* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
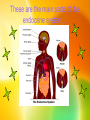
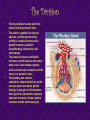
The Endocrine System Hormones Hormones!!! Even though the endocrine system doesn’t seem very important to us, it really is! It affects almost everything in our bodies, and participates in moods, growth and development, sexual functions, reproductive processes, tissue function, and metabolism. These are the main parts of the endocrine system… Hormones & Glands • The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands. • Hormones transfer info and orders from a set of cells to another. Each type of hormone is designed to affect only certain cells. • A gland is a bunch of cells that produce and gives off chemicals. A gland ‘selects and removes materials from the blood, processes them, and secretes the finished chemical product for use somewhere in the body.’ • For example, exocrine glands like the sweat glands release secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. Endocrine System Parts • • • • • • • Hypothalamus Pituitary Gland Thyroid Parathyroids Adrenal Glands Pineal Body Reproductive Glands Hypothalamus • • • In the lower central part of the brain The main link between the endocrine and the nervous systems. Nerve cells in the hypothalamus control the pituitary gland by producing chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary. Pituitary Gland • • • • • The gland is no bigger than a pea. Located at the base of the brain, and the most important part of the entire endocrine system. AKA: The master gland because it makes hormones that control other endocrine glands. The production of hormones and secretions can be affected by emotions and seasons change. Divided into two parts. The Division • • • • The tiny pituitary has two parts: the anterior and the posterior lobe. The anterior regulates the thyroid, adrenals, and the reproductive’s activities. It makes hormones like growth hormones, prolactin (breastfeeding), thyrotropin, and corticotropin. The posterior releases antiduretic hormones, which balances the body’s water level. It also makes oxytocin, which activates the contractions of the uterus in a woman in labor. The pituitary also secretes endorphins, chemicals that act on the nervous sytem and reduce painful feelings. It also gets rid of hormones that signal the reproductive organs to make sex hormones. It also controls ovulation and the menstrual cycle. • • • • • The thyroid is in the front part of the lower neck, and is shaped like a butterfly. It produces the hormones known as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. Thyroid hormones are important because they participate in the growth and development of kids’ and teens’ bones and the nervous system. Attached to the thryoid are four small glands called the parathyroids, which, with the help of calcitonin, control the calcium level. • • • • There are two adrenal glands, one on top of each kidney. There are two parts, each of which makes hormones and has a different function. The outer part, or the Arenal Cortex, makes hormones (corticosteroids) that control the salt and water balance in the body, responses to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. The inner part, or the Adrenal Medulla, makes hormones (catecholamines) that increases blood pressure and heart rate when there is stress. (ex. Epinephrine, or adrenaline) Adrenal Glands • The pineal gland, or the pineal body is in the middle of the brain. It secretes melatonin, a hormone that regulates when you sleep at night and wake up in the morning. Reproductive Glands!!! • The gonads are the main source of sex hormones. Even though you may think that gonads are just in guys, you’re wrong! Girls have them too… Male Gonads • In guys the male gonads, or testes are located in the scrotum. They secrete hormones called androgens, the most important of which is testosterone. These hormones tell a guy's body when it's time to make the changes associated with puberty, like penis and height growth, deepening voice, and growth in facial and pubic hair. Working with hormones from the pituitary gland, testosterone also • The ovaries are located in her pelvis. They produce eggs and secrete the female hormones estrogen and progesterone. Estrogen is involved when a girl begins to go through puberty. During puberty, a girl will experience breast growth, will begin to accumulate body fat around the hips and thighs, and will have a growth spurt. Estrogen and progesterone are also involved in the regulation of a girl's menstrual cycle. These hormones also play a role in pregnancy. Female Gonads What Does the Endocrine System Do? • • • Once a hormone is secreted, it travels from the endocrine gland that produced it through the bloodstream to the cells designed to receive its message. These cells are called target cells. Along the way to the target cells, special proteins bind to some of the hormones. These proteins act as carriers that control the amount of hormone that is available for the cells to use. The target cells have receptors that latch onto only specific hormones, and each hormone has its own receptor, so that each hormone will communicate only with specific target cells that have receptors for that hormone. When the hormone reaches its target cell, it locks onto the cell's specific receptors and these hormone-receptor combinations transmit chemical instructions to the inner workings of the cell. When hormone levels reach a certain normal amount, the endocrine system helps the body to keep that level of hormone in the blood. For example, if the thyroid gland has secreted the right amount of thyroid hormones into the blood, the pituitary gland senses the normal levels of thyroid hormone in the bloodstream. Then the pituitary gland adjusts its release of thyrotropin, the hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroid hormones. Another example of this process is parathyroid hormone. Parathyroid hormone increases the level of calcium in the blood. When the blood calcium level rises, the parathyroid glands sense the change and reduce their secretion of parathyroid hormone. This turnoff process is called a negative feedback system. What can go wrong • Too much or too little of any hormone can be harmful to your body. For example, if the pituitary gland produces too much growth hormone, a teen may grow excessively tall. If it produces too little, a teen may be unusually short. Doctors can often treat the problems by controlling the production of hormones or replacing certain hormones with medication. Some endocrine problems that affect teens are… • • Adrenal insufficiency. This condition occurs when the adrenal glands don't produce enough corticosteroids. The symptoms of adrenal insufficiency may include weakness, fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, dehydration, and skin changes. Growth hormone problems. Too much growth hormone in kids and teens who are still growing will make their bones and other body parts grow excessively. This rare condition (sometimes called gigantism) is usually caused by a pituitary tumor and can be treated by removing the tumor. Problems… • • Hyperthyroidism. Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the levels of thyroid hormones in the blood are very high/low. Precocious puberty. If the pituitary glands release hormones that stimulate the gonads to produce sex hormones too early, some kids may begin to go through puberty at a very young age. The End Made for you by: • Chelsea Hunter • Karina Emeric • Shelby Kesic • Roberto Ramos The Endocrine System Review Questions • TRUE or FALSE? 1. The endocrine system is founded on hormones and tissues. 2. A gland is a bunch of cells that produce and gives off chemicals. 3. The Pituitary gland is no bigger than a bean. Review Questions (cont.) What is a gland? a. Cells that produce and give off gland tissue. b. Cells that produce and give off chemicals. c. Transporters of blood to the heart. What two systems is the hypothalamus linked between? a. The nervous and the endocrine b. The respiratory and the endocrine c. The skeletal and the reproductive Which part of the endocrine is the most important, and nicknamed the Master Gland? a. The thyroid b. The testes c. The pituitary gland Review Questions (again) What gland is important because of the participation in development of kids’ bones and the nervous system; it’s also shaped like a butterfly. a. Pineal Gland b. Ovary c. Thyroid The two parts of the adrenal gland are the Adrenal _______ and the Adrenal _______. What does the pineal gland regulate? Where are the male gonads located? a. In the penis b. In the testes c. In the scrotum The ovaries produce ______ and secrete the female hormones _________ and_____________. • List a few things that could go wrong with the endocrine system….