Laboratory 9: Pons to Midbrain MCB 163 Fall 2005 Slide #108 1
... The pontine nuclei are the gateway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellar cortex (cerebropontocerebellar, anyone?). These fibers arise largely in prefrontal, premotor, and many other cortical areas. Their target is the cerebrocerebellum (the lateral hemispheres). The structures are much bigger i ...
... The pontine nuclei are the gateway from the cerebral cortex to the cerebellar cortex (cerebropontocerebellar, anyone?). These fibers arise largely in prefrontal, premotor, and many other cortical areas. Their target is the cerebrocerebellum (the lateral hemispheres). The structures are much bigger i ...
endocrine system
... 1. Examples include blood pH, oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations, blood glucose, body temp, and water balance 2. By maintaining homeostasis all bodily functions can ...
... 1. Examples include blood pH, oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations, blood glucose, body temp, and water balance 2. By maintaining homeostasis all bodily functions can ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
... Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
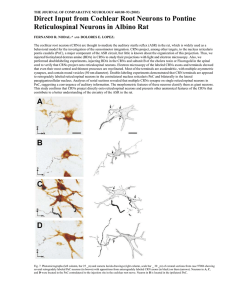
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 460:80–93 (2003)
... behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis (PnC), a major component of the ASR circuit, but little is known about the organization of this projection. Thus, we injected biotinylated dextran ami ...
... behavioral model for the investigation of the sensorimotor integration. CRNs project, among other targets, to the nucleus reticularis pontis caudalis (PnC), a major component of the ASR circuit, but little is known about the organization of this projection. Thus, we injected biotinylated dextran ami ...
Energy Balance as a part of Homeostasis
... Biochemical function determined by necessity ◦ May liberate, store, or transform energy containing molecules ◦ Facilitate transport of molecules ...
... Biochemical function determined by necessity ◦ May liberate, store, or transform energy containing molecules ◦ Facilitate transport of molecules ...
Endocrine System Outline
... • Hormone binds to the receptor and activates G protein • G protein binds and activates a phospholipase enzyme • Phospholipase splits the phospholipid PIP2 into diacylglycerol (DAG) and IP3 (both act as second messengers) • DAG activates protein kinases; IP3 triggers release of Ca2+ stores • Ca2+ (t ...
... • Hormone binds to the receptor and activates G protein • G protein binds and activates a phospholipase enzyme • Phospholipase splits the phospholipid PIP2 into diacylglycerol (DAG) and IP3 (both act as second messengers) • DAG activates protein kinases; IP3 triggers release of Ca2+ stores • Ca2+ (t ...
Endocrine System - S3 amazonaws com
... Most hormones are amino acid based and according to their size may be amines, peptides, polypeptides or proteins; other hormones are steroids (recall that steroids are lipids). This affects the ability of the hormone to enter the target cell. Steroids can pass through the cell membrane (a lipid can ...
... Most hormones are amino acid based and according to their size may be amines, peptides, polypeptides or proteins; other hormones are steroids (recall that steroids are lipids). This affects the ability of the hormone to enter the target cell. Steroids can pass through the cell membrane (a lipid can ...
Lecture 3
... • Anterior to midbrain and forms the walls of the third ventricle. • Consists of two parts, the thalamus and hypothalamus – Thalamus: processes sensory info & relays motor info – Hypothalamus: part of limbic system, controls pituitary ...
... • Anterior to midbrain and forms the walls of the third ventricle. • Consists of two parts, the thalamus and hypothalamus – Thalamus: processes sensory info & relays motor info – Hypothalamus: part of limbic system, controls pituitary ...
Chapter 9 Vocab
... 4. Cretinism – iodine deficiency in children that results in dwarfism (abnormal proportions) and mental retardation 5. Endocrinology – the study of hormones 6. Endocrine – gland that secretes hormones that are ...
... 4. Cretinism – iodine deficiency in children that results in dwarfism (abnormal proportions) and mental retardation 5. Endocrinology – the study of hormones 6. Endocrine – gland that secretes hormones that are ...
Chapter 45.
... The adrenal glands Are adjacent to the kidneys Are actually made up of two glands: the adrenal medulla and the adrenal cortex ...
... The adrenal glands Are adjacent to the kidneys Are actually made up of two glands: the adrenal medulla and the adrenal cortex ...
The term endocrine comes from the Greek The term endocrine
... off its i hormones h include: i l d {Growth Stimulating Hormone: controls the growth of the long bones of the body. body {Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroxin. {Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): affects the ovary in females. It stimulates the maturation and ...
... off its i hormones h include: i l d {Growth Stimulating Hormone: controls the growth of the long bones of the body. body {Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH): stimulates the thyroid to produce thyroxin. {Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH): affects the ovary in females. It stimulates the maturation and ...
Endocrine System Worksheet
... ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Most hormones circulate in blood and come into contact with essentially all cells. However, a specific hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called _____________________________ which contain recepto ...
... ________________________________________________________________________________ 3. Most hormones circulate in blood and come into contact with essentially all cells. However, a specific hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called _____________________________ which contain recepto ...
The Cerebellum
... Paraventricular nucleus → paraventicular nucleus (oxytocin) →paraventriculohypophyseal tract→posterior lobe of hypophysis ...
... Paraventricular nucleus → paraventicular nucleus (oxytocin) →paraventriculohypophyseal tract→posterior lobe of hypophysis ...
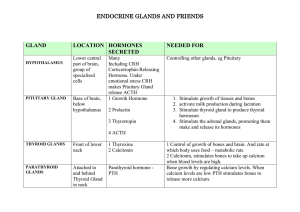
Endocrine Glands
... 1. Peptides, proteins, & glycoproteins o Produced in rER, o Packaged in Golgi o Stored in secretory vesicles o Released at cell surface then exert effects through 2o messenger systems 2. Steroids o Produced by cooperative axn of sER and mitochondria enzymes on substrates found in lipid droplets o Tr ...
... 1. Peptides, proteins, & glycoproteins o Produced in rER, o Packaged in Golgi o Stored in secretory vesicles o Released at cell surface then exert effects through 2o messenger systems 2. Steroids o Produced by cooperative axn of sER and mitochondria enzymes on substrates found in lipid droplets o Tr ...
PITUITARY GLAND: POSTERIOR LOBE
... e. Gonadotropic hormones - tropic hormones a. function: regulate activity of gonads b. types: 1. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): egg/sperm development 2. Luteinizing hormone (LH): sex hormone synthesis; ovulation ...
... e. Gonadotropic hormones - tropic hormones a. function: regulate activity of gonads b. types: 1. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH): egg/sperm development 2. Luteinizing hormone (LH): sex hormone synthesis; ovulation ...
PSYC&100exam1studyguide[1]
... def: psychology Wundt founder of psychoanalysis humanistic perspective positive psychology clinical psychologist v. psychiatrist placebo control group ethics in psychological research neuroscientist (what s/he studies) dendrite action potential myelinated v. non-myelinated axons reuptake communicati ...
... def: psychology Wundt founder of psychoanalysis humanistic perspective positive psychology clinical psychologist v. psychiatrist placebo control group ethics in psychological research neuroscientist (what s/he studies) dendrite action potential myelinated v. non-myelinated axons reuptake communicati ...
Key Endocrine Glands
... ‘master gland’. It formed embryonically from two sections; one coming down from the brain (the posterior part) and the other growing up from the roof of the mouth (the anterior part). It receives its own blood supply, but within the infundibulum there are a specific set of blood vessels connecting i ...
... ‘master gland’. It formed embryonically from two sections; one coming down from the brain (the posterior part) and the other growing up from the roof of the mouth (the anterior part). It receives its own blood supply, but within the infundibulum there are a specific set of blood vessels connecting i ...
Lecture 18, The Endocrine System - Websupport1
... on the surface of cell membranes because they can not cross the membrane to enter the cell • Thyroid and steroid hormones can cross the membrane and bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus ...
... on the surface of cell membranes because they can not cross the membrane to enter the cell • Thyroid and steroid hormones can cross the membrane and bind to receptors in the cytoplasm or nucleus ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS ANSWER SHEET
... and below ribs, and stores and sends out to left of body white blood cells ...
... and below ribs, and stores and sends out to left of body white blood cells ...
Document
... -nuclei found deep within the cerebrum - receives input from the cortex & provides output to the motor areas of the cortex via the thalamus -integrates motor commands provided by the cerebral cortex -regulates the initiation & termination of muscle movement. -anticipates body movements & controls su ...
... -nuclei found deep within the cerebrum - receives input from the cortex & provides output to the motor areas of the cortex via the thalamus -integrates motor commands provided by the cerebral cortex -regulates the initiation & termination of muscle movement. -anticipates body movements & controls su ...
Endocrine Reading Guide
... Choose 4 systems and describe briefly how what that system does for the endocrine system and what the endocrine system does for that system. ...
... Choose 4 systems and describe briefly how what that system does for the endocrine system and what the endocrine system does for that system. ...
The Hypothalamus and Human Nervous System: A Primer
... I reported in – “Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: An Introduction” - that multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is a real physiological disorder with an unknown origin. However, numerous theories have been proposed leaving one wondering where to start in their search for the root cause of MCS. I also pr ...
... I reported in – “Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: An Introduction” - that multiple chemical sensitivity (MCS) is a real physiological disorder with an unknown origin. However, numerous theories have been proposed leaving one wondering where to start in their search for the root cause of MCS. I also pr ...
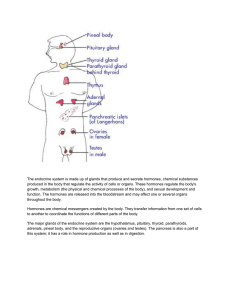
Endocrine System
... stomach that helps the body to maintain healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. The pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone that helps glucose move from the blood into the cells where it is used for energy. The pancreas also secretes glucagon when the blood sugar is low. Glucagon tells the liver to relea ...
... stomach that helps the body to maintain healthy blood sugar (glucose) levels. The pancreas secretes insulin, a hormone that helps glucose move from the blood into the cells where it is used for energy. The pancreas also secretes glucagon when the blood sugar is low. Glucagon tells the liver to relea ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.














![PSYC&100exam1studyguide[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008803293_1-1fd3a80bd9d491fdfcaef79b614dac38-300x300.png)