Chapter 17 Endocrine System
... – causes enlargement of external sexual organs in children & early onset of puberty – masculinizing effects on women (deeper voice & beard growth) ...
... – causes enlargement of external sexual organs in children & early onset of puberty – masculinizing effects on women (deeper voice & beard growth) ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
... Diagram of the olfactory pathway. Information is transmitted from the olfactory bulb by axons of mitral and tufted relay neurons in the lateral olfactory tract. Mitral cells project to five regions of the olfactory cortex: anterior olfactory nucleus, olfactory tubercle, piriform cortex, and parts of ...
... Diagram of the olfactory pathway. Information is transmitted from the olfactory bulb by axons of mitral and tufted relay neurons in the lateral olfactory tract. Mitral cells project to five regions of the olfactory cortex: anterior olfactory nucleus, olfactory tubercle, piriform cortex, and parts of ...
Neurobiology – overview of the human CNS
... ventral tegmental area (A10) amygdala corticomedial basolateral central nucleus septal nuclei medial – ACh to hippocampus lateral nucleus basalis of Meynert – ACh to neocortex bed nucleus of the stria terminalis diencephalon thalamus hypothalamus epithalamus pineal (unpaired) – driven by SCN, secret ...
... ventral tegmental area (A10) amygdala corticomedial basolateral central nucleus septal nuclei medial – ACh to hippocampus lateral nucleus basalis of Meynert – ACh to neocortex bed nucleus of the stria terminalis diencephalon thalamus hypothalamus epithalamus pineal (unpaired) – driven by SCN, secret ...
HORMONES
... ally different enough from the natural hor- laboratory evaluation, your doctor will premones they are attempting to replace. Such scribe hormones to restore your youthful synthetic hormones often produce many levels. Additionally, your doctor will also desirable effects, but more often than not, mak ...
... ally different enough from the natural hor- laboratory evaluation, your doctor will premones they are attempting to replace. Such scribe hormones to restore your youthful synthetic hormones often produce many levels. Additionally, your doctor will also desirable effects, but more often than not, mak ...
Slide ()
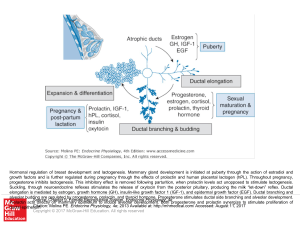
... Hormonal regulation of breast development and lactogenesis. Mammary gland development is initiated at puberty through the action of estradiol and growth factors and is further regulated during pregnancy through the effects of prolactin and human placental lactogen (hPL). Throughout pregnancy, proges ...
... Hormonal regulation of breast development and lactogenesis. Mammary gland development is initiated at puberty through the action of estradiol and growth factors and is further regulated during pregnancy through the effects of prolactin and human placental lactogen (hPL). Throughout pregnancy, proges ...
I. General Characteristics of the Endocrine System
... tropic hormones. 3. Tropic hormones stimulate other endocrine glands to release hormones. 4. An example of an endocrine organ directly stimulated by the nervous system is the adrenal medulla. 5. Some endocrine glands respond to changes in the composition of the internal environment. 5. As a result o ...
... tropic hormones. 3. Tropic hormones stimulate other endocrine glands to release hormones. 4. An example of an endocrine organ directly stimulated by the nervous system is the adrenal medulla. 5. Some endocrine glands respond to changes in the composition of the internal environment. 5. As a result o ...
Bio Endocrine System Art
... in the lower central part of the brain, is the main link between the endocrine and nervous systems. Nerve cells in the hypothalamus control the pituitary gland by producing chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary. ...
... in the lower central part of the brain, is the main link between the endocrine and nervous systems. Nerve cells in the hypothalamus control the pituitary gland by producing chemicals that either stimulate or suppress hormone secretions from the pituitary. ...
Tropic Hormones - D and F: AP Biology
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Additional Nervous System Notes
... • Fluid movement causes hair cells (receptors) attached to basilar membrane to move to rub against the tectorial membrane • Basilar membrane generates an impulse that travels to brain via auditory nerve ...
... • Fluid movement causes hair cells (receptors) attached to basilar membrane to move to rub against the tectorial membrane • Basilar membrane generates an impulse that travels to brain via auditory nerve ...
CLASS 10 CONTROL AND CO – ORDINATION Instructions:
... Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brai Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium. Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord Medulla oblongata- Con ...
... Mid brain- It connects Fore brain and Hind brain. Controls reflex of eyes & ears Hind brain- Connects the Fore brain & Hind brai Cerebellum – Controls & coordinates muscular movements, maintaining body posture and equilibrium. Pons- Acts as a bridge between brain & spinal cord Medulla oblongata- Con ...
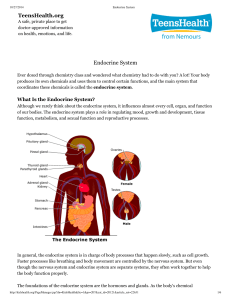
the endocrine system
... Exocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. The ducts then carry the secretions into body cavities or to the body's surface. They include sweat, sebaceous, mucous and digestive glands. Endocrine glands are ductless glands and secret their products directly into the blood. They include the pit ...
... Exocrine glands secrete their products into ducts. The ducts then carry the secretions into body cavities or to the body's surface. They include sweat, sebaceous, mucous and digestive glands. Endocrine glands are ductless glands and secret their products directly into the blood. They include the pit ...
General Physiology
... Consists of: Lungs and air passages Purpose: bring in Oxygen, eliminate CO2 Air is about 21% O2, 79% N, trace of CO2 expired air is 16% O2, 79% N, and 5% CO2 ...
... Consists of: Lungs and air passages Purpose: bring in Oxygen, eliminate CO2 Air is about 21% O2, 79% N, trace of CO2 expired air is 16% O2, 79% N, and 5% CO2 ...
F - Journals
... Informs on interactions among brain structures and between these structures and the spinal cord Noninvasive; can be used for basic research and in clinics Interpretation is ambiguous; can stimulate many structures ...
... Informs on interactions among brain structures and between these structures and the spinal cord Noninvasive; can be used for basic research and in clinics Interpretation is ambiguous; can stimulate many structures ...
3 layers
... -Emotions, autonomic functions, hormone production -mamillary bodies – serve as relay stations for reflexes related to eating -supraoptic and preoptic nuclei that in hormone secretion (ADH) and body temp -major functions: 1. control of the ANS – integrates signals from the ANS (regulated smooth and ...
... -Emotions, autonomic functions, hormone production -mamillary bodies – serve as relay stations for reflexes related to eating -supraoptic and preoptic nuclei that in hormone secretion (ADH) and body temp -major functions: 1. control of the ANS – integrates signals from the ANS (regulated smooth and ...
View Presentation - Green Soul Holistics
... Stress and high cortisol is the number one reason hormones go astray Because the adrenal glands rule the roost (fight or flight) The adrenals can convert one hormone to another They also have a major effect on the pituitary – a master hormone gland located at the base of the brain Reducing s ...
... Stress and high cortisol is the number one reason hormones go astray Because the adrenal glands rule the roost (fight or flight) The adrenals can convert one hormone to another They also have a major effect on the pituitary – a master hormone gland located at the base of the brain Reducing s ...
Chapter 13 Notes
... membrane, but rather attach to receptor sites on the membrane This hormone-receptor complex triggers the production of an enzyme (adenyl catalase) This enzyme converts ATP to cyclic AMP The cyclic AMP turns on enzymes in the cytoplasm so that they carry out their functions ...
... membrane, but rather attach to receptor sites on the membrane This hormone-receptor complex triggers the production of an enzyme (adenyl catalase) This enzyme converts ATP to cyclic AMP The cyclic AMP turns on enzymes in the cytoplasm so that they carry out their functions ...
The Endocrine System
... a number of metabolic processes within cells, as well as reproduction, development and growth. • Endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas and other hormonesecreting glands and tissues. ...
... a number of metabolic processes within cells, as well as reproduction, development and growth. • Endocrine glands include the pituitary gland, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, adrenal glands, pancreas and other hormonesecreting glands and tissues. ...
thyroid gland - Uplift Education
... •Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the uptake of glucose by cells ...
... •Insulin – decreases blood sugar concentrations, affects the uptake of glucose by cells ...
Seybold
... the tumor and whether or not it is secreting a hormone. Often, surgery is done to remove the tumor. Transphenoidal surgery in which the tumor is removed through the nose is most common, but a craniotomy can also be performed. Radiation therapy may be done to kill the tumor. Certain medications may a ...
... the tumor and whether or not it is secreting a hormone. Often, surgery is done to remove the tumor. Transphenoidal surgery in which the tumor is removed through the nose is most common, but a craniotomy can also be performed. Radiation therapy may be done to kill the tumor. Certain medications may a ...
BIO 142 Unit 1 Learning Objectives
... Upon your successful completion of Unit 1, you will be able to do the following. ...
... Upon your successful completion of Unit 1, you will be able to do the following. ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... interstitial fluid from which they diffuse into capillaries to be carried away by the blood 2. The endocrine glands (e.g., pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands) collectively form the endocrine system; there are several organs of the body (e.g., hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, stomach, skin, heart, ...
... interstitial fluid from which they diffuse into capillaries to be carried away by the blood 2. The endocrine glands (e.g., pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands) collectively form the endocrine system; there are several organs of the body (e.g., hypothalamus, thymus, pancreas, stomach, skin, heart, ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.