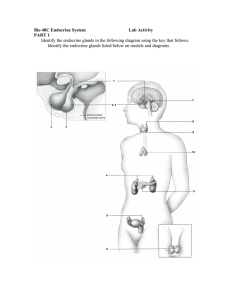
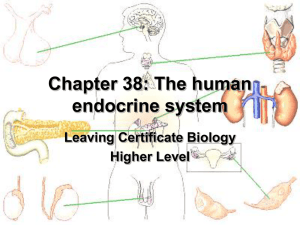
Chapter 10
... So let’s say there’s too much glucose in your blood. Your pancreatic islets cells send insulin into the blood which tells your cells to start absorbing all the glucose, thereby decreasing the concentration of glucose in your blood. The hormone in this situation is insulin, and you can deduce how it ...
... So let’s say there’s too much glucose in your blood. Your pancreatic islets cells send insulin into the blood which tells your cells to start absorbing all the glucose, thereby decreasing the concentration of glucose in your blood. The hormone in this situation is insulin, and you can deduce how it ...
Endocrine Problems after Childhood Cancer: Hypopituitarism
... have enough LH and FSH during puberty, there can be problems with pubertal development. For more information about male and female hormonal issues, see the related Health Links: Male Health Issues after Childhood Cancer Treatment and Female Health Issues after Childhood Cancer Treatment. Thyroid Sti ...
... have enough LH and FSH during puberty, there can be problems with pubertal development. For more information about male and female hormonal issues, see the related Health Links: Male Health Issues after Childhood Cancer Treatment and Female Health Issues after Childhood Cancer Treatment. Thyroid Sti ...
Chemical Regulation Endocrine System communication
... Chemicals released into the blood stream from a gland Needed in very small amounts Contain receptor molecules Act on specific parts of the body – Ex: Insulin will “lock in” to blood cell receptors to lower blood sugar. Insulin cannot “lock in” to other body cells because the receptor sites don’t mat ...
... Chemicals released into the blood stream from a gland Needed in very small amounts Contain receptor molecules Act on specific parts of the body – Ex: Insulin will “lock in” to blood cell receptors to lower blood sugar. Insulin cannot “lock in” to other body cells because the receptor sites don’t mat ...
The Endocrine System
... Endocrine System • Endocrine tissue is made up of cells that release chemicals directly into bloodstream. • Some organs are entirely endocrine in function. They are referred to as endocrine glands like pituitary glands, pineal body, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and adrenal glands. • Groups of ...
... Endocrine System • Endocrine tissue is made up of cells that release chemicals directly into bloodstream. • Some organs are entirely endocrine in function. They are referred to as endocrine glands like pituitary glands, pineal body, thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, and adrenal glands. • Groups of ...
Chapter 13 Endocrine System
... – Plays a part in supporting body’s biological clock • Regulation of patterns of eating, sleeping, and reproduction ...
... – Plays a part in supporting body’s biological clock • Regulation of patterns of eating, sleeping, and reproduction ...
The Endocrine System - Catherine Huff's Site
... • If body does not have receptor, hormone will pass by. • Only certain hormones can fit to receptors and when it occurs, then it changes the activity of the cell. ...
... • If body does not have receptor, hormone will pass by. • Only certain hormones can fit to receptors and when it occurs, then it changes the activity of the cell. ...
“Calm Your Hormones!”
... A system of “ductless” glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream Chemical “messengers” Distributed throughout body Only affect certain “target” cells If they have the corresponding receptor molecules ...
... A system of “ductless” glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream Chemical “messengers” Distributed throughout body Only affect certain “target” cells If they have the corresponding receptor molecules ...
Endocrine Systems - Science Geek.net
... a. Stimulates the uptake of calcium by bones b. Inhibits absorption of calcium in the intestine Other Glands and Hormones A. Pineal Gland 1. Secretes hormone melatonin a. Function is not known b. At lowest level after onset of puberty (1) Possible inhibitor of sexual development 2. Regulates annual ...
... a. Stimulates the uptake of calcium by bones b. Inhibits absorption of calcium in the intestine Other Glands and Hormones A. Pineal Gland 1. Secretes hormone melatonin a. Function is not known b. At lowest level after onset of puberty (1) Possible inhibitor of sexual development 2. Regulates annual ...
Endocrine System
... steroid hormone receptors after they have diffused into the cell through the plasma membrane – the receptors and hormones enter the nucleus and bind to the target regions in genes that regulate transcription turning the genes on and off ...
... steroid hormone receptors after they have diffused into the cell through the plasma membrane – the receptors and hormones enter the nucleus and bind to the target regions in genes that regulate transcription turning the genes on and off ...
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE QUESTIONS
... 14. This hormone from the anterior pituitary stimulates growth and development of the follicles in the ovaries? _______________________________________________ 15. As the maturing follicle grows, it secretes increasing amounts of _______________. This causes a surge of ______________________________ ...
... 14. This hormone from the anterior pituitary stimulates growth and development of the follicles in the ovaries? _______________________________________________ 15. As the maturing follicle grows, it secretes increasing amounts of _______________. This causes a surge of ______________________________ ...
Hormones and puberty
... Health & Human Development Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites ...
... Health & Human Development Hormones and puberty Hormones play an important role in controlling or regulating many processes in the body, including physical development during youth. They are often referred to as ‘chemical messengers’ because they circulate in the bloodstream and act on various sites ...
Endocrine System
... gland that produces hormones that regulate many basic functions such as hunger, thirst and sleep through control of the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus receives sensory input from receptors and perceptual information from the brain, such as changes in emotional state, temperature, and lighting. Th ...
... gland that produces hormones that regulate many basic functions such as hunger, thirst and sleep through control of the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus receives sensory input from receptors and perceptual information from the brain, such as changes in emotional state, temperature, and lighting. Th ...
The Endocrine System
... cleaning products, cancer treatments and pesticides are known endocrine disruptors and have disastrous effects on fish populations. Largemouth Bass commonly affected by endocrine disruptors Endocrine disruptors that mimic estrogen hormones have a severe impact on fish fertility and reproduction. The ...
... cleaning products, cancer treatments and pesticides are known endocrine disruptors and have disastrous effects on fish populations. Largemouth Bass commonly affected by endocrine disruptors Endocrine disruptors that mimic estrogen hormones have a severe impact on fish fertility and reproduction. The ...
The Endocrine System
... immunoglobulin, thyroid growth-stimulating immunoglobulin, TSH-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin Diffuse hypertrophy and hyperplasia with tall, crowded follicular cells ...
... immunoglobulin, thyroid growth-stimulating immunoglobulin, TSH-binding inhibitor immunoglobulin Diffuse hypertrophy and hyperplasia with tall, crowded follicular cells ...
File - Endocrine System
... _____ kidneys (KID-nē) Endocrine cells in the kidneys produce hormones important for calcium metabolism, blood volume, and blood pressure.). _____ heart (Specialized muscle cells in the heart produce a hormone that regulates blood pressure and blood volume.) _____ thymus gland (THĪ-mus) (The thymus ...
... _____ kidneys (KID-nē) Endocrine cells in the kidneys produce hormones important for calcium metabolism, blood volume, and blood pressure.). _____ heart (Specialized muscle cells in the heart produce a hormone that regulates blood pressure and blood volume.) _____ thymus gland (THĪ-mus) (The thymus ...
THYROID/PARATHYROID - Orange Coast College
... 3. Anterior & lateral to larynx, trachea 4. Lobes connected by an isthmus 5. Pyramidal lobe may be present 6. Normally not palpable ...
... 3. Anterior & lateral to larynx, trachea 4. Lobes connected by an isthmus 5. Pyramidal lobe may be present 6. Normally not palpable ...
ENDOCRINE GLANDS • Secrete hormones directly into
... • May be due to lack of iodine (simple goiter) • Major cause of other types is inflammation of thyroid which destroys the ability of the gland to make thyroxine • Symps – dry and itchy skin, dry and brittle hair, constipation, muscle cramps at night Summer 2002 P.26 ...
... • May be due to lack of iodine (simple goiter) • Major cause of other types is inflammation of thyroid which destroys the ability of the gland to make thyroxine • Symps – dry and itchy skin, dry and brittle hair, constipation, muscle cramps at night Summer 2002 P.26 ...
Unit 7 Endocrine
... The thyroid gland is located just below the larynx with its lobes lying on either side of the trachea The right and left lobes are connected to each other by the isthmus The only gland that can store its secretory product in large quantities – normally about a 100 day supply ...
... The thyroid gland is located just below the larynx with its lobes lying on either side of the trachea The right and left lobes are connected to each other by the isthmus The only gland that can store its secretory product in large quantities – normally about a 100 day supply ...
The Endocrine System - Leaving Cert Biology
... biorhythms such as sleep and menstrual cycle • Pituitary (master gland) – controls all other glands: secretes many hormones – one example is growth hormone (GH) stimulates protein synthesis and bone elongation (growth) ...
... biorhythms such as sleep and menstrual cycle • Pituitary (master gland) – controls all other glands: secretes many hormones – one example is growth hormone (GH) stimulates protein synthesis and bone elongation (growth) ...
Endocrine Glands and Hormones Hormone
... world where soil was poor in iodine. T4 has 4 iodine atoms. Hypothyroidism, low metabolic rate, overweight, tired. Treated with radioactive iodine, which will kill off the thyroid. 131I has a short half-life. 2) toxic goiter – autoimmune disease; people produce an antibody that acts like TSH, which ...
... world where soil was poor in iodine. T4 has 4 iodine atoms. Hypothyroidism, low metabolic rate, overweight, tired. Treated with radioactive iodine, which will kill off the thyroid. 131I has a short half-life. 2) toxic goiter – autoimmune disease; people produce an antibody that acts like TSH, which ...
The Endocrine System Coloring Activities
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
Origin and Location of Thyroid Gland - eCurriculum
... week of gestation Forms in the floor of the primitive pharynx Thyroid diverticulum is the anlagen Foramen cecum of the tongue is the site of its origin ...
... week of gestation Forms in the floor of the primitive pharynx Thyroid diverticulum is the anlagen Foramen cecum of the tongue is the site of its origin ...
Endocrine Color Sheet Questions
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
... Assignment: Read the overview on the Coloring Activity and color when instructed to do so. Then answer the questions below. 1. The endocrine glands are__ductless_glands that secrete _hormones_ directly into body fluids. The job of hormones is to help the body maintain _homeostasis_also known as biol ...
Dr. AASHISH H. PANCHAL (M.PHARM., Ph.D.) GSEB, CBSE, ICSE
... CHAPTER-2 Endocrine System Marks:40 ...
... CHAPTER-2 Endocrine System Marks:40 ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.