* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hormonal Control of Growth in Animals
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Adrenal gland wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
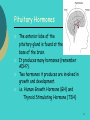
Higher Biology Hormonal Control of Growth in Animals Hormonal Control of Growth By the end of this lesson you should be able to: Know what a hormone is. Know the names of 2 hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland. Describe the role of thyroxine. 2 Introduction Hormones are chemical messengers. They are produced in one part of the body (in tiny quantities) and carried in the blood to another part of the body where they have their effect. Gland produces hormone Hormone carried in blood Hormone affects target organ 3 Pituitary Hormones The anterior lobe of the pituitary gland is found at the base of the brain. It produces many hormones (remember ADH?). Two hormones it produces are involved in growth and development. i.e. Human Growth Hormone (GH) and Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) 4 Human Growth Hormone (GH) Also known as somatotrophin Is produced by the anterior pituitary gland Travels in the blood Target organs- bones (particularly the long bones in the arms and legs) and cartilage Effects- accelerates amino acid transport into bones and cartilage. Permits rapid synthesis of tissue proteins 5 Human Growth Hormone (GH) So causes growth. The growth spurt in adolescence is due to increased production of GH. Human GH animation Underproduction Overproduction Reduction in overall growth In adolescence- very long bones in arms & legs. In adulthood- large hand, feet & jaw bones 6 Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) Is produced by the anterior pituitary gland Travels in the blood Target organs- thyroid gland (in the neck) Effects- controls growth and activity of the thyroid gland & produces thyroxine (another hormone!) Thyroxine regulates metabolic processes in the body. drop in metabolic rate Lack of TSH lack of thyroxine 7 TSH and Thyroxine Put the following stages into the correct order: Increases Thyroid Pituitary metabolic gland gland rate thyroxine TSH TSH Pituitary gland thyroxine Increases metabolic rate Thyroid gland 8 Pituitary Hormones Insert and complete the “Endocrine Summary” diagram from your pack into your notes. 9 Practice Questions 1. Torrance TYK pages 249 Q1 and 2 10 Hormonal Control of Growth Can you do it? Know what a hormone is. Know the names of 2 hormones produced by the anterior pituitary gland. Describe the role of thyroxine. 11