Lecture 8 - Endocrine
... Function • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine sy ...
... Function • Influences growth, metabolism, and homeostasis over prolonged periods • Secretes hormone products into interstitial spaces which are then absorbed into the blood and transported throughout the body • Hormonal control is much slower than nervous control, but the effects of the endocrine sy ...
The Endocrine Syetem
... secretes choriongonadotropin hormone - maintains corpus luteum - high in urine = pregnancy ...
... secretes choriongonadotropin hormone - maintains corpus luteum - high in urine = pregnancy ...
Objectives for Chapter 9
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
... 1. Define negative feedback and understand how the endocrine system uses negative feedback mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. 2. Know the 3 different kinds of hormones and their mechanisms of action (i.e. how they bring about their effect in the body) 3. Locate on a diagram and describe the functio ...
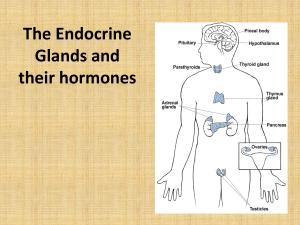
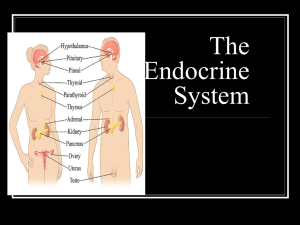
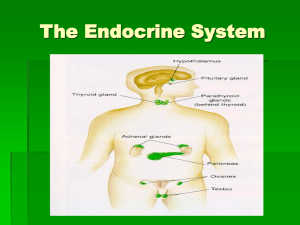
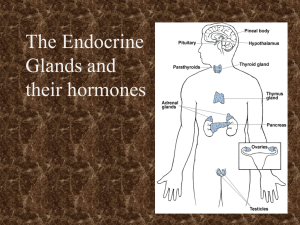
Endocrine Glands
... • Function: increases metabolic rate and oxygen consumption (break down carbohydrates and fats, synthesize proteins) • Can only be made by follicular cells when iodide is available • Controlled by anterior pituitary lobe through TSH levels. ...
... • Function: increases metabolic rate and oxygen consumption (break down carbohydrates and fats, synthesize proteins) • Can only be made by follicular cells when iodide is available • Controlled by anterior pituitary lobe through TSH levels. ...
4. Heavy Metal Detox - I recommend using a
... roll up her sleeves and master the various mechanisms of Hashimoto’s. The more you understand Hashimoto’s the more likely you are to successfully manage your health. ...
... roll up her sleeves and master the various mechanisms of Hashimoto’s. The more you understand Hashimoto’s the more likely you are to successfully manage your health. ...
The Endocrine System - BIOLOGY and HONORS PHYSIOLOGY Mr
... Located at the base of the throat, and shaped like a butterfly, the Thyroid Gland is actually 2 glands in one… Secretes the hormone thyroxine to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the bloodstream. Iodine is an integral element in this hormone. Secretes calcitonin to re ...
... Located at the base of the throat, and shaped like a butterfly, the Thyroid Gland is actually 2 glands in one… Secretes the hormone thyroxine to regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins in the bloodstream. Iodine is an integral element in this hormone. Secretes calcitonin to re ...
Endocrine System
... glycine produces 2,5,3’-triiodotyrosine, known as T3. The coupling of two molecules of diiodotyrosine with loss of H2O and glycine produces thyroxine, known as T4. ...
... glycine produces 2,5,3’-triiodotyrosine, known as T3. The coupling of two molecules of diiodotyrosine with loss of H2O and glycine produces thyroxine, known as T4. ...
The Endocrine System
... • Composed of tiny follicles, where thyroid hormone is produced. • Each follicle consists of globule surrounding thyroid precursor called a colloid. • Only endocrine gland that stores large amounts of hormone precursor for use later. • Produces two hormones: • Thyroid hormone • Calcitonin ...
... • Composed of tiny follicles, where thyroid hormone is produced. • Each follicle consists of globule surrounding thyroid precursor called a colloid. • Only endocrine gland that stores large amounts of hormone precursor for use later. • Produces two hormones: • Thyroid hormone • Calcitonin ...
Chapter 15: Endocrine System
... Na+ by the kidneys; affects blood pressure) 2) _________corticoids(chiefly _________ which helps the body resist stress by keeping blood sugar levels relatively constant and maintaining blood volume and preventing water shift into tissue) ...
... Na+ by the kidneys; affects blood pressure) 2) _________corticoids(chiefly _________ which helps the body resist stress by keeping blood sugar levels relatively constant and maintaining blood volume and preventing water shift into tissue) ...
PowerPoint
... Endocrine: glandular secretion of substances inside the body Exocrine: glandular secretion of substances outside the body (sweat gland, liver, pancreas) The endocrine system uses hormones to convey information through the bloodstream ...
... Endocrine: glandular secretion of substances inside the body Exocrine: glandular secretion of substances outside the body (sweat gland, liver, pancreas) The endocrine system uses hormones to convey information through the bloodstream ...
Endocrine System
... III. Peripheral endocrine organs A. Thymus – Fig. 18.5 - several hormones involved in T cell maturation B. Thyroid gland - Fig. 18.6 - largest endocrine gland in adults, inferior to larynx - left and right lateral lobes connected by isthmus - thyroid hormone uniquely contains iodine - produced and ...
... III. Peripheral endocrine organs A. Thymus – Fig. 18.5 - several hormones involved in T cell maturation B. Thyroid gland - Fig. 18.6 - largest endocrine gland in adults, inferior to larynx - left and right lateral lobes connected by isthmus - thyroid hormone uniquely contains iodine - produced and ...
Nervous co-ordination gives control. Endocrine co
... Hormones are produced by the hypothalamus & stored in posterior pituitary. They are released by nervous impulses from the hypothalamus. ...
... Hormones are produced by the hypothalamus & stored in posterior pituitary. They are released by nervous impulses from the hypothalamus. ...
Endocrine (regulatory) System
... Name the nine major endocrine glands found in the body. Which one ins called the “master gland”? Name three major local regulators that act on nearby target cells. (pgs. 947-948) Name three key molecules that play a role in the signal transduction pathway (typical reactions in the endocrine system). ...
... Name the nine major endocrine glands found in the body. Which one ins called the “master gland”? Name three major local regulators that act on nearby target cells. (pgs. 947-948) Name three key molecules that play a role in the signal transduction pathway (typical reactions in the endocrine system). ...
The Endocrine System
... This bilobed gland contains many follicles. A follicle is a group of cells encircling a lumen. The lumen contains material called colloid (a glycoprotein) within it. As hormones are produced by the cells, the hormones are either released into the colloid or directly into the blood. There are also ex ...
... This bilobed gland contains many follicles. A follicle is a group of cells encircling a lumen. The lumen contains material called colloid (a glycoprotein) within it. As hormones are produced by the cells, the hormones are either released into the colloid or directly into the blood. There are also ex ...
chapter 18 the endocrine system
... 11. Which of the following has both endocrine and exocrine functions? a. pancreas b. anterior pituitary c. thyroid d. adrenal medulla 12. Which of the following produce antagonistic results? a. FSH and LH b. calcitonin and parathyroid hormone c. ADH and vasopressin d. oxytocin and prolactin 13. Tro ...
... 11. Which of the following has both endocrine and exocrine functions? a. pancreas b. anterior pituitary c. thyroid d. adrenal medulla 12. Which of the following produce antagonistic results? a. FSH and LH b. calcitonin and parathyroid hormone c. ADH and vasopressin d. oxytocin and prolactin 13. Tro ...
HUMAN ENDOCRINE SYSTEM 28 MAY 2014
... person in Diagram II needs to be lowered at the end of the race. ...
... person in Diagram II needs to be lowered at the end of the race. ...
Thyroxine (T4): An Overview
... target cells and the liver by active transport and migrate to the nucleus where they bind to specific nuclear receptor proteins. In the target cells, enzymes remove one of thyroxine's four iodine atoms converting the hormone into the highly active triiodothyronine. Thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) ar ...
... target cells and the liver by active transport and migrate to the nucleus where they bind to specific nuclear receptor proteins. In the target cells, enzymes remove one of thyroxine's four iodine atoms converting the hormone into the highly active triiodothyronine. Thyroid hormone receptors (TRs) ar ...
Endocrine System
... two affect non-endocrine organs tropic hormones: stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones all are proteins ...
... two affect non-endocrine organs tropic hormones: stimulate other endocrine glands to secrete hormones all are proteins ...
EndocrineSystem
... The endocrine system is one of the major body systems used for communication. A major function of the endocrine system is to maintain homeostasis. It is composed of tissue called glands. The messages sent are in the form of hormones. A hormone is a compound produced in one part of the body, travels ...
... The endocrine system is one of the major body systems used for communication. A major function of the endocrine system is to maintain homeostasis. It is composed of tissue called glands. The messages sent are in the form of hormones. A hormone is a compound produced in one part of the body, travels ...
Hormones of the Body
... gland regulating its’ development and regulates thyroxine levels using negative feedback loops ...
... gland regulating its’ development and regulates thyroxine levels using negative feedback loops ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.