endocrine system
... hypothalamus to control many body activities ◦ Link between the nervous and endocrine systems ...
... hypothalamus to control many body activities ◦ Link between the nervous and endocrine systems ...
1e InteractiveHormonePPT(Student-made)
... production goiter, pituitary. weight loss, (myxedema) & endemic anterior Rising (calorigenic effect); hypertension, muscle tissue goiter if iodine deficient; in TH levels provide negative indirectly involved in BP, children, Can exopthalmos, breasts in feedback.cretinism. Hypothalamic tissue growth, ...
... production goiter, pituitary. weight loss, (myxedema) & endemic anterior Rising (calorigenic effect); hypertension, muscle tissue goiter if iodine deficient; in TH levels provide negative indirectly involved in BP, children, Can exopthalmos, breasts in feedback.cretinism. Hypothalamic tissue growth, ...
Chapter 14
... cells that secrete erythropoietin, a hormone essential for production of red blood cells. Even the heart contains cells that produce atrial naturetic hormone, which is important in sodium and water balance. ...
... cells that secrete erythropoietin, a hormone essential for production of red blood cells. Even the heart contains cells that produce atrial naturetic hormone, which is important in sodium and water balance. ...
The Endocrine System - Austin Community College
... - Direct gene activation - steroid hormones diffuse into target cells to bind and activate a specific intracellular receptor. Hormone-receptor complex travels to the nucleus and binds a DNAassociated receptor protein prompting DNA transcription and protein synthesis The precise response depends on t ...
... - Direct gene activation - steroid hormones diffuse into target cells to bind and activate a specific intracellular receptor. Hormone-receptor complex travels to the nucleus and binds a DNAassociated receptor protein prompting DNA transcription and protein synthesis The precise response depends on t ...
analyze the nervous system and explain its structure and
... Why do protein hormones need to trigger a second messenger to activate a target cell? (A) They are not water soluble. (B) They bind to multiple types of cells. (C) They cannot cross cell membranes. (D) They require activation by ATP. – identify the following hormones, their source gland, and explain ...
... Why do protein hormones need to trigger a second messenger to activate a target cell? (A) They are not water soluble. (B) They bind to multiple types of cells. (C) They cannot cross cell membranes. (D) They require activation by ATP. – identify the following hormones, their source gland, and explain ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... cortex- = shell (adrenal cortex: the outer portion of an adrenal gland, controlled by ACTH from the anterior pituitary; secretes hormones called glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids) -cortico = the shell (corticosteroid: a steroid sex hormone secreted by the gonads that promotes the development a ...
... cortex- = shell (adrenal cortex: the outer portion of an adrenal gland, controlled by ACTH from the anterior pituitary; secretes hormones called glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids) -cortico = the shell (corticosteroid: a steroid sex hormone secreted by the gonads that promotes the development a ...
Endocrine System - University of Washington
... Bind to receptors in plasma membrane Cannot have direct effect on activities inside target cell Use intracellular intermediary to exert effects First messenger: leads to second messenger may act as enzyme activator, inhibitor, or cofactor results in change in rates of metabolic reactio ...
... Bind to receptors in plasma membrane Cannot have direct effect on activities inside target cell Use intracellular intermediary to exert effects First messenger: leads to second messenger may act as enzyme activator, inhibitor, or cofactor results in change in rates of metabolic reactio ...
File - E - Physiology
... Antidiuretic hormone, as the name indicates, prevents diuresis and is chiefly concerned with the conservation of body water. Since it also causes vasoconstriction, it is also called vasopressin or more precisely ...
... Antidiuretic hormone, as the name indicates, prevents diuresis and is chiefly concerned with the conservation of body water. Since it also causes vasoconstriction, it is also called vasopressin or more precisely ...
The Endocrine System
... job. Hormones are responsible for regulating your metabolism, mood, growth, and organ function. A part of your brain, called the hypothalamus, is critical to your endocrine system. It monitors you’re your body and sends information to your pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is attached to the hypo ...
... job. Hormones are responsible for regulating your metabolism, mood, growth, and organ function. A part of your brain, called the hypothalamus, is critical to your endocrine system. It monitors you’re your body and sends information to your pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is attached to the hypo ...
Endocrine ppt
... into the bloodstream, whereas other glands (exocrine glands) produce their chemicals and excrete them into a duct (ex. digestive enzymes, sweat). ...
... into the bloodstream, whereas other glands (exocrine glands) produce their chemicals and excrete them into a duct (ex. digestive enzymes, sweat). ...
Purpose of the Post - Workspace
... Molecular Endocrinology Group in the MRC Clinical Sciences Centre, also located at the Hammersmith Campus of Imperial College. Summary of project The physiological role of thyroid hormones in the regulation of appetite is poorly understood despite their critical importance in the control of metabol ...
... Molecular Endocrinology Group in the MRC Clinical Sciences Centre, also located at the Hammersmith Campus of Imperial College. Summary of project The physiological role of thyroid hormones in the regulation of appetite is poorly understood despite their critical importance in the control of metabol ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Basic pathways involved in the medullary control of blood pressure. The rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) is one of the major sources of excitatory input to sympathetic nerves controlling the vasculature. These neurons receive inhibitory input from the baroreceptors via an inhibitory neuron in th ...
... Basic pathways involved in the medullary control of blood pressure. The rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM) is one of the major sources of excitatory input to sympathetic nerves controlling the vasculature. These neurons receive inhibitory input from the baroreceptors via an inhibitory neuron in th ...
Endocrine-System-FERRIS3
... respond to hormones ◦ In order for cells to respond they must have the hormone receptor molecule Example: Oxytocin= released by the pituitary gland ◦ Acts on only 2 tissues, the breasts and uterus ◦ Only under certain conditions causes uterine contractions causes breast tissue to produce milk ...
... respond to hormones ◦ In order for cells to respond they must have the hormone receptor molecule Example: Oxytocin= released by the pituitary gland ◦ Acts on only 2 tissues, the breasts and uterus ◦ Only under certain conditions causes uterine contractions causes breast tissue to produce milk ...
Endocrine System
... Pituitary Gland Master Gland Has two Lobes-Anterior & Posterior 1. Tiny structure size of grape. 2. Located at base of the brain in the cranial cavity. 3. Connected to hypothalamus. 4. Divided into anterior and posterior lobes. ...
... Pituitary Gland Master Gland Has two Lobes-Anterior & Posterior 1. Tiny structure size of grape. 2. Located at base of the brain in the cranial cavity. 3. Connected to hypothalamus. 4. Divided into anterior and posterior lobes. ...
Regulation Review ppt
... indicate damage to which part? cerebrum e. What controls activities such as breathing and heart rate? medulla ...
... indicate damage to which part? cerebrum e. What controls activities such as breathing and heart rate? medulla ...
ch_16_lecture_outline_a
... hormones from the final target organs inhibit the release of the anterior pituitary hormones ...
... hormones from the final target organs inhibit the release of the anterior pituitary hormones ...
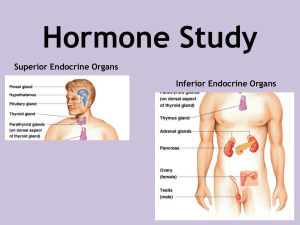
organs are part of the endocrine system?
... • Steroid hormones: diffuse through cell membrane to bind to a protein which starts transcription ...
... • Steroid hormones: diffuse through cell membrane to bind to a protein which starts transcription ...
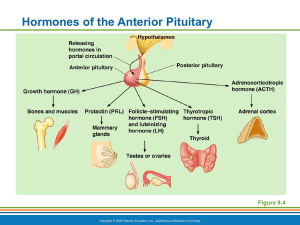
Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary 6 Anterior Pituitary Hormones
... Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes ...
... Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes ...
Chapter 18- The Endocrine System
... B) release oxytocin and ADH into the blood but does not produce them. C) regulates the posterior pituitary gland via releasing and inhibiting hormones. D) A and B are correct. E) A, B and C are correct. 24) The pituitary gland A) lies in the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone. B) consists of two lo ...
... B) release oxytocin and ADH into the blood but does not produce them. C) regulates the posterior pituitary gland via releasing and inhibiting hormones. D) A and B are correct. E) A, B and C are correct. 24) The pituitary gland A) lies in the cribiform plate of the ethmoid bone. B) consists of two lo ...
Cliff - USD Biology
... III. Stress stimulates an integrated Neuroendocrine response A. Regulating endocrine axis function 1. Specific brain regions input a. to Hypothalamus 2. Hypothalamic Neurohormone Regulation 3. Hypothalamic control of homeostasis ...
... III. Stress stimulates an integrated Neuroendocrine response A. Regulating endocrine axis function 1. Specific brain regions input a. to Hypothalamus 2. Hypothalamic Neurohormone Regulation 3. Hypothalamic control of homeostasis ...
Endocrine 1 PPT - My biology resource:free resources
... WHAT IS A HORMONE? An exocrine gland secretes fluids outside the body. An example would be saliva/sweat. An endocrine gland secretes fluids into the blood. A hormone is a chemical messenger which can bring about changes in target cells/tissues/organs. ...
... WHAT IS A HORMONE? An exocrine gland secretes fluids outside the body. An example would be saliva/sweat. An endocrine gland secretes fluids into the blood. A hormone is a chemical messenger which can bring about changes in target cells/tissues/organs. ...
Regulation - nervous and endocrine system
... – Cerebral Palsy – affect the ability to control body movements – Alzheimer’s – progressive degenerative disease; lose memory and ability to think, speak, etc. – Multiple Sclerosis – cells in the brain and spinal cord do not function normally. • Wide variety of symptoms ...
... – Cerebral Palsy – affect the ability to control body movements – Alzheimer’s – progressive degenerative disease; lose memory and ability to think, speak, etc. – Multiple Sclerosis – cells in the brain and spinal cord do not function normally. • Wide variety of symptoms ...
Biology 232
... neural stimuli –endocrine cell stimulated by a neuron (neuroglandular junction) humoral stimuli – endocrine cell stimulated by changes in composition of blood or interstitial fluid hormonal stimuli – presence or absence of another hormone stimulates endocrine cell negative feedback – most endocrine ...
... neural stimuli –endocrine cell stimulated by a neuron (neuroglandular junction) humoral stimuli – endocrine cell stimulated by changes in composition of blood or interstitial fluid hormonal stimuli – presence or absence of another hormone stimulates endocrine cell negative feedback – most endocrine ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.