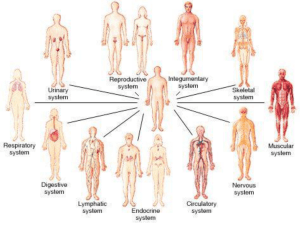
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 9 Review Sheet
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
... released into the blood to be transported to target tissues. Nervous control only works on a small area or target tissues, whereas endocrine control can be widespread because it uses the bloodstream and only a small amount of hormone is needed. 3. What are hormones? Describe the different types, act ...
patient glossary
... A condition whereby undeveloped follicles (cysts) form within the ovaries. It is seen in women with high estrogen and low progesterone levels, and/or high androgen (testosterone) and insulin levels. PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS) A set of physical and emotional symptoms that stem from hormonal imbalanc ...
... A condition whereby undeveloped follicles (cysts) form within the ovaries. It is seen in women with high estrogen and low progesterone levels, and/or high androgen (testosterone) and insulin levels. PREMENSTRUAL SYNDROME (PMS) A set of physical and emotional symptoms that stem from hormonal imbalanc ...
HERE
... messengers”). These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and may affect one or several organs throughout the body (i.e. the difference between target and non-target hormones). • Hormones transfer informat ...
... messengers”). These hormones regulate the body's growth, metabolism, and sexual development and function. The hormones are released into the bloodstream and may affect one or several organs throughout the body (i.e. the difference between target and non-target hormones). • Hormones transfer informat ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... nervousness, many psychoneurotic tendencies including anxiety complexes, extreme worry and paranoia, and muscle tremor. Hyperthyroidism ...
... nervousness, many psychoneurotic tendencies including anxiety complexes, extreme worry and paranoia, and muscle tremor. Hyperthyroidism ...
hyperprolactinemia - Hormone Health Network
... • Serious mental health disorders (antipsychotics such as risperdal and haloperidol) • Menopausal symptoms (estrogen) Other causes include ...
... • Serious mental health disorders (antipsychotics such as risperdal and haloperidol) • Menopausal symptoms (estrogen) Other causes include ...
Nolte Chapter 12 – Cranial Nerves and Their Nuclei
... o main sensory nucleus in the midpons received information about touch and jaw position gives rise to pathways to the thalamus one crosses and joins the medial lemniscus and goes to VPM the other is uncrossed(respresents the inside of the mouth) and goes up its own path in the dorsal trigemi ...
... o main sensory nucleus in the midpons received information about touch and jaw position gives rise to pathways to the thalamus one crosses and joins the medial lemniscus and goes to VPM the other is uncrossed(respresents the inside of the mouth) and goes up its own path in the dorsal trigemi ...
PMHS
... Activate genes that result in __________________ Nonsteroid Hormone Action Hormone binds to a membrane receptor Hormone _________________________________ Sets off a series of reactions that activates an enzyme Catalyzes a reaction that produces a second messenger ...
... Activate genes that result in __________________ Nonsteroid Hormone Action Hormone binds to a membrane receptor Hormone _________________________________ Sets off a series of reactions that activates an enzyme Catalyzes a reaction that produces a second messenger ...
Chapter 11 Endocrine Glands
... Body appears to have negative feedback loops (an adipostat) to maintain a certain amount of adipose tissue Adipose cells (adipocytes) store and release fat under ________________ control And may release their own hormone(s) to influence metabolism Development of Adipose Tissue Number of adip ...
... Body appears to have negative feedback loops (an adipostat) to maintain a certain amount of adipose tissue Adipose cells (adipocytes) store and release fat under ________________ control And may release their own hormone(s) to influence metabolism Development of Adipose Tissue Number of adip ...
Endocrine system
... • Rich in capillaries • The secretion is hormone which transported by blood circulation ...
... • Rich in capillaries • The secretion is hormone which transported by blood circulation ...
Anterior Pituitary/Adenohypophysis Posterior Pituitary
... Adrenal sex hormones (androgens and estrogen in tiny quantities) ...
... Adrenal sex hormones (androgens and estrogen in tiny quantities) ...
the endocrine system
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
DETERMINATION OF THYROID HORMONE T3 AND T4 LEVELS IN
... Introduction: The thyroid gland, through the secretion of hormones, plays a variety of functions within the body related to energy metabolism and affects a number of other organ systems. The present study examined the blood levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4 in Throughbred horses with clinical goi ...
... Introduction: The thyroid gland, through the secretion of hormones, plays a variety of functions within the body related to energy metabolism and affects a number of other organ systems. The present study examined the blood levels of thyroid hormones T3 and T4 in Throughbred horses with clinical goi ...
21 Endocrine
... Hormone (FSH) is present in both males and females, and the pituitary is known to affect these in both sexes. • Prolactin is another hormone known to stimulate lactation in females, but its effects in males is not fully understood. ...
... Hormone (FSH) is present in both males and females, and the pituitary is known to affect these in both sexes. • Prolactin is another hormone known to stimulate lactation in females, but its effects in males is not fully understood. ...
Loss of orexin/NARP neurons in human narcolepsy
... mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice and rats with an engineered loss of ORX neurons have a nearly identical narcolepsy ...
... mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice and rats with an engineered loss of ORX neurons have a nearly identical narcolepsy ...
1.5 Individual human development during youth: Physical
... required for reproduction. So they will involve all the other changes that occur during puberty eg: widening of shoulders, pubic hair, oily skin, breast development. ...
... required for reproduction. So they will involve all the other changes that occur during puberty eg: widening of shoulders, pubic hair, oily skin, breast development. ...
The Endocrine System
... question below and share your answer with me on google drive. [email protected] ...
... question below and share your answer with me on google drive. [email protected] ...
doc Lecture 5-8
... that have a variety of effects throughout the body. These glands are mostly controlled by hormones from the pituitary. The pituitary hormones are mostly controlled by hormones from the HT. Exceptions: Some glands do not follow this scheme i.e. pancreas and the pineal glands in the CNS are not under ...
... that have a variety of effects throughout the body. These glands are mostly controlled by hormones from the pituitary. The pituitary hormones are mostly controlled by hormones from the HT. Exceptions: Some glands do not follow this scheme i.e. pancreas and the pineal glands in the CNS are not under ...
Chapter 25 The Endocrine Glands
... and the hormone produced • Functional tumors: produce hormones that cause clinical manifestations • Nonfunctional tumors: do not produce hormones but exert other effects • May encroach on important structures adjacent to optic chiasm; disrupt hormone-producing functions of anterior lobe cells ...
... and the hormone produced • Functional tumors: produce hormones that cause clinical manifestations • Nonfunctional tumors: do not produce hormones but exert other effects • May encroach on important structures adjacent to optic chiasm; disrupt hormone-producing functions of anterior lobe cells ...
1 The Endocrine System no clear distinction between nervous and
... The Endocrine System no clear distinction between nervous and endocrine systems ...
... The Endocrine System no clear distinction between nervous and endocrine systems ...
Hormone receptors
... The hormone can affect several different cell types; also more than one hormone can affect a given cell type; and that hormones can exert many different effects in one cell or in different cells. ...
... The hormone can affect several different cell types; also more than one hormone can affect a given cell type; and that hormones can exert many different effects in one cell or in different cells. ...
from the brain
... It is divided into two halves called the cerebral hemispheres that are connected by a large band of fibers called the corpus callosum They have different tasks (lateralization) ...
... It is divided into two halves called the cerebral hemispheres that are connected by a large band of fibers called the corpus callosum They have different tasks (lateralization) ...
Chapter 2 - Neuroscience and Behavior
... excites. It mimics the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receiving neuron. Morphine mimics the action of neurotransmitters by stimulating receptors in the brain involved in mood and pain sensation. ...
... excites. It mimics the effects of a neurotransmitter on the receiving neuron. Morphine mimics the action of neurotransmitters by stimulating receptors in the brain involved in mood and pain sensation. ...
Chapter 45 Worksheet Sy Ha Hormones and the Endocrine System
... create the hormone oxytocin which is stimulated from the suckling of the baby for milk. This nerve impulse starts the endocrine system in order to provide the baby with milk which is regulated by the oxytocin hormone. 4. Describe several examples of the essential roles of hormones in the maintenance ...
... create the hormone oxytocin which is stimulated from the suckling of the baby for milk. This nerve impulse starts the endocrine system in order to provide the baby with milk which is regulated by the oxytocin hormone. 4. Describe several examples of the essential roles of hormones in the maintenance ...
Endocrine System
... - Bromocriptine administration during the postpartum(產後) period reduces PRL secretion to nonlactating levels and terminates lactation. Bromocriptine is used to directly inhibit PRL from anterior pituitary. Physiological actions of prolactin - Plays an important role in the development of mammary gla ...
... - Bromocriptine administration during the postpartum(產後) period reduces PRL secretion to nonlactating levels and terminates lactation. Bromocriptine is used to directly inhibit PRL from anterior pituitary. Physiological actions of prolactin - Plays an important role in the development of mammary gla ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.