Procedure For Laryngeal Tie Forward Surgery
... wire passer and retrieved. The procedure is repeated on the other side such that the dorsal (leader) and ventral (trailer) sutures of each side can be tied over the ventral aspect of the basihyoid. A bilateral partial sternothyroidectomy is performed at this time. The sutures on each side are then t ...
... wire passer and retrieved. The procedure is repeated on the other side such that the dorsal (leader) and ventral (trailer) sutures of each side can be tied over the ventral aspect of the basihyoid. A bilateral partial sternothyroidectomy is performed at this time. The sutures on each side are then t ...
The Endocrine System
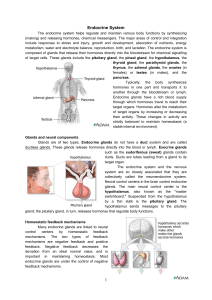
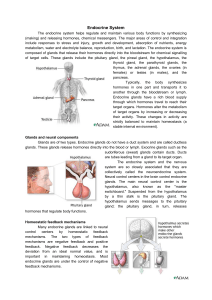
... can be created/excreted by cells, tissues or organs, collectively known as “glands” secreted via epithelial cells extracellular fluid blood stream receptors on target cells ducts are not used by endocrine system ...
... can be created/excreted by cells, tissues or organs, collectively known as “glands” secreted via epithelial cells extracellular fluid blood stream receptors on target cells ducts are not used by endocrine system ...
The Endocrine System Negative Feedback Mechanism
... Thyroid Gland Common Pathologies • Hypothyroidism – Underactive thyroid gland due to thyroid defect, postsurgical damage/removal, radiotherapy, iodine deficiency or congenital/autoimmune conditions. – Low metabolic rate; feeling chilled; constipation; thick, dry skin and puffy eyes; edema; lethargy; ...
... Thyroid Gland Common Pathologies • Hypothyroidism – Underactive thyroid gland due to thyroid defect, postsurgical damage/removal, radiotherapy, iodine deficiency or congenital/autoimmune conditions. – Low metabolic rate; feeling chilled; constipation; thick, dry skin and puffy eyes; edema; lethargy; ...
Giant Hormone Chart
... Stimulates the hydrolysis of stored energy (fat, glygocen) to glucose Lowers blood glucose level Stimulates the uptake of glucose ...
... Stimulates the hydrolysis of stored energy (fat, glygocen) to glucose Lowers blood glucose level Stimulates the uptake of glucose ...
The HUMAN BODY - davis.k12.ut.us
... Accelerates the transfer of glucose from the blood into the body’s cells Accelerates the conversion of glucose to ...
... Accelerates the transfer of glucose from the blood into the body’s cells Accelerates the conversion of glucose to ...
Unit 7 Powerpoint
... Accelerates the transfer of glucose from the blood into the body’s cells Accelerates the conversion of glucose to ...
... Accelerates the transfer of glucose from the blood into the body’s cells Accelerates the conversion of glucose to ...
Giant Hormone Chart
... Stimulates the hydrolysis of stored energy (fat, glygocen) to glucose Lowers blood glucose level Stimulates the uptake of glucose ...
... Stimulates the hydrolysis of stored energy (fat, glygocen) to glucose Lowers blood glucose level Stimulates the uptake of glucose ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS
... Wraps around the upper part of the trachea just below the larynx Produces the hormone, thyroxine; need iodine in your diets affects most cells of the body by regulating metabolic rates Hyperthyroidism: too much thyroxine is produced Hypothyroidism: too little thyroxine is produced ...
... Wraps around the upper part of the trachea just below the larynx Produces the hormone, thyroxine; need iodine in your diets affects most cells of the body by regulating metabolic rates Hyperthyroidism: too much thyroxine is produced Hypothyroidism: too little thyroxine is produced ...
Endocrine Physiology
... C. Transport of Hormones Hormones are transported throughout the body by the bloodstream to ALL cells A given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called target cells Only the TARGET CELLS with the RECEPTOR for the hormone will be affected by that hormone ...
... C. Transport of Hormones Hormones are transported throughout the body by the bloodstream to ALL cells A given hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called target cells Only the TARGET CELLS with the RECEPTOR for the hormone will be affected by that hormone ...
Endocrine System
... glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules in the kidneys. Conversely, if blood calcium increases too much, the parathyroid glands ...
... glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones and increases the calcium uptake into the bloodstream from the collecting tubules in the kidneys. Conversely, if blood calcium increases too much, the parathyroid glands ...
pituitary gland - Sewanhaka Central High School District
... of body and limb, while “midget” referred to those of reduced stature but normal proportions; today neither word is used, the term “little people” is widely accepted ...
... of body and limb, while “midget” referred to those of reduced stature but normal proportions; today neither word is used, the term “little people” is widely accepted ...
Endocrine System
... regulation of the blood calcium level. The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone, which regulates the blood calcium amount. If calcium decreases, the parathyroid glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones ...
... regulation of the blood calcium level. The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone, which regulates the blood calcium amount. If calcium decreases, the parathyroid glands sense the decrease and secrete more parathyroid hormone. The parathyroid hormone stimulates calcium release from the bones ...
Endocrine Control of the Lacrimal Gland
... Endocrine Control of the Lacrimal Gland Eduardo M. Rocha Departamento de Oftalmologia, Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço, FMRP-USP Lacrimal gland structure and function are regulated by hormones; therefore hormone dysfunction may affect not just tears production and ocular surface ...
... Endocrine Control of the Lacrimal Gland Eduardo M. Rocha Departamento de Oftalmologia, Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia de Cabeça e Pescoço, FMRP-USP Lacrimal gland structure and function are regulated by hormones; therefore hormone dysfunction may affect not just tears production and ocular surface ...
1 - davis.k12.ut.us
... known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained for longer periods of time. The endocrine system works primarily on negative feedback mechanisms. 2. Define the term hormone and describe how a hormone functions. Hormones are chemical messengers released ...
... known as hormones. Unlike the nervous system, the effects of the endocrine system are sustained for longer periods of time. The endocrine system works primarily on negative feedback mechanisms. 2. Define the term hormone and describe how a hormone functions. Hormones are chemical messengers released ...
Biology 30 Notes October 3, 2014 Introduction Endocrine System
... the body metabolizes fats, proteins, and carbohydrates for energy. The thyroid gland lies directly below the larynx (voice box) and has two lobes one on either side of trachea (windpipe). Thyroxine is controlled by a negative feedback. 1) The anterior pituitary releases TSH, thyroid stimulating horm ...
... the body metabolizes fats, proteins, and carbohydrates for energy. The thyroid gland lies directly below the larynx (voice box) and has two lobes one on either side of trachea (windpipe). Thyroxine is controlled by a negative feedback. 1) The anterior pituitary releases TSH, thyroid stimulating horm ...
The Thyroid Gland: Function and Regulation
... • To maintain normal levels of metabolic activity in the body, precisely the right amount of thyroid hormone must be secreted at all times • TSH, also known as thyrotropin, is an anterior pituitary hormone, a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of about 28,000. • The most important early effect ...
... • To maintain normal levels of metabolic activity in the body, precisely the right amount of thyroid hormone must be secreted at all times • TSH, also known as thyrotropin, is an anterior pituitary hormone, a glycoprotein with a molecular weight of about 28,000. • The most important early effect ...
lec4 - Zoology, UBC
... More than 98% of the gland is made up of acinar cells producing an enzyme-rich juice that enters a system of ducts and is delivered to the duodenum of the small intestine during food ...
... More than 98% of the gland is made up of acinar cells producing an enzyme-rich juice that enters a system of ducts and is delivered to the duodenum of the small intestine during food ...
Chapter 9- Endocrine System
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
... Hormones are not secreted at a constant rate. Hormone secretion varies with the body’s needs This is accomplished by FEEDBACK. ...
Hormones
... Prolactin • Produces after childbirth causing mammary glands to develop and produce milk. ...
... Prolactin • Produces after childbirth causing mammary glands to develop and produce milk. ...
Endocrine Power PointPresentation1
... TSH - stimulates thyroxine ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE – ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE – FSH -stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in males LUTEINIZING HORMONE – LH – stimulates ovulation and formation of ...
... TSH - stimulates thyroxine ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE – ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE – FSH -stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in males LUTEINIZING HORMONE – LH – stimulates ovulation and formation of ...
Endocrinology - You Can Do It! | Physical Therapy Students
... • Inadequate secretion of cortisol and aldosterone • Characterized by: Hypoglycemia: because of low cortisol. Na+ loss and K+ retention: because of low aldosterone. Dehydration: because of Na+ and water loss. Hypotension: because of Na+ and water loss. Rapid wieght loss: because cortisol i ...
... • Inadequate secretion of cortisol and aldosterone • Characterized by: Hypoglycemia: because of low cortisol. Na+ loss and K+ retention: because of low aldosterone. Dehydration: because of Na+ and water loss. Hypotension: because of Na+ and water loss. Rapid wieght loss: because cortisol i ...
Absence of Isthmus of Thyroid Gland - A Case Report
... Thyroid gland is made of the 2 lateral masses ( lobes ) and central narrow connecting portion ( isthmus ) . Isthmus lies anterior to the upper part of trachea ( over 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings usually ) . Incidence of agenesis of the thyroid isthmus has been reported to vary from 5% to 10% by Pastor ...
... Thyroid gland is made of the 2 lateral masses ( lobes ) and central narrow connecting portion ( isthmus ) . Isthmus lies anterior to the upper part of trachea ( over 2nd and 3rd tracheal rings usually ) . Incidence of agenesis of the thyroid isthmus has been reported to vary from 5% to 10% by Pastor ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.