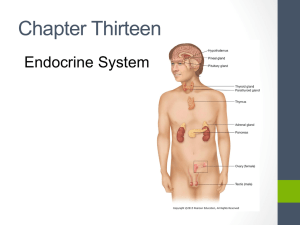
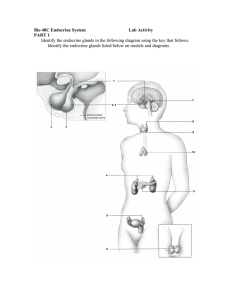
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
Biological Psychology
... appropriate area of the cerebral cortex. B. The Limbic System: involved in motivated behaviors, emotional states, memory, body temperature, & blood pressure. 1) Hypothalamus: helps to regulate emotional and motivated behavior and maintain homeostasis (the body’s internal equilibrium). 2) Amygdala: r ...
... appropriate area of the cerebral cortex. B. The Limbic System: involved in motivated behaviors, emotional states, memory, body temperature, & blood pressure. 1) Hypothalamus: helps to regulate emotional and motivated behavior and maintain homeostasis (the body’s internal equilibrium). 2) Amygdala: r ...
Pathways Handout
... result will be a building process that culminates in an "explosion" or event. It is only after the event occurs that the system ceases. In this case, the initial stretching of the cervix causes local stretch receptors to send an impulse to the hypothalamus where neurosecretory cells will secrete oxy ...
... result will be a building process that culminates in an "explosion" or event. It is only after the event occurs that the system ceases. In this case, the initial stretching of the cervix causes local stretch receptors to send an impulse to the hypothalamus where neurosecretory cells will secrete oxy ...
Endocrine System - East Porter County School Corporation
... Your endocrine system regulates your growth, development, and body chemistry. ...
... Your endocrine system regulates your growth, development, and body chemistry. ...
endocrine system - Living Bhakti Studies
... collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate your body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and transported to the tissues and organs throughout your body. The endocrine glands secrete hormones internally, using the bloodstream. ...
... collection of glands that produce hormones that regulate your body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and transported to the tissues and organs throughout your body. The endocrine glands secrete hormones internally, using the bloodstream. ...
Comparison of coordination by hormones and the nervous system
... Achieved by: The endocrine system. Hormones secreted by endocrine glands carried in the bloodstream to particular target organs whose cells have hormone-specific receptors in their membranes e.g. • adrenal glands/adrenaline, • pancreas/insulin • thyroid gland/thyroxine • pituitary gland/ADH • kidne ...
... Achieved by: The endocrine system. Hormones secreted by endocrine glands carried in the bloodstream to particular target organs whose cells have hormone-specific receptors in their membranes e.g. • adrenal glands/adrenaline, • pancreas/insulin • thyroid gland/thyroxine • pituitary gland/ADH • kidne ...
Blood Glucose
... of normal blood level by using glucose for their energy requirement after ingestion and absorption of carbohydrates 60 % of absorbed glucose is transported to the liver. ...
... of normal blood level by using glucose for their energy requirement after ingestion and absorption of carbohydrates 60 % of absorbed glucose is transported to the liver. ...
11 - Pegasus @ UCF
... The Endocrine System The endocrine system is concerned with the control of the various metabolic functions of the body. It controls the rates of chemical reactions in the cells, and other aspects of cellular metabolism such as growth and secretion. ...
... The Endocrine System The endocrine system is concerned with the control of the various metabolic functions of the body. It controls the rates of chemical reactions in the cells, and other aspects of cellular metabolism such as growth and secretion. ...
FILL IN THE BLANKS: ENDOCRINE HORMONES (Student Copy
... normal effects, may be caused by adrenal medulla tumor called Pheochromocyto ma ...
... normal effects, may be caused by adrenal medulla tumor called Pheochromocyto ma ...
File
... the stimulus, which then leads to a reduction in hormone secretion. • This process is called a negative feedback homeostatic control system to keep hormones at normal levels. (if levels increased it would be called positive feedback) ...
... the stimulus, which then leads to a reduction in hormone secretion. • This process is called a negative feedback homeostatic control system to keep hormones at normal levels. (if levels increased it would be called positive feedback) ...
File
... The organs of the body communicate with each other through the nervous and endocrine systems to coordinate their activities. The nervous system uses neurotransmitters and neurons to convey information to and from the brain. In contrast, the endocrine system uses hormones, which are chemical messenge ...
... The organs of the body communicate with each other through the nervous and endocrine systems to coordinate their activities. The nervous system uses neurotransmitters and neurons to convey information to and from the brain. In contrast, the endocrine system uses hormones, which are chemical messenge ...
Chapter 3: The Biological Bases of Behavior
... human stress response Gonads—hormones regulate sexual characteristics and reproductive processes; testes in males, ovaries in ...
... human stress response Gonads—hormones regulate sexual characteristics and reproductive processes; testes in males, ovaries in ...
Disorders of the Endocrine System
... Low blood sugar, which can cause anxiety, tremors, weakness, and even unconsciousness and death. Hypothyroidism Undersecretion of thyroxine, resulting in a very low metabolic rate and sluggish activity, sometimes accompanied by obesity. Myxedema Accumulation of water in skin resulting from thyroid h ...
... Low blood sugar, which can cause anxiety, tremors, weakness, and even unconsciousness and death. Hypothyroidism Undersecretion of thyroxine, resulting in a very low metabolic rate and sluggish activity, sometimes accompanied by obesity. Myxedema Accumulation of water in skin resulting from thyroid h ...
Unit 10: Feedback Loops
... 5. Pituitary Gland secretes (TSH) Thyroxine Secreting Hormone 6. TSH is sent to Thyroid 7. Thyroid secretes Thyroxine into blood which then spreads through body 8. Thyroxine levels increase in the body and Metabolism increases. Body BODY sends a “ok” signal to the Hypothalamus. Normal Levels 9. Home ...
... 5. Pituitary Gland secretes (TSH) Thyroxine Secreting Hormone 6. TSH is sent to Thyroid 7. Thyroid secretes Thyroxine into blood which then spreads through body 8. Thyroxine levels increase in the body and Metabolism increases. Body BODY sends a “ok” signal to the Hypothalamus. Normal Levels 9. Home ...
Endocrine System Review
... Endocrine System Control Feedback Regulation of Blood Sugar islets of Langerhans ...
... Endocrine System Control Feedback Regulation of Blood Sugar islets of Langerhans ...
Human Endocrine System
... least 208 cm (6 feet 10 in) tall and believed by many to have been over 213 cm (7 feet) at his tallest. His great size was a result of excessive growth hormone, a condition known as pituitary gigantism, and led to him being dubbed "The Eighth Wonder of the World[1][2]." ...
... least 208 cm (6 feet 10 in) tall and believed by many to have been over 213 cm (7 feet) at his tallest. His great size was a result of excessive growth hormone, a condition known as pituitary gigantism, and led to him being dubbed "The Eighth Wonder of the World[1][2]." ...
NAME:
... ___ 9. Groups of cells within this gland secrete hormones that maintain normal levels of simple and complex carbohydrates in the body. 1.) adrenal 2.) pancreas 3.) hypothalamus 4.) thyroid ...
... ___ 9. Groups of cells within this gland secrete hormones that maintain normal levels of simple and complex carbohydrates in the body. 1.) adrenal 2.) pancreas 3.) hypothalamus 4.) thyroid ...
File
... • Growth and development • Homeostasis (the internal balance of body systems) • Metabolism (body energy levels) • Reproduction • Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) ...
... • Growth and development • Homeostasis (the internal balance of body systems) • Metabolism (body energy levels) • Reproduction • Response to stimuli (stress and/or injury) ...
File - Endocrine System
... _____ pituitary gland (pi-TOO-i-tar-ē) (also called the hypophysis) (Located on the inferior side of the brain in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. The pituitary stalk attaches the gland to the hypothalamus portion of the brain. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior lobe (the adenohy ...
... _____ pituitary gland (pi-TOO-i-tar-ē) (also called the hypophysis) (Located on the inferior side of the brain in the sella turcica of the sphenoid bone. The pituitary stalk attaches the gland to the hypothalamus portion of the brain. The pituitary gland is divided into an anterior lobe (the adenohy ...
Chapter 39 - Midway ISD
... Attached to thyroid, maintain homeostasis and calcium levels in blood Ex: if blood calcium levels are high, releases calcitonin to reduce calcium absorption; if levels are low, releases PTH to increase absorption of calcium ...
... Attached to thyroid, maintain homeostasis and calcium levels in blood Ex: if blood calcium levels are high, releases calcitonin to reduce calcium absorption; if levels are low, releases PTH to increase absorption of calcium ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.