Hormones
... What is the endocrine system? • The word Endocrine derives from Greek origin • The endocrine system is the collection of glands in which each gland secretes a different type of hormone that regulates: • Metabolism • Growth & Development • Tissue Function • Sexual Function • Reproduction • Sleep & M ...
... What is the endocrine system? • The word Endocrine derives from Greek origin • The endocrine system is the collection of glands in which each gland secretes a different type of hormone that regulates: • Metabolism • Growth & Development • Tissue Function • Sexual Function • Reproduction • Sleep & M ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system
... "shield", after its shape) is one of the larger endocrine glands in the body. It is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growth and rate of function of many other ...
... "shield", after its shape) is one of the larger endocrine glands in the body. It is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growth and rate of function of many other ...
Endocrinology - NCORD Healthcare LLC
... Thyroid gland - an endocrine gland located just below the Adam's apple in the neck; it produces hormones that play a key role in regulatiing blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, metabolism, and how the body reacts to other hormones. The thyroid gland uses iodine to manufacture hormones. The ...
... Thyroid gland - an endocrine gland located just below the Adam's apple in the neck; it produces hormones that play a key role in regulatiing blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, metabolism, and how the body reacts to other hormones. The thyroid gland uses iodine to manufacture hormones. The ...
Thyroid hormones
... 1- Major effect of T3 & T4 is to enhance general protein synthesis essential for growth. for example: T3 enhances transcription of growth hormone (GH) itself. (anabolic effects of T3) However, very high T3 levels in blood causes inhibition of protein synthesis. 2- Thyroid hormones are essential for ...
... 1- Major effect of T3 & T4 is to enhance general protein synthesis essential for growth. for example: T3 enhances transcription of growth hormone (GH) itself. (anabolic effects of T3) However, very high T3 levels in blood causes inhibition of protein synthesis. 2- Thyroid hormones are essential for ...
Document
... “Hormones coordinate cell, tissue, and organ activities on a sustained basis. They circulate in the extracellular fluid and bind to specific receptors on or in target cells. They then modify cellular activities by altering membrane permeability, activating or inactivating key enzymes, or changing ge ...
... “Hormones coordinate cell, tissue, and organ activities on a sustained basis. They circulate in the extracellular fluid and bind to specific receptors on or in target cells. They then modify cellular activities by altering membrane permeability, activating or inactivating key enzymes, or changing ge ...
Head, Neck and Oral Exam: Chapter 8 (pp 179
... then checks the consistency and configuration of the left thyroid lobe with and without swallowing. To do this, he/she palpates the full length of the left lobe using the fingertips of his/her right hand and palpating in a posteriomedial direction. The hands are reversed and this technique repeated ...
... then checks the consistency and configuration of the left thyroid lobe with and without swallowing. To do this, he/she palpates the full length of the left lobe using the fingertips of his/her right hand and palpating in a posteriomedial direction. The hands are reversed and this technique repeated ...
Endocrine SystemExam
... 9. This is the gland that regulates the levels of calcium in the bloodstream: a. A b. D c. C d. B 10. Testosterone is secreted by this gland: a. H b. G c. A d. F 11. The gland found in the brain that “connects” the nervous system and the endocrine system is called the: a. Parathyroid b. Thyroid c. ...
... 9. This is the gland that regulates the levels of calcium in the bloodstream: a. A b. D c. C d. B 10. Testosterone is secreted by this gland: a. H b. G c. A d. F 11. The gland found in the brain that “connects” the nervous system and the endocrine system is called the: a. Parathyroid b. Thyroid c. ...
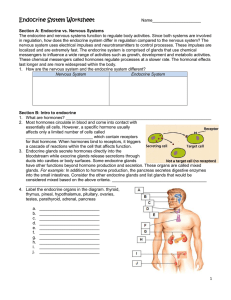
Endocrine System Worksheet
... 1. What are hormones? _______________________________________________________________ 2. Most hormones circulate in blood and come into contact with essentially all cells. However, a specific hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called _____________________________ which contain re ...
... 1. What are hormones? _______________________________________________________________ 2. Most hormones circulate in blood and come into contact with essentially all cells. However, a specific hormone usually affects only a limited number of cells called _____________________________ which contain re ...
Chapter 15
... What happens when the body produces too much or too little GH? • Pituitary dwarfism – too little GH is produced during childhood that results in small stature • Giantism – too much GH is produced during childhood that results in poor health • Acromegaly – overproduction of GH as an adult that result ...
... What happens when the body produces too much or too little GH? • Pituitary dwarfism – too little GH is produced during childhood that results in small stature • Giantism – too much GH is produced during childhood that results in poor health • Acromegaly – overproduction of GH as an adult that result ...
The Endocrine System
... melanocyte-stimulating hormone, prolactin 4. Posterior lobe – antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin 5. Often called “master gland”, but its secretions are actually controlled by the hypothalamus ...
... melanocyte-stimulating hormone, prolactin 4. Posterior lobe – antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin 5. Often called “master gland”, but its secretions are actually controlled by the hypothalamus ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... Secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a person? ...
... Secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a person? ...
The Endocrine System - Valhalla High School
... Secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a person? ...
... Secretes the hormone thyroxine which regulates the metabolism of proteins, carbs and lipids. Diseases of the thyroid lead to either hyperthyroidism(too much thyroxine), or hypothyroidism(not enough thyroxine). How do you these conditions would affect a person? ...
Hormones - overview File - E
... pituitary gland. In addition, it makes hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate many of the other endocrine glands. Parathyroid glands These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulate the level of calcium in the ...
... pituitary gland. In addition, it makes hormones that are stored in the pituitary gland. Pituitary gland The pituitary gland produces hormones that regulate many of the other endocrine glands. Parathyroid glands These four glands release parathyroid hormone, which regulate the level of calcium in the ...
Class PowerPoint - Franklin College
... 5. What is the target tissue for a releasing hormone and how does the releasing hormone get there? 6. What happens when a releasing hormone binds to receptors on its target tissue? 7. What do tropic hormones do? 8. What do direct acting hormones do? ...
... 5. What is the target tissue for a releasing hormone and how does the releasing hormone get there? 6. What happens when a releasing hormone binds to receptors on its target tissue? 7. What do tropic hormones do? 8. What do direct acting hormones do? ...
Hormone synthesis and degradation
... Catecholamines are made from tyrosine • Tyrosine hydroxylase is rate-limiting step for catecholamine synthesis. • It converts L-tyrosine to Ldihydroxyphenylalanine (L-dopa). • As the rate-limiting enzyme, tyrosine hydroxylase is regulated in a variety of ways. ...
... Catecholamines are made from tyrosine • Tyrosine hydroxylase is rate-limiting step for catecholamine synthesis. • It converts L-tyrosine to Ldihydroxyphenylalanine (L-dopa). • As the rate-limiting enzyme, tyrosine hydroxylase is regulated in a variety of ways. ...
Endocrine System
... TSH and will stimulate the release of TH • Increased metabolism, sweating, irregular/ rapid heart beat, nervousness, weight loss • Signs – enlarged thyroid (goiter), exophthalmos • Treatment – Thyroidectomy or treatment with Radioactive Iodine which will destroy most of the active thyroid cells ...
... TSH and will stimulate the release of TH • Increased metabolism, sweating, irregular/ rapid heart beat, nervousness, weight loss • Signs – enlarged thyroid (goiter), exophthalmos • Treatment – Thyroidectomy or treatment with Radioactive Iodine which will destroy most of the active thyroid cells ...
Endocrinology: Endocrine System Function Nervous vs. Endocrine
... • Stimulates breakdown of stored fat and release of fatty acids into blood – used as secondary energy source ...
... • Stimulates breakdown of stored fat and release of fatty acids into blood – used as secondary energy source ...
Parathyroid Glands
... glucocorticoids androgens (male sex hormone) Adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine (adrenalin) powerful stimulant – fight or flight norepinephrine ...
... glucocorticoids androgens (male sex hormone) Adrenal medulla secretes epinephrine (adrenalin) powerful stimulant – fight or flight norepinephrine ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... • Promotes conversion of glucose into fat in adipose tissue • Stimulates amino acid uptake by cells and protein formation ...
... • Promotes conversion of glucose into fat in adipose tissue • Stimulates amino acid uptake by cells and protein formation ...
Endocrine System Vocabulary Acromegaly Adrenal Glands
... 27.Steroids: can enter the nucleus, diffuse through the plasma membranes of target cells, activate genes to transcribe mRNA for protein synthesis & bind to receptor proteins in the nucleus. They are also lipid soluble. 28.Target Organ or Cells: specific cells or organs that a given hormone influence ...
... 27.Steroids: can enter the nucleus, diffuse through the plasma membranes of target cells, activate genes to transcribe mRNA for protein synthesis & bind to receptor proteins in the nucleus. They are also lipid soluble. 28.Target Organ or Cells: specific cells or organs that a given hormone influence ...
1 Part Ten: Thyroid / Parathyroid Chapter 133: Anatomy Daniel O
... pit, the foramen caecum, which can usually be seen on the adult tongue lying between the anterior two thirds and posterior one third of the tongue. Abnormalities in the pattern of thyroid development include arrested growth, accessory tissues, and cystic development of the thyroglossal duct. In the ...
... pit, the foramen caecum, which can usually be seen on the adult tongue lying between the anterior two thirds and posterior one third of the tongue. Abnormalities in the pattern of thyroid development include arrested growth, accessory tissues, and cystic development of the thyroglossal duct. In the ...
the endocrine system
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY & METABOLISM—INTRODUCTION
... minimal dosage to maintain treated effects TSH return to normal TSAb negative normal response to TRH ...
... minimal dosage to maintain treated effects TSH return to normal TSAb negative normal response to TRH ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.