* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Giant Hormone Chart
History of catecholamine research wikipedia , lookup
Glycemic index wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac physiology wikipedia , lookup
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Hyperthyroidism wikipedia , lookup
Hypothalamus wikipedia , lookup
Hyperandrogenism wikipedia , lookup
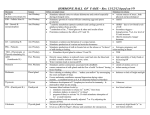
Giant Hormone Chart HORMONE NAME CHEMICAL CLASS RELATIONSHIP TO OTHER HORMONES RELEASING GLAND MAJOR FUNCTIONS ROLE IN HOMEOSTASIS? WHY IMPORTANT? TARGET: CELL, ORGAN, GLAND HYPERSECRETION &/OR HYPOSECRETION DISORDERS Endorphins Pain receptors in the brain Growth Hormone Bones Glucocorticoids Steroid Regulated by ACTH Adrenal Cortex Raise blood glucose level Mineralocorticoids Steroid Adrenal Cortex Aldosterone Steroid Triggered by angiotensin II Epinephrine Amine Synergistic effects w/ norepinephrine Adrenal glands (on top of kidneys) Adrenal medulla Promote re-absorption of Na and excretion of K in kidneys Prevent drop in blood pressure + Reabsorb Na & H2O from urine Fight vs. flight response Increase metabolic activities Raise blood glucose level Constrict certain blood vessels Norepinephrine + Cells in kidney + Synergistic effects w/ epinephrine Adrenal medulla Anterior pituitary Adrenal cortex Structurally similar to LH & TSH Anterior pituitary Testes/ovaries Stimulates adrenal cortex to secrete glucocorticoids/ steroid hormones Stimulates production of ova & sperm Hyposecretion: dwarfism Hypersecretion: giantism Structurally similar to FSH & TSH Anterior pituitary Testes/ovaries Stimulates growth (esp. bones) Metabolic functions Stimulates production of growth factors (ex. Insulinlike growth factors (IGFs), etc.) Stimulates ovaries & testes Anterior pituitary Mammary glands Stimulates production of T3 & T4 Structurally similar to LH & FSH Anterior pituitary Thyroid Stimulates milk production/secretion Varied effects from species to species Stimulates thyroid gland Anterior pituitary Melanocytes Regulates activity of pigment-containing cells in skin Posterior pituitary Collecting ducts in kidneys Posterior pituitary Mammary glands, uterine muscles Hyposecretion : Diabetes insipidus Ovaries ACTH Peptide FSH Glycoprotein GH Protein LH Glycoprotein Prolactin (PRL) Protein TSH Glycoprotein MSH Peptide ADH (Vassopressin) Peptide Oxytocin Peptide N/a; regulated by water/salt balance Estrogens Steroid Regulated by FSH & LH Anterior pituitary Prevent dehydration Reabsorb water from urine Stimulates contraction of uterus & mammary gland cells Mammary glands secrete milk Stimulate uterine lining growth nd Promote development & maint. of female 2 sex chara. Progesterone Steroid Regulated by FSH & LH Ovaries Glucagon Protein Antagonistic to Insulin Pancreas Mostly liver, some body cells Insulin Protein Antagonistic to glucagon Pancreas Fat cells, muscle cells, red blood cells Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Peptide Opposite effect of calcitonin Works with active Vit. D Parathyroid glands (embedded in surface of thyroid) Osteoclasts (in bone) Kidneys Melatonin Amine Pineal gland Prostaglandins Modified fatty acids (lipid) Androgens (ex. Testosterone) Thymosin Steroid SCN cells in brain (biological clock) Uterine muscles Peptide Thymus Calcitonin Peptide Opposite effect of PTH Thyroid Lowers blood calcium level T3 Amine Converted from T4 Thyroid T4 Amine T4 converted to T3 Thyroid Maintains normal blood pressure, heart rate, muscle tone, digestion, reproductive functions Increasing rate of O2 consumption & cellular metabolism HORMONE NAME CHEMICAL CLASS PGE (muscles relax) PGF (muscles contract) Antagonostic to each other Regulated by FSH & LH RELATIONSHIP TO OTHER HORMONES Placenta Testes RELEASING GLAND TARGET: CELL, ORGAN, GLAND Promotes uterine lining growth Raises blood glucose level Stimulates the hydrolysis of stored energy (fat, glygocen) to glucose Lowers blood glucose level Stimulates the uptake of glucose Raises blood calcium level 2+ Osteoclasts – decompose bone & release Ca 2+ Kidneys – resabsorb Ca & convert Vitamin D to active form Involved in biological rhythms (light/dark cycles) Stimulate contraction of smooth muscles in uterine wall Local regulators Helps induce labor Support sperm formation nd Promote development & maint. of male 2 sex chara. Stimulates T lymphocytes- MAJOR FUNCTIONS ROLE IN HOMEOSTASIS? WHY IMPORTANT? Hyposecretion: diabetes mellitus Type 1 – autoimmune disorder, pancreas is attacked Type 2 – reduced responsiveness to insulin Hyposecretion: tetany – convlusive contractions of skeletal muscles (fatal) Hyposecretion: cretinism = slow skeletal growth & poor mental development Lack of iodine: goiter HYPERSECRETION &/OR HYPOSECRETION DISORDERS