Chapters 45, 48, 49 PPT
... NEUROSECRETORY CELLS located in the hypothalamus It is part of the lower brain ...
... NEUROSECRETORY CELLS located in the hypothalamus It is part of the lower brain ...
The Endocrine System - Palm Beach State College
... – Iodine (one or two atoms) is added to tyrosines within Tg – When two tyrosines within Tg meet, they link to each other forming forerunners of T3 (three iodines) and T4 (four ...
... – Iodine (one or two atoms) is added to tyrosines within Tg – When two tyrosines within Tg meet, they link to each other forming forerunners of T3 (three iodines) and T4 (four ...
endocrine system
... pituitary, connects the nervous and endocrine systems The hypothalamus – blurs the distinction between endocrine and nervous systems, – receives input from nerves about the internal conditions of the body and the external environment, – responds by sending out appropriate nervous or endocrine sign ...
... pituitary, connects the nervous and endocrine systems The hypothalamus – blurs the distinction between endocrine and nervous systems, – receives input from nerves about the internal conditions of the body and the external environment, – responds by sending out appropriate nervous or endocrine sign ...
One difference between axons and dendrites is that
... A. Endocrine hormones are released into synapses, whereas neurotransmitters are released into the bloodstream. B. Endocrine hormones can stimulate any cell in the body, whereas neurotransmitters can only influence cells with target receptors. C. Neurotransmitters are released into synapses, whereas ...
... A. Endocrine hormones are released into synapses, whereas neurotransmitters are released into the bloodstream. B. Endocrine hormones can stimulate any cell in the body, whereas neurotransmitters can only influence cells with target receptors. C. Neurotransmitters are released into synapses, whereas ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... Some hormones exert their influence by increasing the synthesis of cAMP ADH, TSH, ACTH, glucagon and epinephrine Some exert their influence by decreasing the level of cAMP growth hormone inhibiting hormone (somatostatin) Other substances can act as 2nd messengers calcium ions cGMP PI3 Tyrosine kinas ...
... Some hormones exert their influence by increasing the synthesis of cAMP ADH, TSH, ACTH, glucagon and epinephrine Some exert their influence by decreasing the level of cAMP growth hormone inhibiting hormone (somatostatin) Other substances can act as 2nd messengers calcium ions cGMP PI3 Tyrosine kinas ...
Lec. 3 - intro to Endo
... A. Circulating hormones = endocrine – 1. Pass into blood – 2. Act on distant target cells – 3. May be found in blood minutes to days after secretion – 4. Hormones may be stored on blood proteins for months (Thyroid hormone), blood concentrations remain constant. – 5. Active hormone – dissolved in pl ...
... A. Circulating hormones = endocrine – 1. Pass into blood – 2. Act on distant target cells – 3. May be found in blood minutes to days after secretion – 4. Hormones may be stored on blood proteins for months (Thyroid hormone), blood concentrations remain constant. – 5. Active hormone – dissolved in pl ...
Introduction to the Hypothalamo- Pituitary
... The short portal veins could enable reverse flow from the anterior pituitary to the posterior pituitary. This would result in a direct communication between the anterior pituitary and the hypothalamus via reverse axonal transport up the axons of the hypothalamic cells. This pathway would allow an eas ...
... The short portal veins could enable reverse flow from the anterior pituitary to the posterior pituitary. This would result in a direct communication between the anterior pituitary and the hypothalamus via reverse axonal transport up the axons of the hypothalamic cells. This pathway would allow an eas ...
Coordination of the human body
... • Goitre is an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can mean that all the thyroid gland is swollen or enlarged, or one or more swellings or lumps develop in a part or parts of the thyroid. • In some people, the goitre is associated with an abnormality of thyroid function. You may make too much thyroxine ...
... • Goitre is an enlarged thyroid gland. A goitre can mean that all the thyroid gland is swollen or enlarged, or one or more swellings or lumps develop in a part or parts of the thyroid. • In some people, the goitre is associated with an abnormality of thyroid function. You may make too much thyroxine ...
Overview of the Reticular Formation (RF)
... imaginary mental imagery. Finally, the cerebral cortex can inhibit other sensory input to allow us to focus our attention Neurotransmitter release: Aminergic neurons: Serotonergic – brainstem midline; reaches “all” CNS gray matter Dopaminergic – ventral tegmental nuclei (midbrain) Noradrenergi ...
... imaginary mental imagery. Finally, the cerebral cortex can inhibit other sensory input to allow us to focus our attention Neurotransmitter release: Aminergic neurons: Serotonergic – brainstem midline; reaches “all” CNS gray matter Dopaminergic – ventral tegmental nuclei (midbrain) Noradrenergi ...
Orientation to the Human Body
... Hormones from endocrine glands are released directly into tissue fluids; not through ducts Some affect many tissues ◦ Growth hormone ◦ Thyroid hormone ◦ Insulin Some affect a specific tissue (target tissue) ◦ Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) ◦ Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ...
... Hormones from endocrine glands are released directly into tissue fluids; not through ducts Some affect many tissues ◦ Growth hormone ◦ Thyroid hormone ◦ Insulin Some affect a specific tissue (target tissue) ◦ Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) ◦ Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) ...
3. Female Reproductive System WEB
... 2. Ovulation (day 14): • levels of LH reach its peak and initiate ovulation • Ovulation = egg is released from the dominant follicle 3. Luteal phase – after ovulation: • Ruptured follicle becomes corpus luteum and secretes estrogen and progesterone • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit ...
... 2. Ovulation (day 14): • levels of LH reach its peak and initiate ovulation • Ovulation = egg is released from the dominant follicle 3. Luteal phase – after ovulation: • Ruptured follicle becomes corpus luteum and secretes estrogen and progesterone • High levels of estrogen and progesterone inhibit ...
Hormones - Cengage
... All hormones bind target cells; this signal is converted into a form that works in the cell to change activity. ...
... All hormones bind target cells; this signal is converted into a form that works in the cell to change activity. ...
Hormones - prakashamarasooriya
... male and female sex hormones. Yet these differences are enough to allow for significant changes in the secondary sex characteristics. Both sexes have both sets of hormones Deficiencies in the sex hormones result in changes in external sex characteristics such as facial hair and genital size. Differe ...
... male and female sex hormones. Yet these differences are enough to allow for significant changes in the secondary sex characteristics. Both sexes have both sets of hormones Deficiencies in the sex hormones result in changes in external sex characteristics such as facial hair and genital size. Differe ...
AP Biology Chapter 45 Endocrine System Guided Notes
... throughout the body: the endocrine system and the nervous system • The __________________ secretes hormones that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses including reproduction, development, energy metabolism, growth, and behavior • The ________________ conveys high-speed electrical signals alo ...
... throughout the body: the endocrine system and the nervous system • The __________________ secretes hormones that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses including reproduction, development, energy metabolism, growth, and behavior • The ________________ conveys high-speed electrical signals alo ...
text - Systems Neuroscience Course, MEDS 371, Univ. Conn. Health
... and the basal ganglia and connect to the motor and premotor cortex, having a role in motor function. Nuclei Related to the Limbic System MD- Mediodorsal nucleus is positioned medially, close to ventricular surface and is connected to prefrontal cortex; it receives connections from the amygdala, glob ...
... and the basal ganglia and connect to the motor and premotor cortex, having a role in motor function. Nuclei Related to the Limbic System MD- Mediodorsal nucleus is positioned medially, close to ventricular surface and is connected to prefrontal cortex; it receives connections from the amygdala, glob ...
Endocrine/Lymph Notes - Website of Neelay Gandhi
... Carries Releasing Hormones (RH) from Hypothalamus to Anterior Pituitary RHs: TRH, GnRH, CRH (See Chart for fxns) Anterior Pituitary (Pars Distalis, Adenohypophysis, Pars Anterior) Collagenous Capsule Cords of Parenchymal Cells Derived from Roof of Pharynx Has Sinusoids supported by reticular fibers ...
... Carries Releasing Hormones (RH) from Hypothalamus to Anterior Pituitary RHs: TRH, GnRH, CRH (See Chart for fxns) Anterior Pituitary (Pars Distalis, Adenohypophysis, Pars Anterior) Collagenous Capsule Cords of Parenchymal Cells Derived from Roof of Pharynx Has Sinusoids supported by reticular fibers ...
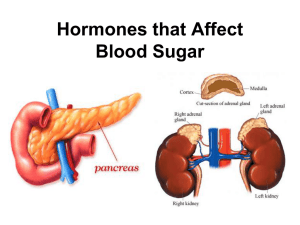
8.2 Hormones that Affect Blood Sugar - Ms. Pasic
... Calcitonin Calcitonin is also released by the thyroid, and it counter-acts parathyroid hormone (PTH) by: • Inhibiting Ca2+ absorption by the intestines • Inhibits Ca2+ reabsorption in the nephrons of the kidney ...
... Calcitonin Calcitonin is also released by the thyroid, and it counter-acts parathyroid hormone (PTH) by: • Inhibiting Ca2+ absorption by the intestines • Inhibits Ca2+ reabsorption in the nephrons of the kidney ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 10e
... Testosterone: development and maintenance of male sexual characteristics Ovaries (female) Estrogens: development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics Progesterone: supports pregnancy ...
... Testosterone: development and maintenance of male sexual characteristics Ovaries (female) Estrogens: development and maintenance of female sexual characteristics Progesterone: supports pregnancy ...
THE BRAIN DAMAGE IN FETAL ALCOHOL SYNDROME
... development in comparison with endogenous and exogenous factors during the postnatal period. Among factors, which negatively affect normal course of pregnancy and cause a variety of deviations in fetus and infant development, along with somatic and infectious diseases of a pregnant woman, a signific ...
... development in comparison with endogenous and exogenous factors during the postnatal period. Among factors, which negatively affect normal course of pregnancy and cause a variety of deviations in fetus and infant development, along with somatic and infectious diseases of a pregnant woman, a signific ...
session 16.rtf - Joyful Living Services
... with emotions. Many structures, including the hypothalamus, make up the limbic system, an area of the brain that processes feelings and emotions. The relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland provides the link between the nervous and glandular systems. The pituitary is a small gl ...
... with emotions. Many structures, including the hypothalamus, make up the limbic system, an area of the brain that processes feelings and emotions. The relationship between the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland provides the link between the nervous and glandular systems. The pituitary is a small gl ...
1-2 Endocrine tissues, hormones and actions 1
... This course covers the endocrinology of animals, including man: physiology and anatomy of the endocrine glands and the biosynthesis and chemistry of hormones. Upon completion of the course, each student should be able to discuss the actions of all hypothalamic, pituitary, and reproductive hormones. ...
... This course covers the endocrinology of animals, including man: physiology and anatomy of the endocrine glands and the biosynthesis and chemistry of hormones. Upon completion of the course, each student should be able to discuss the actions of all hypothalamic, pituitary, and reproductive hormones. ...
Endocrine System
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
... Prolactin – develops breast tissue, stimulates production of milk after childbirth TSH – Thyroid stimulating hormone – stimulates thyroid cells to produce thyroid hormone = thyroxine (low TSH treated with synthroid) ACTH – Adrenocortiocotropic hormone – stimulates adrenal cortex ...
Chapter 18
... • Thyroid Stimulating Hormone • Follicle Stimulating Hormone (testes and ovaries) • Luteinizing Hormone (testosterone and estrogen) • Prolactin ((milk secretion) • Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (adrenal gland) • Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (melanocytes) ...
... • Thyroid Stimulating Hormone • Follicle Stimulating Hormone (testes and ovaries) • Luteinizing Hormone (testosterone and estrogen) • Prolactin ((milk secretion) • Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone (adrenal gland) • Melanocyte Stimulating Hormone (melanocytes) ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.