Endocrine System: The Actions of Hormones on Target Cells
... b. What catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP? _________ _________ c. What is known as the first messenger? _________ Second messenger? _________ d. A molecule of cAMP activates _________ ________ ____, which can phosphorylate many proteins. e. A single molecule of a hormone can have a large effec ...
... b. What catalyzes the conversion of ATP to cAMP? _________ _________ c. What is known as the first messenger? _________ Second messenger? _________ d. A molecule of cAMP activates _________ ________ ____, which can phosphorylate many proteins. e. A single molecule of a hormone can have a large effec ...
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 28 MAY 2014
... A process whereby the response by the effector is opposite to, and reverses the stimulus. ...
... A process whereby the response by the effector is opposite to, and reverses the stimulus. ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 85,29 КБ
... The levels of hormones in the body can be regulated by several factors. The nervous system can control hormone levels through the action of the hypothalamus and its releasing and inhibiting hormones. For example, TRH produced by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to produce TSH. Trop ...
... The levels of hormones in the body can be regulated by several factors. The nervous system can control hormone levels through the action of the hypothalamus and its releasing and inhibiting hormones. For example, TRH produced by the hypothalamus stimulates the anterior pituitary to produce TSH. Trop ...
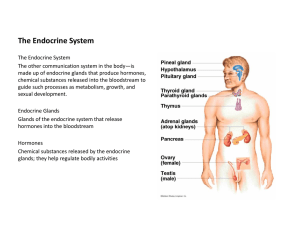
The Endocrine System
... Anterior Pituitary • Anterior Pituitary • Part of the pituitary known as the “master gland” because it produces numerous hormones that trigger the action of other glands • What it does: • Regulates body growth and also affects motivation and emotions ...
... Anterior Pituitary • Anterior Pituitary • Part of the pituitary known as the “master gland” because it produces numerous hormones that trigger the action of other glands • What it does: • Regulates body growth and also affects motivation and emotions ...
1b Endo Sys II - Superior Glands
... stimulated, hypothalamic neurons secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones into the primary capillary plexus. ...
... stimulated, hypothalamic neurons secrete releasing and inhibiting hormones into the primary capillary plexus. ...
Ch 10 ES 207 Notes
... in the body. They’re then gonna interact with the receptors on gland cells. Those cells are gonna be excited and release other hormones. Those hormones are then going to circulate throughout the body and affect a broad variety of target cells. o Anything that’s a releasing hormone is released by the ...
... in the body. They’re then gonna interact with the receptors on gland cells. Those cells are gonna be excited and release other hormones. Those hormones are then going to circulate throughout the body and affect a broad variety of target cells. o Anything that’s a releasing hormone is released by the ...
AHS I
... 12. ____ Any disturbance in the functioning of the endocrine glands may cause changes in the appearance or functioning of the body. 13. ____ The secretion of the hormones operates on a positive feedback system or under the control of the nervous system. 14. ____ The pituitary gland is a tiny structu ...
... 12. ____ Any disturbance in the functioning of the endocrine glands may cause changes in the appearance or functioning of the body. 13. ____ The secretion of the hormones operates on a positive feedback system or under the control of the nervous system. 14. ____ The pituitary gland is a tiny structu ...
HS I Endocrine System Worksheet 1 Choose the best answer to
... 12. ____ Any disturbance in the functioning of the endocrine glands may cause changes in the appearance or functioning of the body. 13. ____ The secretion of the hormones operates on a positive feedback system or under the control of the nervous system. 14. ____ The pituitary gland is a tiny str ...
... 12. ____ Any disturbance in the functioning of the endocrine glands may cause changes in the appearance or functioning of the body. 13. ____ The secretion of the hormones operates on a positive feedback system or under the control of the nervous system. 14. ____ The pituitary gland is a tiny str ...
Test 4 BIO 110 Review Starred (*) questions are related to the
... 1. What are target cells? 2. *Be familiar with the basic locations of the endocrine glands. 3. Compare steroid and non-steroid hormones. 4. What are Prostaglandins? 5. What mechanism is hormone secretion is regulated by? 6. What are the functions of these hormones that come from the anterior lobe of ...
... 1. What are target cells? 2. *Be familiar with the basic locations of the endocrine glands. 3. Compare steroid and non-steroid hormones. 4. What are Prostaglandins? 5. What mechanism is hormone secretion is regulated by? 6. What are the functions of these hormones that come from the anterior lobe of ...
7-2 Chemical Control Cam Wk 2 - Yr-9
... • Pancreas located partially behind the stomach in the abdomen, and it functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. It produces digestive enzymes as well as insulin and glucagon • Adrenal gland one of a pair of ductless glands, located above the kidneys, which produce adrenaline (epinephrine) ...
... • Pancreas located partially behind the stomach in the abdomen, and it functions as both an endocrine and exocrine gland. It produces digestive enzymes as well as insulin and glucagon • Adrenal gland one of a pair of ductless glands, located above the kidneys, which produce adrenaline (epinephrine) ...
DIRECTIONS: Each of the questions or incomplete statements
... release an endogenous pyrogen to trigger this response: (A) The hepatocyte (B) The Kupfer cell (macrophage) (C) The sinusoidal endocyte (D)Hepatic capillary endothelial cells (D) none of the above 10. An individual exhibiting an elevated core body thermoregulatory set-point during fever has (A) an i ...
... release an endogenous pyrogen to trigger this response: (A) The hepatocyte (B) The Kupfer cell (macrophage) (C) The sinusoidal endocyte (D)Hepatic capillary endothelial cells (D) none of the above 10. An individual exhibiting an elevated core body thermoregulatory set-point during fever has (A) an i ...
Hormones - Zanichelli online per la scuola
... Cortisol (a glucocorticoid) mediates metabolic stress responses. Cortisol and similar drugs are used to reduce inflammation and allergic responses. The anterior pituitary controls cortisol release by corticotropin (adrenocorticotropic hormone, or ACTH). ACTH release is controlled in turn by corticot ...
... Cortisol (a glucocorticoid) mediates metabolic stress responses. Cortisol and similar drugs are used to reduce inflammation and allergic responses. The anterior pituitary controls cortisol release by corticotropin (adrenocorticotropic hormone, or ACTH). ACTH release is controlled in turn by corticot ...
Physio Lab 4 Endocrine in PhysioEx
... mechanism would be the endocrine glands of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-X axis (where X- stands for another endocrine gland such as the thyroid, gonads, or adrenal glands). An example of a neural mechanism would be the release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla: A preganglionic neuron of the symp ...
... mechanism would be the endocrine glands of the Hypothalamus-Pituitary-X axis (where X- stands for another endocrine gland such as the thyroid, gonads, or adrenal glands). An example of a neural mechanism would be the release of epinephrine from the adrenal medulla: A preganglionic neuron of the symp ...
Endocrine
... Negative Feedback Mechanism Involved in Control of Blood Calcium The presence of calcium ions is critical to the functioning of all cells. In mammals, the two hormones parathyroid hormone and calcitonin regulate and stabilize the blood calcium level at about 10 mg/100 mL. When blood calcium levels f ...
... Negative Feedback Mechanism Involved in Control of Blood Calcium The presence of calcium ions is critical to the functioning of all cells. In mammals, the two hormones parathyroid hormone and calcitonin regulate and stabilize the blood calcium level at about 10 mg/100 mL. When blood calcium levels f ...
Function
... Bekhterev - the role of the hippocampus in memory the 1950s - HM (patient) (Henry Gustav Molaison (1926– ...
... Bekhterev - the role of the hippocampus in memory the 1950s - HM (patient) (Henry Gustav Molaison (1926– ...
NewSChapter18
... hormones or paracrine factors that have effects beyond their tissues of origin. ▪Classes of Hormones- hormones can be divided into three groups based on their chemical structure; amino acid derivatives, peptide hormones, lipid derivatives. ▫Amino Acid Derivatives▫Peptide Hormones▫Lipid Derivatives- ...
... hormones or paracrine factors that have effects beyond their tissues of origin. ▪Classes of Hormones- hormones can be divided into three groups based on their chemical structure; amino acid derivatives, peptide hormones, lipid derivatives. ▫Amino Acid Derivatives▫Peptide Hormones▫Lipid Derivatives- ...
A Brief Look at Our Major Hormones
... 10% estrone, and 10% estradiol. This blend, called tri-estrogen, has been found to rapidly alleviate the symptoms of menopause without increasing the danger of breast cancer. Tri-estrogen is the blend of estrogens naturally found in a healthy young woman’s body. Phyto-estrogens are estrogenic compou ...
... 10% estrone, and 10% estradiol. This blend, called tri-estrogen, has been found to rapidly alleviate the symptoms of menopause without increasing the danger of breast cancer. Tri-estrogen is the blend of estrogens naturally found in a healthy young woman’s body. Phyto-estrogens are estrogenic compou ...
Structure and Functions of Important Endocrine Glands
... • In fish, sex hormones are produced by the gonads and these control maturation and development of secondary sexual characters • In male fish, hormones are believed to be secreted by the interstitial cells of the testis and these cells are involved in steriodogenesis • LH stimulates the testes to p ...
... • In fish, sex hormones are produced by the gonads and these control maturation and development of secondary sexual characters • In male fish, hormones are believed to be secreted by the interstitial cells of the testis and these cells are involved in steriodogenesis • LH stimulates the testes to p ...
Worksheet
... Inside cells, T4 can be converted to T3 (the more active form) by deiodinases DIO1 or DIO2. Deiodinase DIO3 does not appear to create active T3. Given these facts and the figures on the next page (from J. Bernal et al., Nature Reviews Endocrinology 11: 406-417, 2015), why might an MCT8 mutation af ...
... Inside cells, T4 can be converted to T3 (the more active form) by deiodinases DIO1 or DIO2. Deiodinase DIO3 does not appear to create active T3. Given these facts and the figures on the next page (from J. Bernal et al., Nature Reviews Endocrinology 11: 406-417, 2015), why might an MCT8 mutation af ...
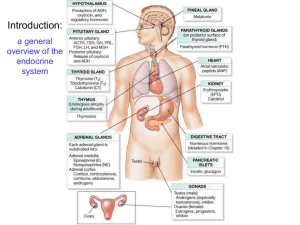
the Endocrine System
... Adapting to Stress • Hormones that regulate blood pressure/volume are also released during times of stress. • The nervous system activates the RAAS pathway in response to reduced blood flow to the kidneys (increasing Na+ reabsorption = increase fluid volume & BP) • The stressor activates the hypoth ...
... Adapting to Stress • Hormones that regulate blood pressure/volume are also released during times of stress. • The nervous system activates the RAAS pathway in response to reduced blood flow to the kidneys (increasing Na+ reabsorption = increase fluid volume & BP) • The stressor activates the hypoth ...
Body Rhythms & Mental States Chapter 5: Consciousness
... receptors in the back of the eye transmit into the SCN & allow it to respond to changes in light & dark • SCN sends out messages to respond to these changes ...
... receptors in the back of the eye transmit into the SCN & allow it to respond to changes in light & dark • SCN sends out messages to respond to these changes ...
PTA 198 Anatomy and Physiology
... 7. Be able to identify/locate the endocrine glands on charts and models, also explain/describe hormones produced by each gland, the effect of these hormones, their target tissue and disorders associated with increased or decreased production.. a. Hypothalamus: neurosecretory cells, infundibulum Horm ...
... 7. Be able to identify/locate the endocrine glands on charts and models, also explain/describe hormones produced by each gland, the effect of these hormones, their target tissue and disorders associated with increased or decreased production.. a. Hypothalamus: neurosecretory cells, infundibulum Horm ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.