* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ENDOCRINE GLANDS
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
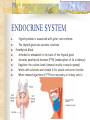
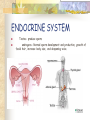
ENDOCRINE GLANDS Endocrine glands secrete hormones into the bloodstream. Hormones are chemical messengers traveling through the bloodstream Target cells: Bodies response to hormones are slower and longer lasting Glands: (fig. 42-3) organ that produces a secretion and released from that cell Endocrine glands: Produce secretions and release directly Exocrine glands: Release secretions through ducts: sweat glands THYROID GLAND (see fig. 42-5) Wraps around the upper part of the trachea just below the larynx Produces the hormone, thyroxine; need iodine in your diets affects most cells of the body by regulating metabolic rates Hyperthyroidism: too much thyroxine is produced Hypothyroidism: too little thyroxine is produced ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Hypothyroidism is associated with goiter and cretinism The thyroid gland also secretes calcitonin Parathyroid Gland Attached or embedded to the back of the thyroid gland Secretes parathyroid hormone (PTH) (reabsorption of Ca in kidneys) Regulates the calcium levels (removal results in muscle spasms) Works with calcitonin and vitamin D for muscle and nerve function When removed injections of PTH are necessary or tetany sets in ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Adrenal Glands Sits on top of each kidney Adrenal Cortex: 80% mass of the gland corticosteroids: essential for normal body functions aldosterone- regulates reabsorption of Na and excretion of K cortisol- controls the rate of metabolism of carbos, lipids, and proteins, & helps us cope with stress. Decreased activity results in Addison Disease weight loss, low blood pressure and possible death treatment: doses of adrenal cortical hormone Increased activity results in Cushing syndrome obesity, increase blood sugar, weakening bones ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Adrenal Medulla Produces neurohormones adrenaline- Increases heart rate, blood pressure, and blood to skeletal muscles. Increases conversion of glycogen to glucose and stimulates the rate of metabolism during stressful situations noradrenaline- stimulates the heart muscle These actions get us ready for fight or flight Reproductive Glands gonads- body’s reproductive glands ovaries- produces eggs estrogen- development of ova and physical characteristics such as reproductive system, widening hips, and breast development. progesterone- Prepares the uterus for the arriving embryo ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Testes- produce sperm androgens- Normal sperm development and production, growth of facial hair, increase body size, and deepening voice. ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pancreas Both an exocrine and endocrine gland islets of Langerhans Each islet is composed of beta cells that secrete insulin and alpha cells that secrete glucagon which regulate glucose level in the body Insulin: Results from glucose levels rising.Beta cells release insulin and target cells of the liver, muscles, & fat tissue. Glucagon: 1-2 hrs. after eating, blood glucose drops, alpha cells release glucagon. This stimulates cells to break down glycogen and increase glucose levels. Fat cells break down fats to be used to make carbohydrates Diabetes Mellitus: undersecretion of insulin (Fig. 42-9) Glucose in the blood is so high the kidneys can’t absorb all the glucose, so it is excreted it the urine. Two Types: Juvenile-onset (Type-I) & Adult-onset (Type-II) ENDOCRINE SYSTEM ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pituitary Gland & Hypothalamus Why known as the Master Gland? Place where nervous system and endocrine interact Secretes 9 hormones that directly regulate body functions Controls the release of hormones by several other glands Divided into two parts: anterior and posterior pituitary Posterior: secretes antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and oxytocin ADH-reabsorb water from kidneys Oxytocin- contraction of uterus, release of breast milk In males ????????????????? Anterior: follicle stimulating and luteinizing hormones control the growth, development and functioning of ovaries and testes thyroid stimulating, adrenocorticotropic, growth (somatatropin,) melancocyte-stimulating prolactin, & (SEE FIG. 42-11) ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Pituitary Gland Disorders; giantism, & dwarfism acromegaly: no height increase due to bones ossifying; but diameter of toes and fingers increases, enlarged jaw treatment: surgery, radiation, &/or hormone therapy treatment: surgery, radiation, or hormone therapy Hypothalamus: Attached to the posterior pituitary controls secretions of the pituitary, influenced by levels of hormones in the blood. Neurosecretory cells extend axons into posterior pituitary vesicles release contents (ADH & oxytocin) so it controls the posterior pituitary & the activity of the body Produces releasing hormones which are secreted directly into capillaries and then into veins, and more capillaries. It enters the anterior pituitary, affecting the production of pituitary hormones.