Human Anatomy and Physiology
... this concentration reaches a certain level, the endocrine gland is inhibited (a negative effect), and its secretory activity decreases; as concentration of the gland’s hormone decreases, the concentration of the regulated product decreases too; inhibition of the gland ceases; when gland is no longer ...
... this concentration reaches a certain level, the endocrine gland is inhibited (a negative effect), and its secretory activity decreases; as concentration of the gland’s hormone decreases, the concentration of the regulated product decreases too; inhibition of the gland ceases; when gland is no longer ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... •Controls the function of internal organs. •The autonomic nervous system provides internal homeostasis. •Autonomic reflexes control blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, water balance, body temperature and other homeostatic functions. •Divided into two major subdivisions: the sympathetic and par ...
... •Controls the function of internal organs. •The autonomic nervous system provides internal homeostasis. •Autonomic reflexes control blood pressure, heart rate, respiration, water balance, body temperature and other homeostatic functions. •Divided into two major subdivisions: the sympathetic and par ...
Slide 1
... libido and erectile dysfunction. Deficiency of LH and GH may result in decreased muscle bulk, decreased body hair, central obesity and small, soft testes. In children,it commonly presents with delayed puberty or impairment of growth. ...
... libido and erectile dysfunction. Deficiency of LH and GH may result in decreased muscle bulk, decreased body hair, central obesity and small, soft testes. In children,it commonly presents with delayed puberty or impairment of growth. ...
in the cell
... • Parafollicular (C) cells are found between follicles secrete the hormone calcitonin ...
... • Parafollicular (C) cells are found between follicles secrete the hormone calcitonin ...
Benign Brain Tumors - American Brain Tumor Association
... -soft tissue swelling with thickening of skin in hands, feet, nose, lips and ears -brow protrusion -lower jaw protrusion -hyperpigmentation ...
... -soft tissue swelling with thickening of skin in hands, feet, nose, lips and ears -brow protrusion -lower jaw protrusion -hyperpigmentation ...
Endocrine System
... When hormone levels reach a certain normal amount, the endocrine system helps the body to keep that level of hormone in the blood. For example, if the thyroid gland has secreted the right amount of thyroid hormones into the blood, the pituitary gland senses the normal levels of thyroid hormone in th ...
... When hormone levels reach a certain normal amount, the endocrine system helps the body to keep that level of hormone in the blood. For example, if the thyroid gland has secreted the right amount of thyroid hormones into the blood, the pituitary gland senses the normal levels of thyroid hormone in th ...
November 1 CNS INTRO
... A. The Caudal portion of the neural tube B. The Rostral portion of the neural tube C. Neural Crest Cells D. Somites 3. Neurulation refers specifically to: A. Neural Tube Defects B. The process of neural tube closure C. The differentiation of the neural tube to three brain vesicles D. The development ...
... A. The Caudal portion of the neural tube B. The Rostral portion of the neural tube C. Neural Crest Cells D. Somites 3. Neurulation refers specifically to: A. Neural Tube Defects B. The process of neural tube closure C. The differentiation of the neural tube to three brain vesicles D. The development ...
The Endocrine System This system is made up of glands
... 6) _________: the pancreas is an exocrine gland with regard to digestion. It also releases hormones into the blood making it an endocrine gland as well. The clusters of cells within the pancreas that produce these hormones are called __________________. The islets of Langerhans contain two types of ...
... 6) _________: the pancreas is an exocrine gland with regard to digestion. It also releases hormones into the blood making it an endocrine gland as well. The clusters of cells within the pancreas that produce these hormones are called __________________. The islets of Langerhans contain two types of ...
Full-Text PDF
... Experiments in which the natural state of the animals has been disturbed have also been conducted. Bolt [2] found that the cyclic fluctuations of LH in rams could be supported by infusion of T. Moger and Armstrong [10] observed elevations of T concentrations in rats following acute LH treatment and f ...
... Experiments in which the natural state of the animals has been disturbed have also been conducted. Bolt [2] found that the cyclic fluctuations of LH in rams could be supported by infusion of T. Moger and Armstrong [10] observed elevations of T concentrations in rats following acute LH treatment and f ...
Hormones in Meat
... a regulatory substance produced in an organism and transported in tissue fluids such as blood or sap to stimulate specific cells or tissues into action. • a synthetic substance with an effect similar to that of an animal or plant hormone. • a person's sex hormones as held to influence behavior or mo ...
... a regulatory substance produced in an organism and transported in tissue fluids such as blood or sap to stimulate specific cells or tissues into action. • a synthetic substance with an effect similar to that of an animal or plant hormone. • a person's sex hormones as held to influence behavior or mo ...
Unit One – Concept Two - Calgary Christian School
... hormones posterior lobe – in back, hormones stored here neurosecretion – nerve cells secreting hormones in the posterior lobe – happens in adrenal gland pituitary portal system (pg. 445) – releasing factors in the hypothalamus control releasing factors in the anterior lobe Tropic hormone – a hormone ...
... hormones posterior lobe – in back, hormones stored here neurosecretion – nerve cells secreting hormones in the posterior lobe – happens in adrenal gland pituitary portal system (pg. 445) – releasing factors in the hypothalamus control releasing factors in the anterior lobe Tropic hormone – a hormone ...
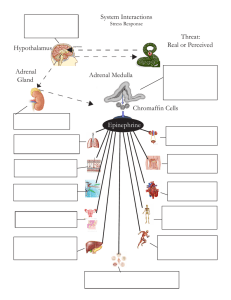
Adrenal Medulla Chromaffin Cells Epinephrine Threat: Real or
... against germs in wounds. Other endocrine organs such as the pancreas and liver are stimulated to increase blood levels of glucose which in turn produce the ATP necessary for all the increased activity. The skin of the integumentary system begins producing sweat to cool down the body so muscles can w ...
... against germs in wounds. Other endocrine organs such as the pancreas and liver are stimulated to increase blood levels of glucose which in turn produce the ATP necessary for all the increased activity. The skin of the integumentary system begins producing sweat to cool down the body so muscles can w ...
Thyroid Hormone Replacement in the Potential Brain
... aerobic to anaerobic Depletion of glycogen and myocardial high-energy cells Accumulation of lactate ...
... aerobic to anaerobic Depletion of glycogen and myocardial high-energy cells Accumulation of lactate ...
BSC 2086 Class Notes Chapter 16 – Part 1 Summer 2010
... __________________________ due to tumor causes bones to _____________ and _________________. ___________________________ following gland trauma or removal results in tetany, respiratory paralysis, and death. Structurally and functionally, the _________________ gland is two glands in one. The adrenal ...
... __________________________ due to tumor causes bones to _____________ and _________________. ___________________________ following gland trauma or removal results in tetany, respiratory paralysis, and death. Structurally and functionally, the _________________ gland is two glands in one. The adrenal ...
Abstract - IJCMAAS
... The Role of Maternal Thyroid Hormone on Brain Development of the Foetus. Valsa C.A.* *Assistant Professor, Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Pushpagiri Medical College & Hospital, Thiruvalla, Kerala, India. Corresponding E-mail ID: [email protected] ...
... The Role of Maternal Thyroid Hormone on Brain Development of the Foetus. Valsa C.A.* *Assistant Professor, Department of Obstetrics & Gynaecology Pushpagiri Medical College & Hospital, Thiruvalla, Kerala, India. Corresponding E-mail ID: [email protected] ...
Islamic University
... ( )-Fibrocartilage is present between vertebrae. ( )-The CNS consists of the brain and cranial nerves. ( )-The cornea has no blood vessels. ( )-The dynamic equilibrium receptors are found in the semicircular canals. ( )-In cretinism, the body proportions remain childlike. ( )-anterior pituitary is c ...
... ( )-Fibrocartilage is present between vertebrae. ( )-The CNS consists of the brain and cranial nerves. ( )-The cornea has no blood vessels. ( )-The dynamic equilibrium receptors are found in the semicircular canals. ( )-In cretinism, the body proportions remain childlike. ( )-anterior pituitary is c ...
Nervous and Endocrine Systems
... The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmit ...
... The nervous system is the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all the nerve cells. It’s broken down into two sections: the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The peripheral nervous system is responsible for gathering information and for transmit ...
Topic 2
... Six primary hormones produced by the pancreas: 1. Insulin - causes cells in the liver, muscle and fat to uptake gluclose from the blood to store as glycogen in muscle and liver. 2. Glucagon – released when blood glucose levels are too low , causing the liver to convert stores of glycogen into gluc ...
... Six primary hormones produced by the pancreas: 1. Insulin - causes cells in the liver, muscle and fat to uptake gluclose from the blood to store as glycogen in muscle and liver. 2. Glucagon – released when blood glucose levels are too low , causing the liver to convert stores of glycogen into gluc ...
Endocrine System
... • Glands – are ductless (tubeless) organs that specialize in the secretion of substances needed by an organism directly into the bloodstream. • Hormones – chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate your body’s functions. The secretions produced by the endocrine glands - releas ...
... • Glands – are ductless (tubeless) organs that specialize in the secretion of substances needed by an organism directly into the bloodstream. • Hormones – chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate your body’s functions. The secretions produced by the endocrine glands - releas ...
Test bank module 3 4 5 6 11 12
... (A) It is the major system in the brain for controlling emotions. (B) It functions primarily in the control of motor responses. (C) It regulates levels of arousal. (D) It regulates body temperature. (E) It controls the uptake of pituitary hormones. 4 100. The thalamus processes information for all o ...
... (A) It is the major system in the brain for controlling emotions. (B) It functions primarily in the control of motor responses. (C) It regulates levels of arousal. (D) It regulates body temperature. (E) It controls the uptake of pituitary hormones. 4 100. The thalamus processes information for all o ...
A. Nervous Multiple Choice, 1pt each 1. Lipofuscin A
... D. Increased heat production E. Increased blood calcium level F. Increased blood glucose levels I. Endocrine T/F, 1 pt each T 1. The hypodermis has endocrine functions T 2. The posterior lobe does not synthesize oxytocin F 3. Thyrotropin promotes secretion of pentaiodothyronine T 4. The pituitary gl ...
... D. Increased heat production E. Increased blood calcium level F. Increased blood glucose levels I. Endocrine T/F, 1 pt each T 1. The hypodermis has endocrine functions T 2. The posterior lobe does not synthesize oxytocin F 3. Thyrotropin promotes secretion of pentaiodothyronine T 4. The pituitary gl ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.