Pituitary Gland
... Also released during physical contact, it may play a role in sexual arousal and social bonding ...
... Also released during physical contact, it may play a role in sexual arousal and social bonding ...
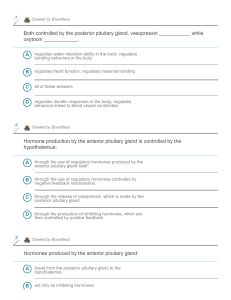
Both controlled by the posterior pituitary gland, vasopressin ______
... avoid insufficient amounts of calcium. ...
... avoid insufficient amounts of calcium. ...
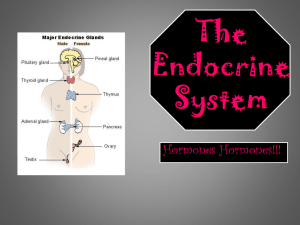
Endocrine System and Hormones
... signal by way of the hormone oxytocin to the uterus causing contractions. The pressure of the fetus on the cervix sends a signal back to the brain which then stimulates the release of more oxytocin. This causes more contractions. The fetus pushes harder on the cervix. More oxytocin is released. The ...
... signal by way of the hormone oxytocin to the uterus causing contractions. The pressure of the fetus on the cervix sends a signal back to the brain which then stimulates the release of more oxytocin. This causes more contractions. The fetus pushes harder on the cervix. More oxytocin is released. The ...
Hormones of the Body
... uterine wall smooth muscles • In females, helps to eject milk when lactating • No known function in males, although in both males and females, OT can have some antidiuretic effects ...
... uterine wall smooth muscles • In females, helps to eject milk when lactating • No known function in males, although in both males and females, OT can have some antidiuretic effects ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... What are the three chemical classes of hormones? How do the classes of hormones differ with respect to their half-life in the blood, the location of their receptors on the target cells, and the modes of synthesis and storage? Which endocrine glands secrete amine hormones? In which part of the thyroi ...
... What are the three chemical classes of hormones? How do the classes of hormones differ with respect to their half-life in the blood, the location of their receptors on the target cells, and the modes of synthesis and storage? Which endocrine glands secrete amine hormones? In which part of the thyroi ...
MK Biokimia - Metabolisme Mineral
... Large Numbers of Genes a. Most of the thyroxine secreted by the thyroid is converted to triiodothyronine (T3) ...
... Large Numbers of Genes a. Most of the thyroxine secreted by the thyroid is converted to triiodothyronine (T3) ...
November 7, 2011 Warm UP
... signal by way of the hormone oxytocin to the uterus causing contractions. The pressure of the fetus on the cervix sends a signal back to the brain which then stimulates the release of more oxytocin. This causes more contractions. The fetus pushes harder on the cervix. More oxytocin is released. The ...
... signal by way of the hormone oxytocin to the uterus causing contractions. The pressure of the fetus on the cervix sends a signal back to the brain which then stimulates the release of more oxytocin. This causes more contractions. The fetus pushes harder on the cervix. More oxytocin is released. The ...
Endocrine System
... The thyroid is in the front part of the lower neck, and is shaped like a butterfly. It produces the hormones known as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. Thyroid hormones are important because they participate in the growth an ...
... The thyroid is in the front part of the lower neck, and is shaped like a butterfly. It produces the hormones known as thyroxine and triiodothyronine. These control the rate at which cells burn fuels from food to produce energy. Thyroid hormones are important because they participate in the growth an ...
The Endocrine System - Immaculateheartacademy.org
... The word implies that intercellular chemical signals are produced within and secreted from endocrine glands, but that the chemical signal have effects at locations that are away from or or separate from the endocrine glands that secrete them. The chemical signals are transported by way of the blood ...
... The word implies that intercellular chemical signals are produced within and secreted from endocrine glands, but that the chemical signal have effects at locations that are away from or or separate from the endocrine glands that secrete them. The chemical signals are transported by way of the blood ...
The Thyroid Gland Lecture
... Follicles are lined with single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells, which secrete into interior . ...
... Follicles are lined with single layer of cuboidal epithelial cells, which secrete into interior . ...
Lymphatic System
... Diabetes Mellitus Type two • results when the pancreas produces insulin, but not enough to meet the needs of the body. This type of diabetes is linked with obesity and is most common in adults over the age of 45. Treatment may involve oral medication, exercise, weight loss, and insulin injections. ...
... Diabetes Mellitus Type two • results when the pancreas produces insulin, but not enough to meet the needs of the body. This type of diabetes is linked with obesity and is most common in adults over the age of 45. Treatment may involve oral medication, exercise, weight loss, and insulin injections. ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Grade 12 Biology
... ATP, and ATP is consumed during activity, therefore there is no weight gain. ...
... ATP, and ATP is consumed during activity, therefore there is no weight gain. ...
Animal By-Products
... adrenal gland function; treatment of psoriasis; allergies; mononucleosis and leukemia ...
... adrenal gland function; treatment of psoriasis; allergies; mononucleosis and leukemia ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... The gland is no bigger than a pea. Located at the base of the brain, and the most important part of the entire endocrine system. AKA: The master gland because it makes hormones that control other endocrine glands. The production of hormones and secretions can be affected by emotions and seasons chan ...
... The gland is no bigger than a pea. Located at the base of the brain, and the most important part of the entire endocrine system. AKA: The master gland because it makes hormones that control other endocrine glands. The production of hormones and secretions can be affected by emotions and seasons chan ...
Chapter 11 Study Guide Outline: Endocrine System
... Consists of two large lobes Located below the larynx on either side and in front of the trachea Synthesize two hormones _____________ (T4) & Triodothyronine (T3): regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins ...
... Consists of two large lobes Located below the larynx on either side and in front of the trachea Synthesize two hormones _____________ (T4) & Triodothyronine (T3): regulate metabolism of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins ...
Human Endocrine System
... Location: in the scrotum of male Hormones Produced: ◦ Testosterone- development of male secondary sex ...
... Location: in the scrotum of male Hormones Produced: ◦ Testosterone- development of male secondary sex ...
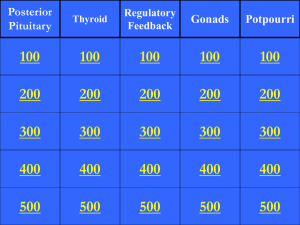
Endocrine Review Package
... 8. The gland that is directly stimulated by the nervous system to secrete hormones is the structure labelled A. 2 C. 4 B. 3 D. 5 9. The structure that produces only hormones is labelled A. 1 C. 5 B. 2 D. 6 10. A target organ for aldosterone is the structure labelled A. 3 B. 5 12. When the hypothalam ...
... 8. The gland that is directly stimulated by the nervous system to secrete hormones is the structure labelled A. 2 C. 4 B. 3 D. 5 9. The structure that produces only hormones is labelled A. 1 C. 5 B. 2 D. 6 10. A target organ for aldosterone is the structure labelled A. 3 B. 5 12. When the hypothalam ...
Human Growth and Development
... Pituitary Gland It is the master gland that controls other glands and ...
... Pituitary Gland It is the master gland that controls other glands and ...
File
... 1. The thyroid gland is located in the neck just below the ____________________. 2. What element is needed to synthesize thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)? 3. What is the function of T3 and T4? 4. What is the third thyroid hormone? 5. Complete the table of thyroid disorders. Disorder Name Hor ...
... 1. The thyroid gland is located in the neck just below the ____________________. 2. What element is needed to synthesize thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3)? 3. What is the function of T3 and T4? 4. What is the third thyroid hormone? 5. Complete the table of thyroid disorders. Disorder Name Hor ...
The Endocrine System - FW Johnson Collegiate
... of the pancreas in dogs lead to what we now identify as symptoms of diabetes. Although this shed some light on the endocrine system, many glands produce more than one hormone, and levels of some hormones affect the level of other hormones. - To study hormones today, scientists inject radioactive tra ...
... of the pancreas in dogs lead to what we now identify as symptoms of diabetes. Although this shed some light on the endocrine system, many glands produce more than one hormone, and levels of some hormones affect the level of other hormones. - To study hormones today, scientists inject radioactive tra ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.