* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Endocrine System
Hormone replacement therapy (female-to-male) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Growth hormone therapy wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Artificial pancreas wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
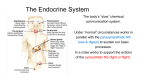
Endocrine System Endocrine System • Regulates overall metabolism, homeostasis, growth and reproduction • Glands – are ductless (tubeless) organs that specialize in the secretion of substances needed by an organism directly into the bloodstream. • Hormones – chemical substances that are produced in glands and help regulate your body’s functions. The secretions produced by the endocrine glands - released into the bloodstream Endocrine Glands • Hypothalamus – part of the CNS, but it produces hormones that influence the pituitary gland • Pituitary Gland – the “master gland” – regulates and controls the activities of all of the other endocrine glands. - Located at the base of the brain - Secretes growth hormone which affects growth of bone and cartilage Why is the Hypothalamus so Important? • Secretes regulatory homones • RH • RIH • "Directs" pituitary Pituitary Pituitary The pituitary gland produces a growth hormone which controls growth and homeostasis. Endocrine Glands (continued) • Thyroid Gland - Located in the neck - Secretes thyroxine which regulates the rate of metabolism in the body • Parathyroid Gland - Embedded in the back of the thyroid - Secretes parathormone which controls metabolism of calcium and phosphate Thyroid Thyroid The thyroid gland produces thyroxin to regulate metabolism. Parathyroid Parathyroid The parathyroid gland produces parathormone which controls calcium levels in the body. Endocrine Glands (continued) • Adrenal Glands - Located on top of the kidneys - Secrete adrenaline which helps deal with stress and accelerates the heart and breathing rates - Fight or Flight • Islets of Langerhans – specialized cells - Located in the pancreas - Secrete insulin and glucagon - Insulin lowers blood sugar - Glucagon raises blood sugar Adrenal Insufficiency • Addison’s disease--hyposecretion of cortisol • JFK • Darkened skin (ACTH mimics MSH) • Weight loss, hypoglycemia • Find the anomaly in the feedback loop. • Inability to handle stress Adrenals The adrenal glands Adrenals Adrenals produce adrenaline in response to physical and emotional stress. Adrenal gland Adrenal Problems Liver and Pancreas Pancreas Pancreas The pancreas produces insulin which controls sugar levels in the blood. Endocrine Glands (continued) • Gonads – sex glands - Male gonads are called testes - Located in the scrotum - Secrete testosterone which regulates male secondary sex characteristics - Female gonads are called ovaries - Located in the pelvic region - Secrete estrogen and progesterone which regulate female secondary sex characteristics Testes (in males) Testes The testes produce testosterone used in sperm production and the development of male traits. Ovaries (in Females) Ovaries The ovaries produce estrogen used in egg production and the development of female traits. Feedback Mechanisms • Negative Feedback – is when an activity alters a condition in the body, and this triggers a series of events that reverses the altered condition Ex. Body temperature - When body temp. goes up, we sweat - When body temp. goes down, we shiver Ex. Blood sugar levels - When blood sugar goes up, insulin lowers blood sugar - When blood sugar goes down, glucagon raises blood sugar A. Positive Feedback • Not common • Classic example: Action of OXYTOCIN on uterine muscle during birth. Disorders • Diabetes – is a disease where a person cannot produce insulin - Inability of the body to store sugar as glycogen • Goiter – is enlargement of the thyroid gland caused by iodine deficiency DIABETES DIABETES Goiter Other Disorders • Grave’s Disease: hyperthyroidism, an autoimmune disorder in which an overactive and enlarged thyroid gland produces excessive amounts of thyroxine. • Cushing’s Disease: overproduction of adrenal hormones. • Growth Disorders: abnormal amounts of growth hormone. GH as Juvenile (Gigantism) GH = pituitary dwarfism GH as an Adult