HYPOPHYSIS (PITUITARY GLAND)
... 2.Visceras- in hypophysectomised animal the liver cells and reduced in size with impared functions. 3. It stimulates the growth of thymus. 4. Increases secretion of milk during lactation. 5. Nervous system is not affected by STH. Metabolism – a. on protein metabolism:- it increases the neuclic acid ...
... 2.Visceras- in hypophysectomised animal the liver cells and reduced in size with impared functions. 3. It stimulates the growth of thymus. 4. Increases secretion of milk during lactation. 5. Nervous system is not affected by STH. Metabolism – a. on protein metabolism:- it increases the neuclic acid ...
Slide 1
... cells – Targets milk-producing glands in the breast stimulates milk production after childbirth & during lactation – There are prolactin-secreting tumors that result in milk production in both women & men (galactorrhea; can lead to problems with fertility) ...
... cells – Targets milk-producing glands in the breast stimulates milk production after childbirth & during lactation – There are prolactin-secreting tumors that result in milk production in both women & men (galactorrhea; can lead to problems with fertility) ...
Preclinical studies suggest that sexual steroids
... Project Title: Studies of the effects of androgens on serotonergic neurons Preclinical studies suggest that sexual steroids influence brain serotonergic transmission, and that an important physiological role of brain serotonin neurons is to modulate sex steroid-driven behaviour, such as aggression a ...
... Project Title: Studies of the effects of androgens on serotonergic neurons Preclinical studies suggest that sexual steroids influence brain serotonergic transmission, and that an important physiological role of brain serotonin neurons is to modulate sex steroid-driven behaviour, such as aggression a ...
Chapter 32: Chemical Control of the Animal Body: The Endocrine
... c. a chemical is called a hormone on the basis of the kind of function it performs, but hormone molecules assume a wide variety of forms of 4 general types 1. Peptide hormones – Most animal hormones are composed of peptides, which are chains of amino acids. The term peptide technically refers to sho ...
... c. a chemical is called a hormone on the basis of the kind of function it performs, but hormone molecules assume a wide variety of forms of 4 general types 1. Peptide hormones – Most animal hormones are composed of peptides, which are chains of amino acids. The term peptide technically refers to sho ...
Owl 1038-1041 Questions
... 3. Why are Glucagon and Insulin considered antagonistic hormones? (refer to the diagram at bottom of 1038 if you need to) 4. Read the short definition of Negative and Positive Feedback, then make a “Diagram Definition” of each, but simply creating a diagram with the words used in the definitions. 5. ...
... 3. Why are Glucagon and Insulin considered antagonistic hormones? (refer to the diagram at bottom of 1038 if you need to) 4. Read the short definition of Negative and Positive Feedback, then make a “Diagram Definition” of each, but simply creating a diagram with the words used in the definitions. 5. ...
TAKE HOME EXAM –URINARY SYSTEM REPRODUCTIVE
... Fill in the blank-with the correct answer. 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as _______________ ...
... Fill in the blank-with the correct answer. 1. The _______________ gland is located in the brain and is often called the Master Gland. 2. Melatonin is a hormone that is secreted by the _________________ gland. 3. The hormones epinephrine and norepinephrine are sometimes referred to as _______________ ...
05 Endocrine System note
... a collection of glands that release hormones into the blood stream hormones are classified according to their activation site. Some affect many cells throughout the body (i.e. growth hormone, insulin, epinephrine (adrenaline)) and others target specific cells or tissues (i.e. parathyroid, gast ...
... a collection of glands that release hormones into the blood stream hormones are classified according to their activation site. Some affect many cells throughout the body (i.e. growth hormone, insulin, epinephrine (adrenaline)) and others target specific cells or tissues (i.e. parathyroid, gast ...
Ch. 45 - Ltcconline.net
... endocrine system glands and their actions B. Hypothalamus connects nervous and endocrine systems C. Hypothalamus and pituitary have multiple endocrine functions 1. hypothalamus exerts master control over endocrine system, serves as feedback center 2. uses pituitary to relay directives to other gland ...
... endocrine system glands and their actions B. Hypothalamus connects nervous and endocrine systems C. Hypothalamus and pituitary have multiple endocrine functions 1. hypothalamus exerts master control over endocrine system, serves as feedback center 2. uses pituitary to relay directives to other gland ...
NVCC Bio 212 - gserianne.com
... Other Endocrine Glands • Adipose Tissue – Leptin • After eating, adipose tissue absorbs glucose and lipids • Peptide hormone, leptin, is released • Binds to receptors in hypothalamus (esp. arcuate and paraventricular nuclei) ...
... Other Endocrine Glands • Adipose Tissue – Leptin • After eating, adipose tissue absorbs glucose and lipids • Peptide hormone, leptin, is released • Binds to receptors in hypothalamus (esp. arcuate and paraventricular nuclei) ...
The Endocrine System - An Overview
... The hormones produced by these glands travel to various organs, glands and tissues in the body and communicate with them. Once they have reached their particular organ or tissue they bind to specific proteins on the surface of the cell. These proteins are called receptors. When they have bound to t ...
... The hormones produced by these glands travel to various organs, glands and tissues in the body and communicate with them. Once they have reached their particular organ or tissue they bind to specific proteins on the surface of the cell. These proteins are called receptors. When they have bound to t ...
Medications Affecting the Endocrine System by Linda Self
... TRH, others TRH causes release of TSH GRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone) causes release of FSH and LH Prolactin-releasing factor active during lactation Prolactin inhibitory factor active at times other than lactation ...
... TRH, others TRH causes release of TSH GRH (gonadotropin releasing hormone) causes release of FSH and LH Prolactin-releasing factor active during lactation Prolactin inhibitory factor active at times other than lactation ...
The Endocrine System
... and pressure receptors in the cervix are again triggered.... see #2. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is born. --> When doctors induce labor, the woman receives several doses of a synthetic oxytocin to get the positive feedback loop of labor ...
... and pressure receptors in the cervix are again triggered.... see #2. This positive feedback loop continues until the baby is born. --> When doctors induce labor, the woman receives several doses of a synthetic oxytocin to get the positive feedback loop of labor ...
The Endocrine System - An Overview
... The endocrine system is a collection of glands that produce hormones (chemical messengers). These hormones pass directly into the bloodstream to control metabolism, growth and sexual development. The endocrine system consists of the following glands: the hypothalamus the pituitary gland the pi ...
... The endocrine system is a collection of glands that produce hormones (chemical messengers). These hormones pass directly into the bloodstream to control metabolism, growth and sexual development. The endocrine system consists of the following glands: the hypothalamus the pituitary gland the pi ...
Steroid Hormones
... If there is no embryo the new outer layers disintegrate which causes blood flow ...
... If there is no embryo the new outer layers disintegrate which causes blood flow ...
Document
... T3 and T4 are synthesized in the thyroid gland. Inorganic iodine is trapped with great avidity by the gland, oxidized and attached to tyrosine. Combination of mono- and/ordi-iodinated tyrosine forms T3 and T4. The thyroxine peroxidase is important both in the initial oxidation and the final combina ...
... T3 and T4 are synthesized in the thyroid gland. Inorganic iodine is trapped with great avidity by the gland, oxidized and attached to tyrosine. Combination of mono- and/ordi-iodinated tyrosine forms T3 and T4. The thyroxine peroxidase is important both in the initial oxidation and the final combina ...
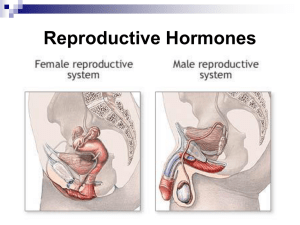
Female Reproductive System
... two hormones originating in the hypothalamus. The pituitary's target endocrine glands are the thyroid, adrenal gland, and the gonads. Through these glands it Controls on the development of sexual organs and Physical properties that distinguish men from women sound and body shape and size. ...
... two hormones originating in the hypothalamus. The pituitary's target endocrine glands are the thyroid, adrenal gland, and the gonads. Through these glands it Controls on the development of sexual organs and Physical properties that distinguish men from women sound and body shape and size. ...
Chapter 46
... • Second-messenger systems – Receptors are linked to a second-messengergenerating enzyme via membrane proteins called G proteins • G protein–coupled receptors (GPCR) ...
... • Second-messenger systems – Receptors are linked to a second-messengergenerating enzyme via membrane proteins called G proteins • G protein–coupled receptors (GPCR) ...
Thyroid and its Hormones The normal adults thyroid gland weight
... ACTH is one of the pituitary hormones secreted as a large precursor molecular which is cleaved to give several peptides each with important biological effect . The precursor or polypeptides is known as pro-opio melanocortin (POMC) . The secretion of POMC is under the control of CRF . The active ACTH ...
... ACTH is one of the pituitary hormones secreted as a large precursor molecular which is cleaved to give several peptides each with important biological effect . The precursor or polypeptides is known as pro-opio melanocortin (POMC) . The secretion of POMC is under the control of CRF . The active ACTH ...
Endocrine System - TAFE SWSi Moodle
... Each target cell responds to hormone differently Liver cells: insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis Adipose: insulin stimulates triglyceride synthesis ...
... Each target cell responds to hormone differently Liver cells: insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis Adipose: insulin stimulates triglyceride synthesis ...
Abstract
... very intriguing physiological phenomenon. We fall asleep at least once per day. After sleeping for a while, we can wake up naturally. However, the mechanism regulating sleep/wakefulness cycle has not been completely understood so far, while it appears to be regulated by neurons in the hypothalamus. ...
... very intriguing physiological phenomenon. We fall asleep at least once per day. After sleeping for a while, we can wake up naturally. However, the mechanism regulating sleep/wakefulness cycle has not been completely understood so far, while it appears to be regulated by neurons in the hypothalamus. ...
The Endocrine System – Chapter 9 Notes Second messenger
... __________ – outer glandular region in three layers __________ – inner neural tissue region Sits on top of the ________________ Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex (Fig 9.10) Mineralocorticoids (mainly ______________________) Produced in outer adrenal cortex Regulate mineral content in blood; ...
... __________ – outer glandular region in three layers __________ – inner neural tissue region Sits on top of the ________________ Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex (Fig 9.10) Mineralocorticoids (mainly ______________________) Produced in outer adrenal cortex Regulate mineral content in blood; ...
A. Nervous Multiple Choice 1. Lipofuscin A. Increases in
... A. Kidney stone formation B. Excess sodium retention C. Soft, fragile bones D. Increased heat production E. Increased blood calcium level F. Increased blood glucose levels I. Endocrine T/F _____ 1. The hypodermis has endocrine functions _____ 2. The posterior lobe does not synthesize oxytocin _____ ...
... A. Kidney stone formation B. Excess sodium retention C. Soft, fragile bones D. Increased heat production E. Increased blood calcium level F. Increased blood glucose levels I. Endocrine T/F _____ 1. The hypodermis has endocrine functions _____ 2. The posterior lobe does not synthesize oxytocin _____ ...
The PowerPoint - helpmemrr.com
... bacteria and cancer cells. And when secreted by endothelial cells, it dilates the walls of blood vessels. ...
... bacteria and cancer cells. And when secreted by endothelial cells, it dilates the walls of blood vessels. ...
Lewy Body Diseases
... synaptic protein, found at presynaptic terminal sits in cytosol, transiently binds to cell memb and other synaptic proteins role in synaptic transport, synaptic change, learning aggregation may cause neuronal dysfunction potential disease marker lewy body distribution can occur in - subs ...
... synaptic protein, found at presynaptic terminal sits in cytosol, transiently binds to cell memb and other synaptic proteins role in synaptic transport, synaptic change, learning aggregation may cause neuronal dysfunction potential disease marker lewy body distribution can occur in - subs ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.