Chapter 45 Objective Questions
... 15. Distinguish between alpha and beta cells in the pancreas and explain how their antagonistic hormones (insulin and glucagon) regulate carbohydrate metabolism. 16. Distinguish between type I diabetes mellitus and type II diabetes mellitus. 17. Describe the development of the adrenal medulla. List ...
... 15. Distinguish between alpha and beta cells in the pancreas and explain how their antagonistic hormones (insulin and glucagon) regulate carbohydrate metabolism. 16. Distinguish between type I diabetes mellitus and type II diabetes mellitus. 17. Describe the development of the adrenal medulla. List ...
Chapter 45 - Madeira City Schools
... Which one is fat soluble? How do you know? What is an example? ...
... Which one is fat soluble? How do you know? What is an example? ...
body system 2 hormones
... The hormone system functions best when it has abundant supplies of minerals, which are available directly from sunlight or found in nutrient and enzyme rich foods. Brain hormone producing glands need selenium, thyroid needs iodine, mammary glands need iron, kidneys need zinc, pancreas needs chromium ...
... The hormone system functions best when it has abundant supplies of minerals, which are available directly from sunlight or found in nutrient and enzyme rich foods. Brain hormone producing glands need selenium, thyroid needs iodine, mammary glands need iron, kidneys need zinc, pancreas needs chromium ...
Chapter 26 Hormones and the Endocrine System
... - responds by sending out appropriate nervous or endocrine signals. - uses the pituitary gland to exert master control over the endocrine system. The pituitary gland consists of two parts. ...
... - responds by sending out appropriate nervous or endocrine signals. - uses the pituitary gland to exert master control over the endocrine system. The pituitary gland consists of two parts. ...
Introduction To Endocrinology: The Hypothalamic
... Greek origin and classically refers to chemical messengers that circulate in body fluids and produce specific effects on cells distant from their point of origin. The major functions of hormones include the regulation of energy storage, production, and utilization; the adaptation to new environments ...
... Greek origin and classically refers to chemical messengers that circulate in body fluids and produce specific effects on cells distant from their point of origin. The major functions of hormones include the regulation of energy storage, production, and utilization; the adaptation to new environments ...
Circulatory System Directs blood from the heart to the rest of the
... throughout the body Protein Hormones Circulate through blood; bind to specific receptor on cell membrane This binding turns on an enzyme (called the 1st messenger) that makes cAMP (2nd messenger) cAMP then activates other enzymes in the cell Steroid Hormones Steroid is small enough to penetrate plas ...
... throughout the body Protein Hormones Circulate through blood; bind to specific receptor on cell membrane This binding turns on an enzyme (called the 1st messenger) that makes cAMP (2nd messenger) cAMP then activates other enzymes in the cell Steroid Hormones Steroid is small enough to penetrate plas ...
No Slide Title
... • Adult human these cells fuse with anterior lobe • Produce POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) which is processed into ACTH and endorphins ...
... • Adult human these cells fuse with anterior lobe • Produce POMC (pro-opiomelanocortin) which is processed into ACTH and endorphins ...
Sensory Neurons
... Adrenal glands (adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla) – the adrenal medulla, the inner part of the adrenal gland, releases stress hormones, epinephrine/adrenaline – in response to short-term stress. ...
... Adrenal glands (adrenal cortex and the adrenal medulla) – the adrenal medulla, the inner part of the adrenal gland, releases stress hormones, epinephrine/adrenaline – in response to short-term stress. ...
Unit Test Neuro: Core ( Topic 6.5) and Options E ( Topics 1,2,4) HL
... Explain how animal experiments, lesions and FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanning can be used in the identification of the brain part involved in specific functions. (3) ...
... Explain how animal experiments, lesions and FMRI (functional magnetic resonance imaging) scanning can be used in the identification of the brain part involved in specific functions. (3) ...
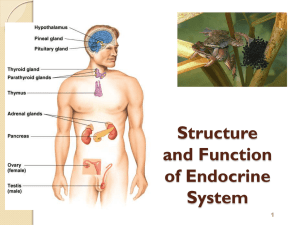
Endocrine System
... Female Reproductive System • The main function of the female reproductive system is to produce ova & prepare the female’s body to nourish a ...
... Female Reproductive System • The main function of the female reproductive system is to produce ova & prepare the female’s body to nourish a ...
Endocrine System Vocabulary Acromegaly Adrenal Glands
... 25.Prostaglandins: a third type of chemical classification of local hormones that are made from highly active lipids found in nearly all cell membranes. They respond & stimulation smooth muscles of arterioles or uterus; increase HCl & pepsin secretion by stomach; cause platelet aggregation; cause co ...
... 25.Prostaglandins: a third type of chemical classification of local hormones that are made from highly active lipids found in nearly all cell membranes. They respond & stimulation smooth muscles of arterioles or uterus; increase HCl & pepsin secretion by stomach; cause platelet aggregation; cause co ...
Human Reproduction
... Purpose of Sex Hormones: – Send messages between the brain and the genital organs to either begin or continue development or to prepare for reproduction. ...
... Purpose of Sex Hormones: – Send messages between the brain and the genital organs to either begin or continue development or to prepare for reproduction. ...
Name_____________________________________________
... Goiter: enlargement of the thyroid gland, associated with iodine deficiency in the diet. Diabetes: inability to store excess glucose as glycogen. Type 1 Diabetes: insulin deficiency results in high blood sugar levels. Type 2 Diabetes: lack of insulin receptors on the cells of the liver cause an inab ...
... Goiter: enlargement of the thyroid gland, associated with iodine deficiency in the diet. Diabetes: inability to store excess glucose as glycogen. Type 1 Diabetes: insulin deficiency results in high blood sugar levels. Type 2 Diabetes: lack of insulin receptors on the cells of the liver cause an inab ...
Chemistry Problem Solving Drill
... blood compositions, no matter what the conditions are outside of the body. The hypothalamus regulates these levels in response to a changing external environment through a regulatory process known as homeostasis, or the maintenance of the body‟s internal environment. The hypothalamus contains temper ...
... blood compositions, no matter what the conditions are outside of the body. The hypothalamus regulates these levels in response to a changing external environment through a regulatory process known as homeostasis, or the maintenance of the body‟s internal environment. The hypothalamus contains temper ...
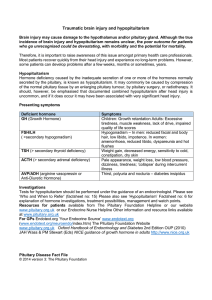
traumatic brain injury hypopituitarism booklet
... incidence of brain injury and hypopituitarism remains unclear, the poor outcome for patients who go unrecognised could be devastating, with morbidity and the potential for mortality. Therefore, it is important to raise awareness of this issue amongst primary health care professionals. Most patients ...
... incidence of brain injury and hypopituitarism remains unclear, the poor outcome for patients who go unrecognised could be devastating, with morbidity and the potential for mortality. Therefore, it is important to raise awareness of this issue amongst primary health care professionals. Most patients ...
ADENOHYPOPHYSIAL HORMONES
... Corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) ===> corticotrophin or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) ===> cortisol, aldosterone - cortisol in inhibits protein synthesis, stimulates gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from proteins), inhibits conversion of carbohydrates to fats - aldosterone regulates ...
... Corticotrophin releasing factor (CRF) ===> corticotrophin or adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) ===> cortisol, aldosterone - cortisol in inhibits protein synthesis, stimulates gluconeogenesis (synthesis of glucose from proteins), inhibits conversion of carbohydrates to fats - aldosterone regulates ...
Endocrine System
... A biochemical pathway where the products of the reaction inhibit production of the enzyme that ...
... A biochemical pathway where the products of the reaction inhibit production of the enzyme that ...
The Endocrine System - bananateachersworld
... endocrine gland because it releases hormones that regulate pituitary hormones •Hormones released have either a releasing or an ...
... endocrine gland because it releases hormones that regulate pituitary hormones •Hormones released have either a releasing or an ...
Human Anatomy & Physiology
... – alpha cells produce glucagon » it raises blood sugar by increasing liver glycogenolysis – beta cells produce insulin » it lowers blood sugar by escorting glucose into the cells – lack or improper response to insulin gives diabetes mellitus ...
... – alpha cells produce glucagon » it raises blood sugar by increasing liver glycogenolysis – beta cells produce insulin » it lowers blood sugar by escorting glucose into the cells – lack or improper response to insulin gives diabetes mellitus ...
Biochemistry, Secretion, and Transport of Hormones
... Besides increased levels of plasma glucose and amino acids (humoral regulation), increased levels of _______ (hormone) and stimulation of the __________ nervous system also increase plasma insulin levels. ...
... Besides increased levels of plasma glucose and amino acids (humoral regulation), increased levels of _______ (hormone) and stimulation of the __________ nervous system also increase plasma insulin levels. ...
The Endocrine System
... excreted in urine and serves to maintain blood volume and pressure. Secretes hormones that aid metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. ...
... excreted in urine and serves to maintain blood volume and pressure. Secretes hormones that aid metabolism of fats, proteins, and carbohydrates. ...
BIOL 104 Test 3 11/1/11 Name .£#`1 C. I i () ./The central nervous
... i. Which of the following is not involved in blood calcium homeostasis? bones thyroid gland parathyroid glands kidneys )posterior pituitary (Which of the following does not act to increase the amount of calcium in the blood? · bones · kidneys 1intestines ...
... i. Which of the following is not involved in blood calcium homeostasis? bones thyroid gland parathyroid glands kidneys )posterior pituitary (Which of the following does not act to increase the amount of calcium in the blood? · bones · kidneys 1intestines ...
Endocrine System
... Hormones are chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands that are secreted in the bloodstream. Hormones affect the brain and many other tissues of the body. ...
... Hormones are chemicals synthesized by the endocrine glands that are secreted in the bloodstream. Hormones affect the brain and many other tissues of the body. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.