* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PMHS
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Hormonal contraception wikipedia , lookup
Breast development wikipedia , lookup
Xenoestrogen wikipedia , lookup
Menstrual cycle wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Hormone replacement therapy (male-to-female) wikipedia , lookup
Mammary gland wikipedia , lookup
Neuroendocrine tumor wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
Bioidentical hormone replacement therapy wikipedia , lookup
Endocrine disruptor wikipedia , lookup
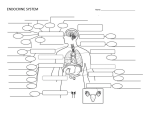
1 Endocrine System Nervous System controls the Endocrine System • The endocrine system, along with the nervous system, functions in the regulation of body activities. (________ ____________________) • The nervous system acts through electrical impulses and neurotransmitters to cause muscle contraction and glandular secretion. Nervous VS Endocrine • The nervous system coordinates rapid and precise responses to stimuli using action potentials. • The endocrine system maintains long-term control using ___________________. – The endocrine system works in parallel with the nervous system to control _____________________. Two major categories of glands in the body • Exocrine – Exocrine glands have ________________that carry their secretory product to a surface • Endocrine – The endocrine glands do ______________________________ to carry their product to a surface Endocrine Glands • The endocrine glands do not have ducts to carry their product to a surface. (ductless glands) • Only ____________________________________________________________ • The secretory products of endocrine glands (hormone) are secreted ___________ __________________________________________________ • The Hormone is transported throughout the body, by blood, where they influence only those cells that have receptor sites for that hormone. Exocrine Glands • Exocrine glands _________________ that carry their secretory product to a surface. • These glands include – ___________________________ – ____________________________ – glands that secrete digestive enzymes • These type of glands _______________________________________________ Endocrine System • Second messenger system of the body • Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood • Hormones control several major processes – – – – – 2 Hormones • 2 Types of hormones • ________________________________ – are lipid like carbon rings – These hormones are able to pass though the cell membrane. – This type of hormones is produced in the adrenal glands and the Gonads (testis and ovaries) • ________________________________ – made up of amino acids - These hormones cannot pass though the cell membrane because they cannot dissolve in fats. Ex. Insulin Mechanisms of Hormone Action Hormones can only affect certain tissues or organs (called target cells or target organs) Target cells/organs must have specific protein receptors Hormone binding to receptor then influences the working of the cells Effects Caused by Hormones Changes in plasma membrane permeability or electrical state Synthesis of __________________, such as enzymes Activation or inactivation of enzymes Stimulation of ________________________________ Steroid Hormone Action Diffuse through the plasma membrane of target cells Enter the __________________ Bind to a specific protein within the nucleus Bind to specific sites on the cell’s DNA Activate genes that result in __________________ Nonsteroid Hormone Action Hormone binds to a membrane receptor Hormone _________________________________ Sets off a series of reactions that activates an enzyme Catalyzes a reaction that produces a second messenger molecule Oversees additional intracellular changes to promote a specific response Control of Hormone Release Hormone levels in the blood are maintained by ____________ _______________________ A stimulus or low hormone levels in the blood triggers the release of more hormone Hormone release stops once an appropriate level in the blood is reached Hormonal Stimuli of Endocrine Glands Endocrine glands are activated by __________________ Humoral Stimuli of Endocrine Glands ____________________________stimulate hormone release Neural Stimuli of Endocrine Glands __________________ stimulate hormone release Most are under control of the sympathetic nervous system (ex. fight or flight) 3 Location of Major Endocrine Organs Pituitary Gland Size of a grape Hangs by a stalk from the ___________________ Protected by the sphenoid bone Has two functional lobes ___________________– glandular tissue ___________________– nervous tissue Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Six anterior pituitary hormones Two affect non-endocrine targets Four stimulate other endocrine glands (referred to as tropic hormones) Characteristics of all anterior pituitary hormones ___________________ (or peptides) Act through ___________________ (no direct communication) Regulated by hormonal stimuli, mostly negative feedback 4 Growth Hormone (GH) General metabolic hormone Major effects are directed to growth of ____________ Causes amino acids to be built into proteins Causes fats to be broken down for a __________________ Functions of Other Anterior Pituitary Hormones Prolactin (PRL) Stimulates and maintains ____ ____________ following childbirth Function in males is ___________________ Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Regulates endocrine activity of the _________________ Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Influences growth and activity of the _______________ Functions of Other Anterior Pituitary Hormones Gonadotropic hormones Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads _____________________________(FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes ___________________ (LH) Triggers ___________________ Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum Stimulates ___________________ production in males Referred to as interstitial cellstimulating hormone (ICSH) Pituitary - Hypothalamus Relationship Hypothlamus produces two hormones that are transported to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary The posterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland (doesn’t make hormones), but does store and release hormones Hormones of the Posterior Pituitary Oxytocin Stimulates _______________________________________________ Causes milk ejection Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Can inhibit ___________________ 5 In large amounts, causes vasoconstriction leading to ___________________ (vasopressin) Thyroid Gland Found ___________________ Consists of two lobes and a connecting isthmus Produces two hormones ___________________ Calcitonin Major metabolic hormone Composed of two active iodine-containing hormones Thyroxine (T4) – secreted by thyroid follicles Triiodothyronine (T3) – conversion of T4 at target tissues Parathyroid Gland Tiny masses on the posterior of the thyroid Secrete parathyroid hormone Stimulate osterclasts to _________________________ Stimulate the kidneys and intestine to absorb more calcium Raise ___________________in the blood Adrenal Glands Two glands ________________ – outer glandular region in three layers ______________ – inner neural tissue region Sits on top of the ___________________ Hormones of the Adrenal Cortex Mineralocorticoids (mainly aldosterone) Produced in outer adrenal cortex Regulate ___________________in blood, water, and electrolyte balance Target organ is the ________________ Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone Production inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide Glucocorticoids (including cortisone and cortisol) Produced in the middle layer of the adrenal cortex Promote normal ___________________ Help resist ___________________ Released in response to increased blood levels of ACTH Sex hormones Produced in the inner layer of the adrenal cortex _______________ (male) and some ________________ (female) Hormones of the Adrenal Medulla Produces two similar hormones (catecholamines) ___________________ ___________________ These hormones prepare the body to deal with ___________________ 6 Pancreatic Islets The pancreas is a mixed gland The islets of the pancreas produce hormones _______________ – allows glucose to cross plasma membranes into cells from beta cells _______________ – allows glucose to enter the blood from alpha cells These hormones are antagonists that maintain ___________________homeostasis Pineal Gland Found on the third ventricle of the brain Secretes ___________________ Helps establish the body’s ______________ May have other as-yet-unsubstantiated functions Thymus Located posterior to the sternum Largest in infants and children Produces thymosin Matures some types of white blood cells Important in developing ___________________ Hormones of the Ovaries Estrogens Produced by Graafian follicles or the placenta Stimulates the development of secondary female characteristics Matures female ___________________ Helps prepare the uterus to ___________________ Helps maintain ___________________ Prepares the breasts to produce milk Progesterone Produced by the corpus luteum Acts with estrogen to bring about the ___________________ Helps in the implantation of an ___________________ in the uterus Hormones of the Testes Interstitial cells of testes are hormone-producing Produce several androgens ___________________ is the most important androgen Responsible for adult male secondary sex characteristics Promotes growth and maturation of ___________________ Required for ___________________