taking the first year of human anatomy and physiology. Most students should be able to complete the module within 30 minutes if they have had prior exposure to the material. Part One is a learning activity intended to check student understanding of the negative f ...
... It is intended for students that are taking the first year of human anatomy and physiology. Most students should be able to complete the module within 30 minutes if they have had prior exposure to the material. Part One is a learning activity intended to check student understanding of the negative f ...
Hormones Endocrine System Function Endocrine Systems
... – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
... – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
... – Principally involved in regeneration, growth, development, and reproduction – Little homeostatic function ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.