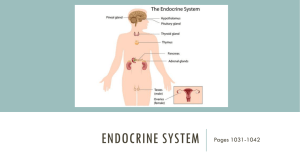
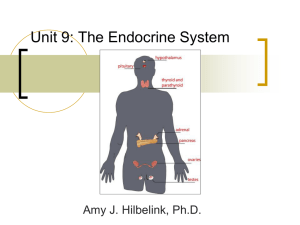
The Endocrine System Coloring Activities
... & ______________increase the rate of energy release from carbohydrates, increase the rate of protein synthesis, accelerates growth and stimulates the nervous system. _____________ lowers calcium & phosphate ion concentrations in the blood by inhibiting their release from the bones and increases thei ...
... & ______________increase the rate of energy release from carbohydrates, increase the rate of protein synthesis, accelerates growth and stimulates the nervous system. _____________ lowers calcium & phosphate ion concentrations in the blood by inhibiting their release from the bones and increases thei ...
Lecture 11: Thyroid and Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands: Learning
... Usually near inferior poles of thyroid, but position is more variable than superiors Variability Most people have these 4; some have 2; ~5% have >4 Inadvertent Removal of Parathyroid Glands Variable position of (esp. inferior) parathyroid glands puts them at risk for damage/removal during ...
... Usually near inferior poles of thyroid, but position is more variable than superiors Variability Most people have these 4; some have 2; ~5% have >4 Inadvertent Removal of Parathyroid Glands Variable position of (esp. inferior) parathyroid glands puts them at risk for damage/removal during ...
21 Endocrine Flashcards, INDEX back
... No, because th was not present during fetal development, when myelination and synaptic formation needed it. Congenital hypothyroidism This is a problem with the baby, not the mother. TH Hashimoto's thyroiditis Adrenal medulla Hormones that are also neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system ...
... No, because th was not present during fetal development, when myelination and synaptic formation needed it. Congenital hypothyroidism This is a problem with the baby, not the mother. TH Hashimoto's thyroiditis Adrenal medulla Hormones that are also neurotransmitters in the sympathetic nervous system ...
Endocrinology - Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center
... a. Function of thyroid hormones is to increase metabolic activity. b. T 3 and T4 regulate basal metabolic rate (BMR). c. Increased BMR generates heat through the sodium-potassium pump. d. Heart rate is increased because thyroid hormones increase the heart’s receptors for Norepinephrine and Epinephri ...
... a. Function of thyroid hormones is to increase metabolic activity. b. T 3 and T4 regulate basal metabolic rate (BMR). c. Increased BMR generates heat through the sodium-potassium pump. d. Heart rate is increased because thyroid hormones increase the heart’s receptors for Norepinephrine and Epinephri ...
Chapter 41 Endocrine System
... The thyroid gland is located just below the larynx. The thyroid is composed of follicular cells, which secrete thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) and parafollicular cells, which secrete calcitonin (CT). Thyroid hormones are synthesized from iodine. Thyroid hormones regulate organic metabolism ...
... The thyroid gland is located just below the larynx. The thyroid is composed of follicular cells, which secrete thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) and parafollicular cells, which secrete calcitonin (CT). Thyroid hormones are synthesized from iodine. Thyroid hormones regulate organic metabolism ...
lec18
... – Hypersecretion: increased metabolic rate, high body temperature, weight loss, increased appetite, rapid heart rate etc….. – Hyposecretion; decreased metabolic rate, low body temperature, weight gain, loss of appetite, reduced heart rate etc…. – Essential for the normal growth of children. ...
... – Hypersecretion: increased metabolic rate, high body temperature, weight loss, increased appetite, rapid heart rate etc….. – Hyposecretion; decreased metabolic rate, low body temperature, weight gain, loss of appetite, reduced heart rate etc…. – Essential for the normal growth of children. ...
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Monterey Peninsula College
... a) Thyroxin -a metabolic hormone -made when iodine is available -increases BMR & ATP production/use -increases oxygen consumption -increases rate of heat production -stimulates protein synthesis -works permissively w/ GH & insulin to accelerate growth ...
... a) Thyroxin -a metabolic hormone -made when iodine is available -increases BMR & ATP production/use -increases oxygen consumption -increases rate of heat production -stimulates protein synthesis -works permissively w/ GH & insulin to accelerate growth ...
Practical 1 Endocrine Tissues Handout
... The pancreas has both a major exocrine role and important endocrine functions. During development the potential endocrine cells migrate from the pancreatic duct epithelium and aggregate around capillaries to form isolated clumps of cells scattered throughout the exocrine tissue. The endocrine clumps ...
... The pancreas has both a major exocrine role and important endocrine functions. During development the potential endocrine cells migrate from the pancreatic duct epithelium and aggregate around capillaries to form isolated clumps of cells scattered throughout the exocrine tissue. The endocrine clumps ...
Endocrine System
... Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of co ...
... Growth hormone or GH - GH stimulates growth in childhood and is important for maintaining a healthy body composition. In adults it is also important for maintaining muscle mass and bone mass. It can affect fat distribution in the body. Adrenocorticotropin or ACTH - ACTH stimulates production of co ...
Ultrasound Imaging of Thyroid Gland
... With advent of high frequency linear transducers in field of ultrasound, the imaging of superficial structures has dynamically changed. The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland, superficial in location can be evaluated in day-to-day clinical practice for all thyroid diseases. The most common clinical ...
... With advent of high frequency linear transducers in field of ultrasound, the imaging of superficial structures has dynamically changed. The thyroid gland is an endocrine gland, superficial in location can be evaluated in day-to-day clinical practice for all thyroid diseases. The most common clinical ...
Endocrine system
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target ...
... regulating reproduction & development. B. A Hormone is a chemical messenger produced by a cell that effects specific change in the cellular activity of other cells (target ...
Endocrine System
... Epinephrine and norepinephrine Increases heart rate, increased force of cardiac muscle contraction, increased breathing rate, elevated blood pressure, increased blood glucose, and decreased digestive activity Stimulated by sympathetic impulses fight or flight ...
... Epinephrine and norepinephrine Increases heart rate, increased force of cardiac muscle contraction, increased breathing rate, elevated blood pressure, increased blood glucose, and decreased digestive activity Stimulated by sympathetic impulses fight or flight ...
Endocrine by IVS
... Management of thyroid storm—oxygen, IV fluids with dextrose, hypothermic measures, steroids to treat shock or adrenal deficiency, iodine to decrease output of T4, beta blockers, PTU or Tapazole impedes formation of thyroid hormone and blocks conversion of T4 to T3 ...
... Management of thyroid storm—oxygen, IV fluids with dextrose, hypothermic measures, steroids to treat shock or adrenal deficiency, iodine to decrease output of T4, beta blockers, PTU or Tapazole impedes formation of thyroid hormone and blocks conversion of T4 to T3 ...
The endocrine system -- a brief overview. I. Introduction
... hypothalamus; when neurons are activated, hormones released at posterior pituitary. 2. Adenohypophyseal hormones (AP) - secretion under influence of hypothalamic releasing hormones. - four of adenohypophyseal hormones are tropic hormone s -- regulate secretory activity of other endocrine glands (ACT ...
... hypothalamus; when neurons are activated, hormones released at posterior pituitary. 2. Adenohypophyseal hormones (AP) - secretion under influence of hypothalamic releasing hormones. - four of adenohypophyseal hormones are tropic hormone s -- regulate secretory activity of other endocrine glands (ACT ...
General Adaptation Syndrome – Internet Assignment
... ions (which lead to the retention of __________). Aldosterone also leads to the excretion of ____________ ions, so blood pH does not become too _____ during times of stress. 14. Cortisol – a hormone released by the adrenal cortex. This hormone acts to increase _______________________ levels. It does ...
... ions (which lead to the retention of __________). Aldosterone also leads to the excretion of ____________ ions, so blood pH does not become too _____ during times of stress. 14. Cortisol – a hormone released by the adrenal cortex. This hormone acts to increase _______________________ levels. It does ...
Endocrinology
... The anterior pituitary is also called the adenohypophysis. Adeno means gland and is given to this organ because it actually secretes a group of hormones known as the tropic hormones. These hormones control other glands or act on other tissues. The glands controlled by the tropic hormones are also en ...
... The anterior pituitary is also called the adenohypophysis. Adeno means gland and is given to this organ because it actually secretes a group of hormones known as the tropic hormones. These hormones control other glands or act on other tissues. The glands controlled by the tropic hormones are also en ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
the endocrine system
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
... It is an organ that develops a secretion which performs specific functions. ...
Objectives Endocrine System
... hypothalamus: located near the pituitary gland in the brain; which secretes “releasing” hormone that functions to stimulate or inhibit the release of pituitary gland hormones ...
... hypothalamus: located near the pituitary gland in the brain; which secretes “releasing” hormone that functions to stimulate or inhibit the release of pituitary gland hormones ...
BIO 262 Unit 4 Review Sheet
... ___3. Which pair of glands produces hormones that have opposing effects? a. anterior pituitary-posterior pituitary ...
... ___3. Which pair of glands produces hormones that have opposing effects? a. anterior pituitary-posterior pituitary ...
The Endocrine System
... reproduction and regeneration • Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone: (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3)which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body ...
... reproduction and regeneration • Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone: (TSH) stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3)which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body ...
The Major endocrine glands 3.
... ● Example Local Hormone NO (Nitric Oxide) – Blood Vessel endothelial cells ● Acts on Smooth muscle – Vasodilatation ● Viagra enhances NO effects – Role in penile erection ...
... ● Example Local Hormone NO (Nitric Oxide) – Blood Vessel endothelial cells ● Acts on Smooth muscle – Vasodilatation ● Viagra enhances NO effects – Role in penile erection ...
File
... Causes development of secondary sex characteristics in males; promotes maturity of male ...
... Causes development of secondary sex characteristics in males; promotes maturity of male ...
Methodological Instruction to Practical Lesson № 19
... which excess thyroid hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland. Specific diseases that can cause hyperthyroidism include Graves disease and toxic multinodular goiter. Note: Hypothyroidism is more common than hyperthyroidism. Thyrotoxicosis other than hyperthyroidism is seen in subacute thyroiditis, ...
... which excess thyroid hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland. Specific diseases that can cause hyperthyroidism include Graves disease and toxic multinodular goiter. Note: Hypothyroidism is more common than hyperthyroidism. Thyrotoxicosis other than hyperthyroidism is seen in subacute thyroiditis, ...
Document
... Caused by inability of pancreas to secrete insulin or a resistance to insulin, affecting glucose levels. Can lead to renal disease, blindness, gangrene – leading to amputation. ...
... Caused by inability of pancreas to secrete insulin or a resistance to insulin, affecting glucose levels. Can lead to renal disease, blindness, gangrene – leading to amputation. ...
Thyroid

The thyroid gland, or simply the thyroid /ˈθaɪrɔɪd/, is one of the largest endocrine glands in the body, and consists of two connected lobes. It is found in the neck, below the laryngeal prominence (Adam's apple). The thyroid gland controls how quickly the body uses energy, makes proteins, and controls the body's sensitivity to other hormones. It participates in these processes by producing thyroid hormones, the principal ones being thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), which is more active. These hormones regulate the growth and rate of function of many other systems in the body. T3 and T4 are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine. The thyroid also produces calcitonin, which plays a role in calcium homeostasis.Hormonal output from the thyroid is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) produced by the anterior pituitary, which itself is regulated by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) produced by the hypothalamus.The thyroid may be affected by some frequent thyroid diseases. Hyperthyroidism occurs when the gland produces excessive amounts of thyroid hormones, the most common cause being Graves' disease—an autoimmune disorder. In contrast, hypothyroidism is a state of insufficient thyroid hormone production. Worldwide, the most common cause is iodine deficiency. Thyroid hormones are important for development, and hypothyroidism secondary to iodine deficiency remains the leading cause of preventable intellectual disability. In iodine-sufficient regions, the most common cause of hypothyroidism is Hashimoto's thyroiditis—also an autoimmune disease. In addition, the thyroid gland may also develop several types of nodules and cancer.